pubdoc_12_14206_996
advertisement

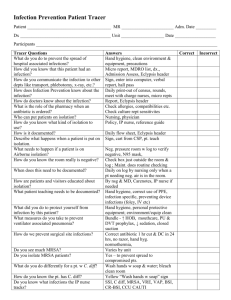
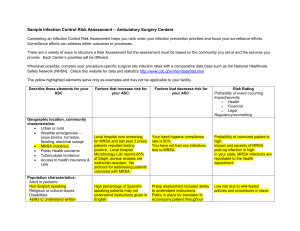
3rd lecture for third year mycosis By: Dr.Kareema Amine Al-Khafajii, professor ,Department Of Microbiology, College Of Medicine, University of Babylon. Mycosis: means fungal diseases .as fungi grow slowly mycosis may be chronic. Mycosis are classified into the following categories: 1-The Superficial Mycoses 2-The Cutaneous Mycoses 3-The Subcutaneous Mycoses4-Dimorphic Systemic Mycoses 5-Opportunistic Systemic Mycoses 1-Superficial mycosis: These are superficial cosmetic fungal infections of the skin or hair shaft. No living tissue is invaded and there is no cellular response from the host. Essentially no pathological changes are elicited. These infections are often so innocuous that patients are often unaware of their condition. Malassezia infections Description Malassezia furfur is the causative agent of Pityriasis versicolor, Pityriasis folliculitis and it has recently been implicated as a causative agent of seborrhoeic dermatitis and dandruff. It has also been recovered in blood cultures from neonate and adult patients undergoing lipid replacement therapy. M. furfur is a lipophilic yeast living on the skin as part of the normal flora. Pityriasis versicolor: This is a chronic, superficial fungal disease of the skin characterized by well-demarcated white, pink, fawn, or brownish lesions, often coalescing, and covered with thin fine scales. The colour varies according to the normal pigmentation of the patient, exposure of the area to sunlight, and the severity of the disease. Lesions occur on the trunk, shoulders and arms, rarely on the neck and face, and fluoresce a pale yellow or greenish colour under Wood's ultra-violet light. Young adults are affected most often, but the disease may occur in childhood and old age. Diagnosis :depends on clinical picture of the patient, Wood`s light and, is usually possible by direct microscopic examination of KOH-treated skin scrapings which show thick-walled round, budding yeast-like cells and short angular hyphal forms described as "spaghetti and meatballs." Culture: Culture is only necessary in cases of suspected fumgaemia. Management: The most appropriate antifungal treatment for pityriasis versicolor is to use a topical imidazole in a solution or lathering preparation. Ketoconazole shampoo has proven to be very effective. Alternative treatments include zinc pyrithione shampoo or selenium sulfide lotion applied daily for 10-14 days or the use of propylene glycol 50% in water twice daily for 14 days. In severe cases with extensive lesions, or in cases with lesions resistant to topical treatment or in cases of frequent relapse oral therapy with either ketoconazole [400 mg single dose or 200 mg/day for 5-10 days] or itraconazole [200 mg/day for 5-7 days] is usually effective. Mycologically, yeast cells may still be seen in skin scrapings for up to 30 days following treatment, thus patients should be monitored on clinical grounds. Patients also need to be warned that it may take many months for their skin pigmentation to return to normal, even after the infection has been successfully treated. Relapse is a regular occurrence and prophylactic treatment with a topical agent once or twice a week is often necessary to avoid recurrence. The Cutaneous Mycoses These are superficial fungal infections of the skin, hair or nails. No living tissue is invaded, however a variety of pathological changes occur in the host because of the presence of the infectious agent and its metabolic products. Dermatophytosis Description: Dermatophytosis (tinea or ringworm) of the scalp, glabrous skin, and nails is caused by a closely related group of fungi known as dermatophytes which have the ability to utilise keratin as a nutrient source, i.e. they have a unique enzymatic capacity [keratinase]. The disease process in dermatophytosis is unique for two reasons: Firstly, no living tissue is invaded the keratinised stratum corneum is simply colonised. However, the presence of the fungus and its metabolic products usually induces an allergic and inflammatory eczematous response in the host. The type and severity of the host response is often related to the species and strain of dermatophyte causing the infection. Secondly, the dermatophytes are the only fungi that have evolved a dependency on human or animal infection for the survival and dissemination of their species. Clinical manifestations: The common anthropophilic species are primarily parasitic on man .They are unable to colonize other animals and they have no other environmental sources. On the other hand, geophilic species normally inhabit the soil where they are believed to decompose keratinaceous debris. Some species may cause infections in animals and man following contact with soil. Zoophilic species are primarily parasitic on animals and infections may be transmitted to humans following contact with the animal host . Zoophilic infections usually elicit a strong host response and on the skin where contact with the infective animal has occurred ie arms, legs, body or face. Dermatophytes are found in one of the three genera: Microsporum: infects only skin + hair . characterized by the presence of Thick walled Macroconidia , spindle shape with pointed-end, contains 7-9 cells , with the presence of microconidia also. Epidermophyton: infects only skin + nail . characterized by the presence of Bifurcated hyphae with multiple, smooth, club shaped macroconidia