Test: Rocks Study Guide - Norwood Public Schools
advertisement
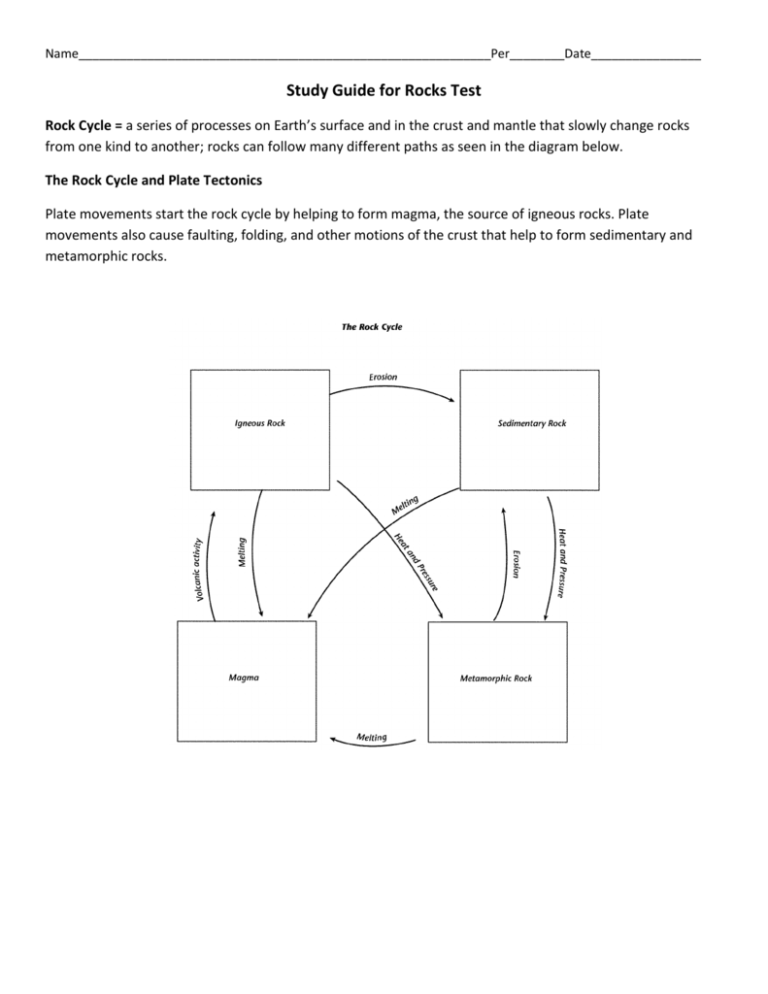
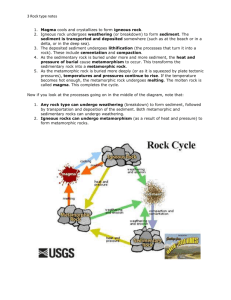
Name____________________________________________________________Per________Date________________ Study Guide for Rocks Test Rock Cycle = a series of processes on Earth’s surface and in the crust and mantle that slowly change rocks from one kind to another; rocks can follow many different paths as seen in the diagram below. The Rock Cycle and Plate Tectonics Plate movements start the rock cycle by helping to form magma, the source of igneous rocks. Plate movements also cause faulting, folding, and other motions of the crust that help to form sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Name____________________________________________________________Per________Date________________ Type of Rock igneous How its Formed when magma / lava cools and hardens Example granite basalt obsidian pumice sedimentary when the remains of plants, animals, or other rocks are pressed (compacted) and cemented together * most likely to contain fossils when dead organisms are buried by sediment sandstone shale limestone metamorphic when an existing rock is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions; most formed deep underground; heat comes from the mantle gneiss slate gneiss quartzite marble Uses building material used to build bridges and public buildings in the 1800’s and early 1900’s used in curbstones, floors, kitchen counters today building material tools (arrowheads) the White House is made of sandstone! limestone can be used in making cement and steel building material sculpture Abraham Lincoln is carved out of white marble in the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, DC! used in roofing, flooring, walkways, chalkboards Key Vocabulary Terms rock-forming minerals= minerals that are found in rocks rock = nonliving part of the environment made up of minerals and other material extrusive rock = igneous rock formed from lava that erupted onto Earth’s surface intrusive rock= igneous rock that formed when magma hardened beneath Earth’s surface foliated = metamorphic rocks that have their grains arranged in parallel layers or bands nonfoliated= metamorphic rocks that have their grains arranged randomly texture = the look and feel of the rock’s surface; geologists use terms based on the size, shape, and pattern of the rock’s grains to describe its texture Classifying Rocks rocks are classified by: mineral composition color texture how the rock is formed How a Sedimentary Rock is Formed: 1. Erosion= running water, wind, or ice loosen and carry away fragments of rock 2. Deposition = the process by which sediment settles out of the water or wind carrying it 3. Compaction = process that presses sediments together 4. Cementation = process in which dissolved minerals crystallize and glue particles of sediment together