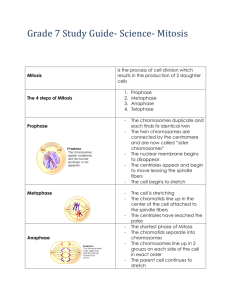
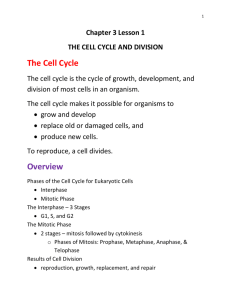
7th grade Section 1 Essential Questions Cell Division 1. Why is it
advertisement
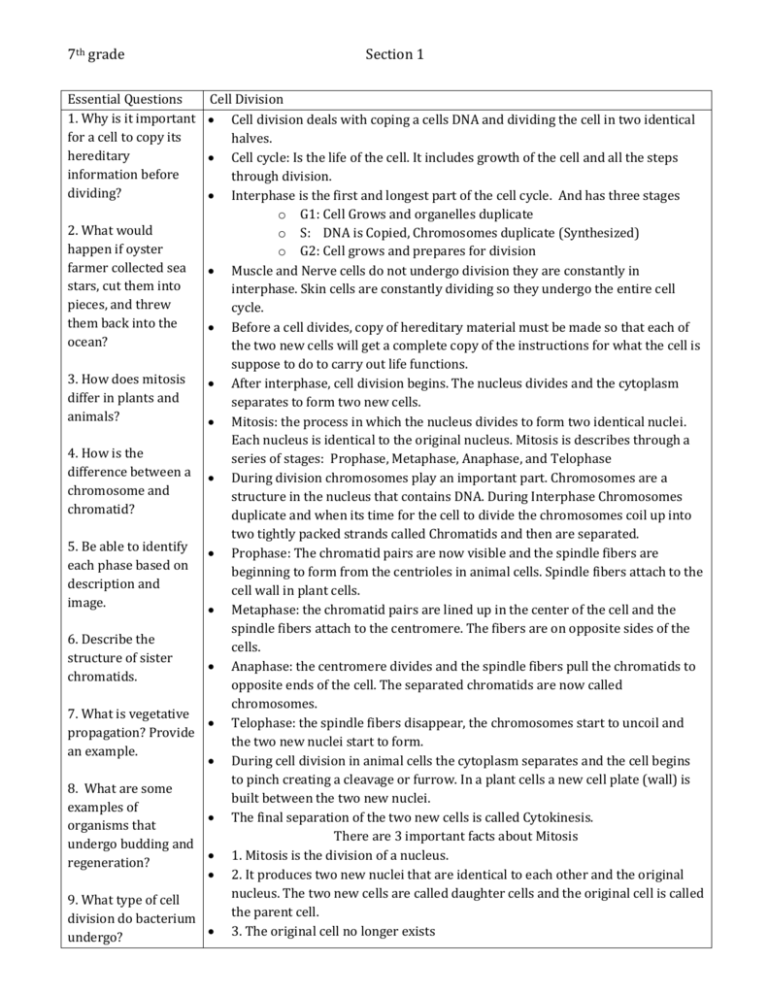
7th grade Section 1 Essential Questions Cell Division 1. Why is it important Cell division deals with coping a cells DNA and dividing the cell in two identical for a cell to copy its halves. hereditary Cell cycle: Is the life of the cell. It includes growth of the cell and all the steps information before through division. dividing? Interphase is the first and longest part of the cell cycle. And has three stages o G1: Cell Grows and organelles duplicate 2. What would o S: DNA is Copied, Chromosomes duplicate (Synthesized) happen if oyster o G2: Cell grows and prepares for division farmer collected sea Muscle and Nerve cells do not undergo division they are constantly in stars, cut them into interphase. Skin cells are constantly dividing so they undergo the entire cell pieces, and threw cycle. them back into the Before a cell divides, copy of hereditary material must be made so that each of ocean? the two new cells will get a complete copy of the instructions for what the cell is suppose to do to carry out life functions. 3. How does mitosis After interphase, cell division begins. The nucleus divides and the cytoplasm differ in plants and separates to form two new cells. animals? Mitosis: the process in which the nucleus divides to form two identical nuclei. Each nucleus is identical to the original nucleus. Mitosis is describes through a 4. How is the series of stages: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase difference between a During division chromosomes play an important part. Chromosomes are a chromosome and structure in the nucleus that contains DNA. During Interphase Chromosomes chromatid? duplicate and when its time for the cell to divide the chromosomes coil up into two tightly packed strands called Chromatids and then are separated. 5. Be able to identify Prophase: The chromatid pairs are now visible and the spindle fibers are each phase based on beginning to form from the centrioles in animal cells. Spindle fibers attach to the description and cell wall in plant cells. image. Metaphase: the chromatid pairs are lined up in the center of the cell and the spindle fibers attach to the centromere. The fibers are on opposite sides of the 6. Describe the cells. structure of sister Anaphase: the centromere divides and the spindle fibers pull the chromatids to chromatids. opposite ends of the cell. The separated chromatids are now called chromosomes. 7. What is vegetative Telophase: the spindle fibers disappear, the chromosomes start to uncoil and propagation? Provide the two new nuclei start to form. an example. During cell division in animal cells the cytoplasm separates and the cell begins to pinch creating a cleavage or furrow. In a plant cells a new cell plate (wall) is 8. What are some built between the two new nuclei. examples of The final separation of the two new cells is called Cytokinesis. organisms that There are 3 important facts about Mitosis undergo budding and 1. Mitosis is the division of a nucleus. regeneration? 2. It produces two new nuclei that are identical to each other and the original nucleus. The two new cells are called daughter cells and the original cell is called 9. What type of cell the parent cell. division do bacterium 3. The original cell no longer exists undergo? 7th grade 10. How do the daughter cells compare to the parent cells during mitosis and asexual reproduction? 11. How many chromosomes does a normal human cell contain? Section 1 Images: Cell division allows growth and replaces worn out or damaged cells. Except for sex cells each normal human cell contains 46 chromosomes. Asexual reproduction: a new organism is produced from one organism. The new organism’s DNA is identical to the parent’s DNA. (Strawberries like many fruit plants and weeds undergo a special type of asexual reproduction called vegetative propagation.) Since bacteria do not have a nucleus they do not undergo mitosis. Instead the go through Binary Fission. This is where one bacteria’s DNA is copied and divides into two new bacteria. Hydra reproduces by budding. Budding is a type of asexual reproduction made possible because of mitosis. When the bud on the adult becomes large enough, it breaks away to live on its own. Some organisms can regrow damaged or lost body parts. Regeneration is the process that uses mitosis to regrow body parts.