contains 2-4 cells, with absence of microconidia. Trichophyton: infects skin+ hair + nail . . characterized by the presence of Globose microconidia in grape-like clusters. Macroconidia are not commonly available but when present, are cigar-shaped, smooth, thin wall, septate and rounded ends DERMATOPHYTOSIS: Clinical Classification Infection is named according to the anatomic location involved: Tinea manuum (dermatophytes infection of palmer surface of the hands). Tinea pedis (athlete's feet: dermatophytes infections of the feet). Tinea corporis (dermatophytes infection of trunk, neck and back).Tinea cruris (dermatophytes infection of proximal medial thighs, perenium and buttocks).Tinea barbae (dermatophytes infection of hairy skin in the beard area of the face in adults). Tinea capitis (dermatophytes infection of scalp usually occurs in children). Tinea ungium(dermatophytes infection of the nails, commonly affected house wives and service men). Subcutaneous Mycoses Mycetoma (clincal syndrome of localized, indolent, deforming, swollen lesions and sinuses, involving cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues, fascia, and bone; usually occurring on the foot or hand) - etiologic agent may be bacterial or fungi. Discussion here will be restricted to fungal mycetoma or eumycetoma. Chromoblastomycosis (subcutaneous and cutaneous tissues of the hands and feet). Phaeohyphomycosis (face, cornea of eye, subcutaneous and cutaneous part of skin, occasionally cerebral and systemic).Sporotrichosis (cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues and adjacent lymphatics that suppurate, ulcerate and drain).Lobomycosis (subcutaneous and cut. tissues over different parts of body). Rhinosporidiosis (nasal cavities, mucocutaneous tissue - rarely it does effect the vagina, penis, anus, ears, and throat region). Mycetoma Mycetoma - clincal syndrome of localized, indolent, deforming, swollen lesions and sinuses, involving cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues, fascia, and bone; usually occurring on the foot or hand) - etiologic agent may be bacteria or fungi. one potential causal agent can be Pseudallescheria boydii, a soil/water inhabiting fungus with worldwide distribution. However other fungi can be involved. Fungi associated with fungal mycetoma are opportunistic. mycotic mycetoma - usually more common in men (3:1 to 5:1) than in women usually results from trauma or puncture wounds to feet, legs, arms and hands (usually on the feet) starts out as tumor-like to subcutaneous swelling ruptures near the surface; infects deeper tissues including subcutaneous tissues and ligaments (tendons, muscles and bone are usually spared)small particles or grains leak out of the lesions - these represent the to yellowish microcolonies. lesions of mycetoma seldom heal spontaneously disease is chronic may continue for 40-50 years. Treatment: P. boydii is resistant to all systemically useful drugs, including amphotericin B, KI, 5-fluorocytosine, 2-hydroxystilbamidine ketoconazole appears to be ineffective in clinical trials intravenous miconazole (9 mg per Kg of body weight sometimes higher doses) shows promise ,surgery and removal of tumor ( if small it is encapsulate, if larger amputation my be required),Combining miconazole and surgery may prove useful in effectively treating the disease. Chromoblastomycosis - chromomycosis or verrucous dermatitis Disease is one of hyperplasia, characterized by the formation of verrucoid (rough), warty, cutaneous nodules, which may be raised 1-3 cm above the skin surface. The roughened, irregular, pedunculated vegetations often resembles the florets of cauliflower. This disease is caused by Fonsecaea pedrosoi and Phialophora verrucosa (identical to Cadophora americana which causes bluing of lumber), both of which are dematiaceous fungi (darkly pigmented) occurs rarely in animals (such as, horses, cats, dogs, and frogs) soil-inhabiting fungi susceptibility enhanced by going barefoot or wearing sandals found almost exclusively in laborers enters hand or feet after trauma found primarily in the tropics or subtropics, dull red or violet color on skin may resemble a ringworm lesion develops into a verrucous lesion ,pruritus (itchiness) and papules may develop fungus gets under the skin (produces bumps),bumps may block lymphatic system and cause elephantiasis sometimes bacterial infection may enter and cause a secondary infection rarely this fungus spreads to other areas of the subcutaneous tissue. potentially may spread to brain (life-threatening in that case).biopsy tissue - look at the skin for fungus hematoxylin stain - look for fungal cells scattered among skin cells attempt to culture fungus from biopsy tissue must always take place to identify the etiological or causal agent colonies of fungi are dark or blackish Two species implicated in this mycosis - each may produce several spore types Fonsecaea pedrosoi - Cladosporium type and Rhinocladiella type of conidiation Phialalophora verrucosa Phialophora type (flowers in the vase conidiation) fungi found growing on plant debris, wood, soil. Treatment usually not fatal or necessarily painful unsightly diseasethiabendazole ,shows promise (given orally and on skin mixed with dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO] - to deliver drug) - experimental drug surgical excision, electrodesiccation, or cryosurgery are useful in early stages of disease application of heat to infect site has been reported to effect a cure of the disease after