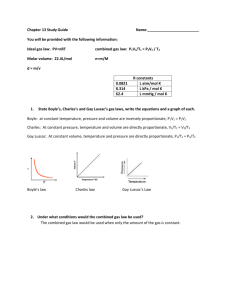
Chemistry: Mixed Review
advertisement
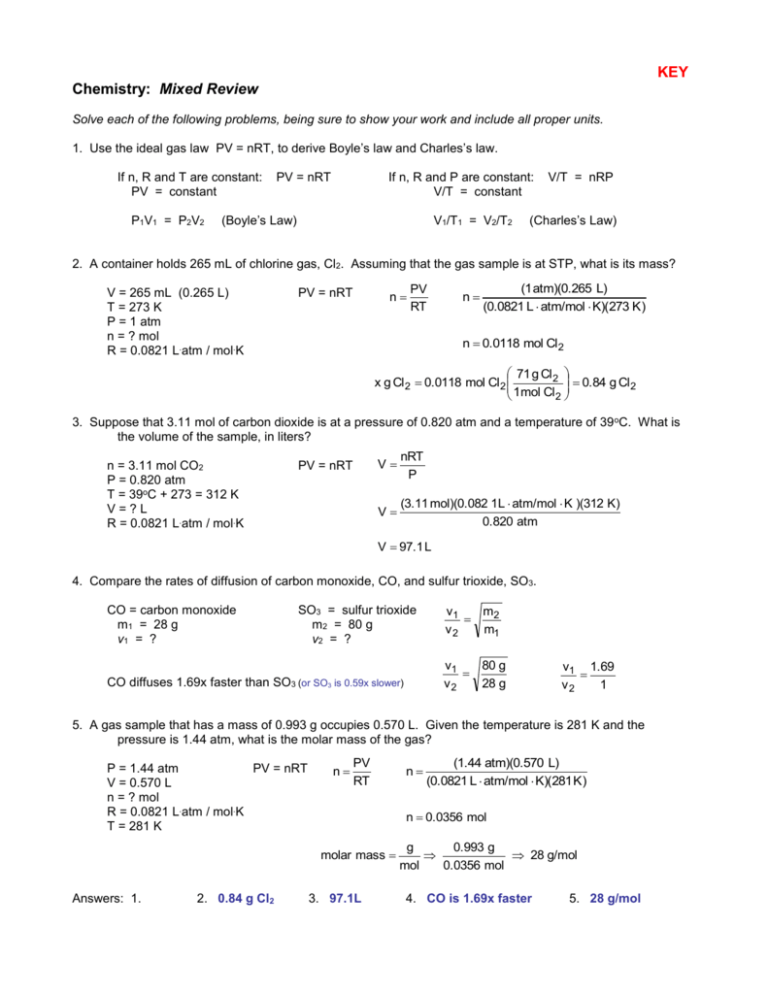
KEY Chemistry: Mixed Review Solve each of the following problems, being sure to show your work and include all proper units. 1. Use the ideal gas law PV = nRT, to derive Boyle’s law and Charles’s law. If n, R and T are constant: PV = constant P1V1 = P2V2 PV = nRT If n, R and P are constant: V/T = constant (Boyle’s Law) V1/T1 = V2/T2 V/T = nRP (Charles’s Law) 2. A container holds 265 mL of chlorine gas, Cl2. Assuming that the gas sample is at STP, what is its mass? V = 265 mL (0.265 L) T = 273 K P = 1 atm n = ? mol R = 0.0821 L.atm / mol.K PV = nRT n PV RT n (1 atm)(0.265 L) (0.0821 L atm/mol K)(273 K ) n 0.0118 mol Cl 2 71 g Cl 2 0.84 g Cl 2 x g Cl 2 0.0118 mol Cl 2 1mol Cl 2 3. Suppose that 3.11 mol of carbon dioxide is at a pressure of 0.820 atm and a temperature of 39 oC. What is the volume of the sample, in liters? n = 3.11 mol CO2 P = 0.820 atm T = 39oC + 273 = 312 K V=?L R = 0.0821 L.atm / mol.K PV = nRT V nRT P V (3.11 mol)(0.082 1L atm/mol K )(312 K) 0.820 atm V 97.1 L 4. Compare the rates of diffusion of carbon monoxide, CO, and sulfur trioxide, SO3. CO = carbon monoxide m1 = 28 g v1 = ? SO3 = sulfur trioxide m2 = 80 g v2 = ? v1 m2 v2 m1 v1 80 g v2 28 g CO diffuses 1.69x faster than SO3 (or SO3 is 0.59x slower) v1 1.69 v2 1 5. A gas sample that has a mass of 0.993 g occupies 0.570 L. Given the temperature is 281 K and the pressure is 1.44 atm, what is the molar mass of the gas? P = 1.44 atm PV = nRT V = 0.570 L n = ? mol R = 0.0821 L.atm / mol.K T = 281 K n PV RT 2. 0.84 g Cl2 (1.44 atm)(0.570 L) (0.0821 L atm/mol K)(281 K ) n 0.0356 mol molar mass Answers: 1. n 3. 97.1L g 0.993 g 28 g/mol mol 0.0356 mol 4. CO is 1.69x faster 5. 