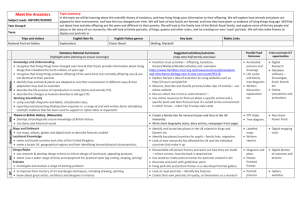
Photograph as Document: Student PLC
advertisement
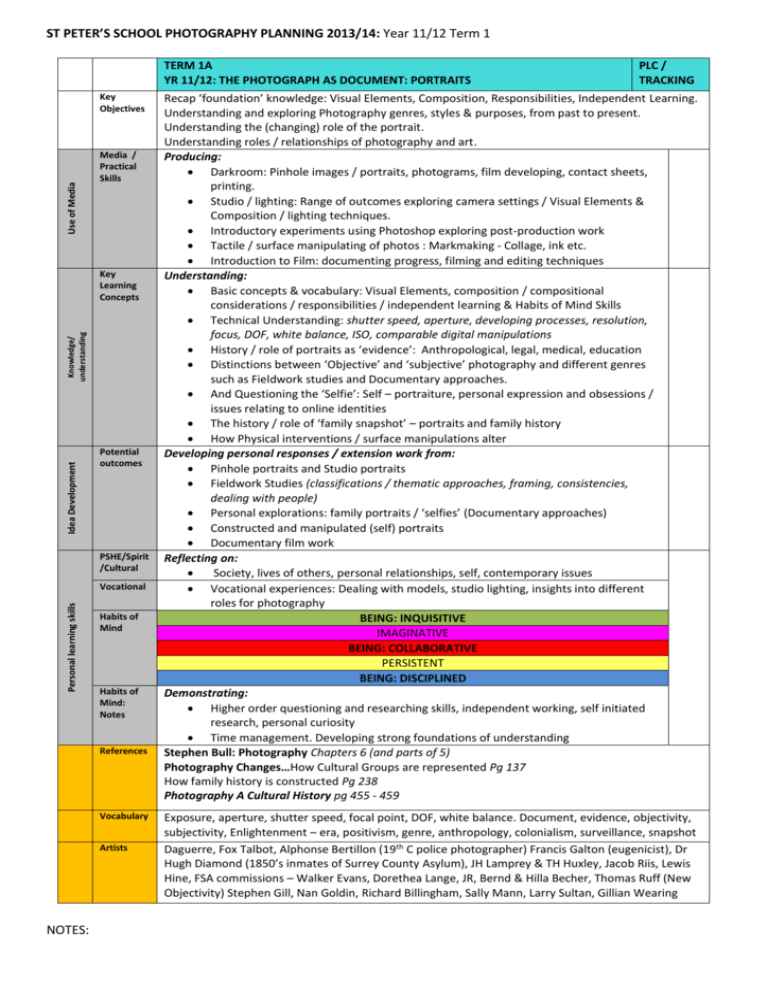
ST PETER’S SCHOOL PHOTOGRAPHY PLANNING 2013/14: Year 11/12 Term 1 TERM 1A YR 11/12: THE PHOTOGRAPH AS DOCUMENT: PORTRAITS Use of Media Key Objectives Media / Practical Skills Idea Development Knowledge/ understanding Key Learning Concepts Potential outcomes PSHE/Spirit /Cultural Personal learning skills Vocational Habits of Mind Habits of Mind: Notes References Vocabulary Artists NOTES: PLC / TRACKING Recap ‘foundation’ knowledge: Visual Elements, Composition, Responsibilities, Independent Learning. Understanding and exploring Photography genres, styles & purposes, from past to present. Understanding the (changing) role of the portrait. Understanding roles / relationships of photography and art. Producing: Darkroom: Pinhole images / portraits, photograms, film developing, contact sheets, printing. Studio / lighting: Range of outcomes exploring camera settings / Visual Elements & Composition / lighting techniques. Introductory experiments using Photoshop exploring post-production work Tactile / surface manipulating of photos : Markmaking - Collage, ink etc. Introduction to Film: documenting progress, filming and editing techniques Understanding: Basic concepts & vocabulary: Visual Elements, composition / compositional considerations / responsibilities / independent learning & Habits of Mind Skills Technical Understanding: shutter speed, aperture, developing processes, resolution, focus, DOF, white balance, ISO, comparable digital manipulations History / role of portraits as ‘evidence’: Anthropological, legal, medical, education Distinctions between ‘Objective’ and ‘subjective’ photography and different genres such as Fieldwork studies and Documentary approaches. And Questioning the ‘Selfie’: Self – portraiture, personal expression and obsessions / issues relating to online identities The history / role of ‘family snapshot’ – portraits and family history How Physical interventions / surface manipulations alter Developing personal responses / extension work from: Pinhole portraits and Studio portraits Fieldwork Studies (classifications / thematic approaches, framing, consistencies, dealing with people) Personal explorations: family portraits / ‘selfies’ (Documentary approaches) Constructed and manipulated (self) portraits Documentary film work Reflecting on: Society, lives of others, personal relationships, self, contemporary issues Vocational experiences: Dealing with models, studio lighting, insights into different roles for photography BEING: INQUISITIVE IMAGINATIVE BEING: COLLABORATIVE PERSISTENT BEING: DISCIPLINED Demonstrating: Higher order questioning and researching skills, independent working, self initiated research, personal curiosity Time management. Developing strong foundations of understanding Stephen Bull: Photography Chapters 6 (and parts of 5) Photography Changes…How Cultural Groups are represented Pg 137 How family history is constructed Pg 238 Photography A Cultural History pg 455 - 459 Exposure, aperture, shutter speed, focal point, DOF, white balance. Document, evidence, objectivity, subjectivity, Enlightenment – era, positivism, genre, anthropology, colonialism, surveillance, snapshot Daguerre, Fox Talbot, Alphonse Bertillon (19th C police photographer) Francis Galton (eugenicist), Dr Hugh Diamond (1850’s inmates of Surrey County Asylum), JH Lamprey & TH Huxley, Jacob Riis, Lewis Hine, FSA commissions – Walker Evans, Dorethea Lange, JR, Bernd & Hilla Becher, Thomas Ruff (New Objectivity) Stephen Gill, Nan Goldin, Richard Billingham, Sally Mann, Larry Sultan, Gillian Wearing