six months of treatment (using pocket warmers) itraconazole shows promise in clinical trials. For trial studies using posaconazole therapy check the following link at: (dimorphic fungi( Systemic Infections by True Pathogens Histoplasma capsulatum Coccidioides immitis Blastomyces dermatitidis Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Histoplasmosis: Ohio Valley Fever Histoplasma capsulatum – most common true pathogen; causes histoplasmosis Typically dimorphic Distributed worldwide, most prevalent in eastern and central regions of US Grows in moist soil high in nitrogen content Inhaled conidia produce primary pulmonary infection that may progress to systemic involvement of a variety of organs and chronic lung disease. Amphotericin B, ketoconazole. Coccidioidomycosis: Valley Fever Coccidioides immitis - causes coccidioidomycosis .Distinctive morphology – blocklike arthroconidia in the free-living stage and spherules containing endospores in the lungs lives in alkaline soils in semiarid, hot climates and is endemic to southwestern U.S. Arthrospores inhaled from dust, creates spherules and nodules in the lungs. Amphotericin B treatment. Blastomyces dermatitidis: North American Blastomycosis Blastomyces dermatitidis- causes blastomycosis Dimorphic Free-living species distributed in soil of a large section of the midwestern and southeastern U.S.Inhaled 10-100 conidia convert to yeasts and multiply in lungs,Symptoms include cough and fever.Chronic cutaneous, bone, and nervous system complications. Amphotericin B. Paracoccidioidomycosis Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Distributed in Central and South America .Lung infection occurs through inhalation or inoculation of spores.Systemic disease is not common. Ketoconazole, amphotericin B, sulfa drugs. Opportunistic Mycoses Most important fungal pathogens: Aspergillus , Candida,Cryptococcus ,Pneumocystis ,Rhizopus Mucor, Absidia. Infections by Candida: Candidiasis.Candida albicans .Widespread yeast.Infections can be short-lived, superficial skin irritations to overwhelming, fatal systemic diseases. Budding cells of varying size that may form both elongate pseudohyphae and true hyphae Forms off-white, pasty colony with a yeasty odor. Candida albicans Normal flora of oral cavity, genitalia, large intestine or skin of 20% of humans Account for 80% of nosocomial fungal infections .Account for 30% of deaths from nosocomial infections Thrush – occurs as a thick, white, adherent growth on the mucous membranes of mouth and throat Vulvovaginal yeast infection – painful inflammatory condition of the female genital region that causes ulceration and whitish discharge Cutaneous candidiasis – occurs in chronically moist areas of skin and in burn patients. Diagnosis and Treatment Presumptive diagnosis made if budding yeast cells and pseudohyphae are found; germ tube .Growth on selective, differential media differentiates Candida species Topical antifungals for superficial infections, amphotericin B and fluconazole for systemic. Cryptococcosis and Cryptococcus neoformans Cryptococcus neoformans causes cryptococcosis. A widespread encapsulated yeast that inhabits soil around pigeon roosts.Common infection of AIDS, cancer or diabetes patients.Infection of lungs leads to cough, fever, and lung nodules. Dissemination to meninges and brain can cause severe neurological disturbance and death. Diagnosis and Treatment Negative stain demonstrating encapsulated budding yeast Biochemical tests, serological testing.Systemic infection requires amphotericin B and fluconazole. Pneumocystis (carinii) jiroveci and Pneumocystis Pneumonia A small, unicellular fungus that causes pneumonia (PCP), the most prominent opportunistic infection in AIDS patients This pneumonia forms secretions in the lungs that block breathing and can be rapidly fatal if not controlled with medication.Pentamidine and cotrimoxazole. Aspergillosis: Diseases of the Genus Aspergillus Very common airborne soil fungus. 600 species, 8 involved in human disease; A. fumigatus most commonly.Serious opportunistic threat to AIDS, leukemia, and transplant patients.Infection usually occurs in lungs – spores germinate in lungs and form fungal balls; can colonize sinuses, ear canals, eyelids, and conjunctiva.Invasive aspergillosis can produce necrotic pneumonia, and infection of brain, heart, and other organs. Amphotericin B and nystatin. Zygomycosis Zygomycota are extremely abundant saprobic fungi found in soil, water, organic debris, and food.Genera most often involved are Rhizopus, Absidia, and Mucor. Usually harmless air contaminants invade the membranes of the nose, eyes, heart, and brain of people with diabetes and malnutrition, with severe consequences. Miscellaneous Opportunists Any fungus can be implicated in infections when immune defenses are severely compromised.Geotrichum candidum – geotrichosis; mold found in soil, dairy products; primarily involved in secondary lung infections Fusarium species – soil; occasionally infects eyes, toenails, burned skin. Fungal Allergies and Intoxications Fungal spores are common sources of atopic allergies. Seasonal allergies and asthma.farmer’s lung, teapicker’s lung, bark stripper’s disease. Fungal toxins lead to mycotoxicoses usually caused by eating poisonous or hallucinogenic mushrooms. aflatoxin toxic and carcinogenic; grains, corn peanuts; lethal to poultry and livestock. Stachybotrys chartarum – sick building syndrome; severe hematologic and neurological damage. تمنياتي للجميع بالنجاح والموفقيه