28 g/mol 6. The density of a gas is 3.07 g/L at STP. Calculate the gas’s molar mass. P = 1 atm V=?L T = 273 K n = ? mol D mass volume 3.07 g / L R = 0.0821 D = 3.07 g/L Density is an intensive property. Assume mass = 1.0 g D n n M M 68.8 g 22.4 L (1 atm)(0.325 7 L) (0.0821 L atm/mol K)(273 K ) n 0.01453 mol M M 3.07 g/L V V V PV RT molar mass 1.0 g 0.3257 L 3.07 g/L g 1.0 g mol 0.01453 mol molar mass 68.8 g/mol 7. How many moles of helium gas would it take to fill a gas balloon with a volume of 1000. cm 3 when the temperature is 32oC and the atmospheric pressure is 752 mm Hg? 1 atm 0.9895 atm 752 mm Hg P = 752 mm Hg PV = nRT 760 mm Hg V=1L n = ? mol n PV RT n R = 0.0821 L.atm / mol.K T = 32oC + 273 = 305 K (0.9895 atm)(1 L) (0.0821 L atm/mol K)(305 K ) n 0.0395 mol 8. A gas sample is collected at 16oC and 0.982 atm. If the sample has a mass of 7.40 g and a volume of 3.96 L, find the volume of the gas at STP and the molar mass. (0.982 atm)(3.96 L) (1 atm)(V 2 ) 289 K 273 K P1V1 P2 V2 P1 = 0.982 atm T1 T2 V1 = 3.96 L o T1 = 16 C + 273 = 289 K P2 = 1 atm PV n V2 = ? L PV = nRT RT T2 = 273 K n molar mass (0.982 atm)(3.96 L) (0.0821 L atm/mol K)(289 K ) g 7.4 g mol 0.164 mol V2 3.67 L n 0.164 mol molar mass 45 g/mol 9. An unknown gas effuses at 0.850 times the effusion rate of nitrogen dioxide, NO 2. Estimate the molar mass of the unknown gas. Unknown Gas m1 = ? g v1 = 0.850 Nitrogen dioxide, NO2 m2 = 46 g v2 = 1 v1 m2 v2 m1 0.850 1 46 g xg V2 63.7 g 10. What will be the pressure if we open: a. just valve A? 0.75 atm b. just valve C? c. 0.5 atm any two valves? 0.5 atm Use Boyle’s law: (a) 1.5 atm of gas divided in 2 spheres = 0.75 atm (b) 1.0 atm of gas divided in 2 spheres = 0.5 atm (c) 1.5 atm of gas divided in 3 spheres = 0.5 atm Answers: 6. 68.8 g/mol 7. 0.0395 mol 8. 3.67 L & 45 g/mol 9. 63.7 g/mol