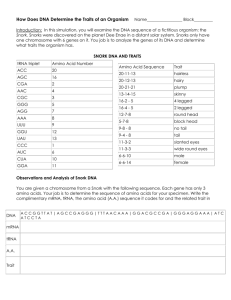
DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis Test Review - High School

Unit 4 Test: DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis REVIEW
**You may turn this review in for an extra 5 points on your test. The answer key is on my website under the “test reviews” tab.**
DNA, Replication
1. What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid
2. What are the three parts of the nucleotide?
Phosphate, sugar, nitrogen base
3. What are the four bases found in DNA?
G, A, T, C
4. How do the bases pair up (what pairs w/ what)?
A and T, G and C
5. What is the sugar found in DNA called? deoxyribose
6. What is the shape of the DNA molecule?
Double helix
7. What is the type of bond that holds the base pairs together?
Hydrogen bond
8. What makes up the backbone of the DNA molecule (the sides of the ladder)?
The sugars and the phosphates
RNA and Protein Synthesis
9. What are the three differences between RNA and DNA?
RNA=uracil, DNA=double stranded, RNA=more than one kind
10. What does RNA stand for?
Ribonucleic acid
11. What are the three types of RNA and what is their function? mRNA-copies the DNA template tRNA-carries amino acids to the ribosome to assemble proteins rRNA- component of ribosome and help to make proteins
12. How many nucleotides does it take to make one amino acid?
3
13. Where are proteins built? (on which cell organelle?) ribosomes
14. List three reasons proteins are important.
Provide structure, used as enzymes, act as antibodies
15. Where does transcription take place and what happens?
Takes place in the nucleus and mRNA is made from a DNA template
16. What is the process called that changes DNA to mRNA? transcription
17. What is the process called that uses tRNA to carry amino acids to mRNA to build a polypeptide? translation
18. Fill in the matching base:
DNA DNA
(process name :__replication__)
Adenine-- T
DNA m RNA
(process name :_transcription_) mRNA tRNA
(process name :_translation)
Thymine--
Cytosine--
Guanine--
A
G
C
Adenine--
Thymine--
Cytosine--
Guanine--
U
A
G
C
Adenine-- U
Uracil-- A
Cytosine-G
Guanine— C
19. Where does translation take place and what happens?
Takes place on the ribosomes in the cytoplasm; tRNA carries amino acids to the ribosome to pair their anticodon with the mRNA codon to assemble amino acids in a chain to make a polypeptide
20. Where in the cell are the amino acids when tRNA is trying to find them?
Amino acids are floating in the cytoplasm before they attach to tRNA to be used during protein synthesis
21. Define the following words:
Codon- group of 3 nitrogen bases
Anticodon- group of 3 noncoding bases found on tRNA
Nucleotide- monomer of a nucleic acid; made of a phosphate, a sugar, and a nitrogen base
22. Describe the mutations below:
(deletion, insertion, substitution-missense, substitution-silent, substitution-nonsense)
Deletion- loss of one base in a DNA sequence
Insertion- addition of one base in a DNA sequence missense: one base change that changes the amino acid meaning ex: GGA to GCA is Gly to Ala silent- one base change does not change the amino acids meaning ex: GGA to GGU is Gly, to Gly nonsense- one base change make the amino acid a “stop” codon ex: GAA to UAA is Glu to Stop
23. