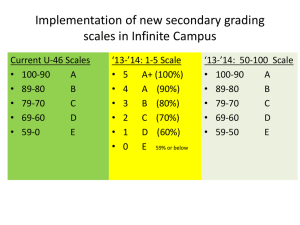
ED418StigginsCh11ChartPart1
advertisement
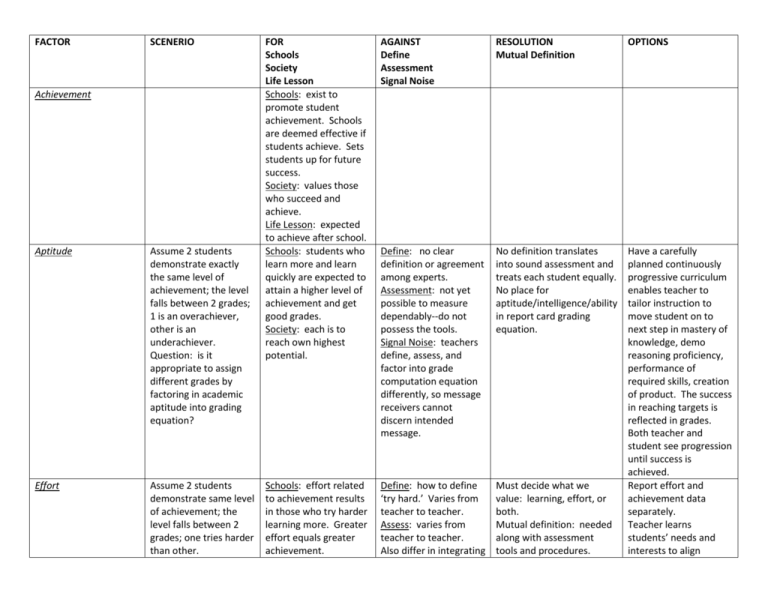
FACTOR SCENERIO Achievement Aptitude Assume 2 students demonstrate exactly the same level of achievement; the level falls between 2 grades; 1 is an overachiever, other is an underachiever. Question: is it appropriate to assign different grades by factoring in academic aptitude into grading equation? Effort Assume 2 students demonstrate same level of achievement; the level falls between 2 grades; one tries harder than other. FOR Schools Society Life Lesson Schools: exist to promote student achievement. Schools are deemed effective if students achieve. Sets students up for future success. Society: values those who succeed and achieve. Life Lesson: expected to achieve after school. Schools: students who learn more and learn quickly are expected to attain a higher level of achievement and get good grades. Society: each is to reach own highest potential. AGAINST Define Assessment Signal Noise RESOLUTION Mutual Definition OPTIONS Define: no clear definition or agreement among experts. Assessment: not yet possible to measure dependably--do not possess the tools. Signal Noise: teachers define, assess, and factor into grade computation equation differently, so message receivers cannot discern intended message. No definition translates into sound assessment and treats each student equally. No place for aptitude/intelligence/ability in report card grading equation. Schools: effort related to achievement results in those who try harder learning more. Greater effort equals greater achievement. Define: how to define ‘try hard.’ Varies from teacher to teacher. Assess: varies from teacher to teacher. Also differ in integrating Must decide what we value: learning, effort, or both. Mutual definition: needed along with assessment tools and procedures. Have a carefully planned continuously progressive curriculum enables teacher to tailor instruction to move student on to next step in mastery of knowledge, demo reasoning proficiency, performance of required skills, creation of product. The success in reaching targets is reflected in grades. Both teacher and student see progression until success is achieved. Report effort and achievement data separately. Teacher learns students’ needs and interests to align Question: is it appropriate to assign different grades by factoring in effort into the grading equation? Society: values effort because it contributes to collective well-being. Life Lesson: greater effort equals greater achievement. information into grading equation. Signal noise: message receivers cannot uncover subtleties of teachers’ intended message. Students: in control of decision to follow rules and deadlines. No penalty for those who need little effort to learn. instruction to them. Teacher and student work together to establish clear and specific targets to know they are succeeding. Instructional activities are interesting. Keep action moving. Keep targets in mind. Compliance Assume 2 students demonstrate same level of achievement; one obeys rules and one does not. Question: is it appropriate to lower the grade of later student? Define: values differ on when and when not to comply. Assess: teachers gather evidence of different sorts, give different weights to the elements. Signal noise: message receiver cannot determine message being sent. Don’t permit information’s accuracy to be sacrificed by lowering grade as punishment. Laws protect against grading policies that permit grade reduction and effect equal access to future educational opportunities. Courts compel teachers to separate punishment from achievement records. Options for alternative punishments include detention, limiting access to desirable activities, community service, etc. Attitude Assume 2 students demonstrate same level of achievement; level falls between 2 grades; one has a positive attitude and the other has a negative one. Question: are you justified in assigning different grades by factoring in attitude into the grading equation? School: compels attendance and punctuality; is a classroom management tool; cheating results in an F. Society: Law says must attend school. Values following rules to preserve social order. Life Lesson: personal responsibility is necessary for success. School: positive attitude is a valued outcome of school. Is an effective classroom management tool if based on treating others well, listening to teacher, interact appropriately. Life Lesson: a positive attitude will gain more of life’s rewards. Define: not always clear which attitudes are positive. Assess: how? Students can manipulate it. Signal noise: teachers have different values for which attitude is positive, different assessments, different weights in grading equation. Receivers cannot read message. Define which use of attitude information produces greatest good for students. It is bad practice to factor attitudes into report card grading equation. Do not entangle student achievement in grading equation with other student characteristics of aptitude, effort, compliance, and attitude. Reflect student attainment of achievement targets matching standards in grading equation.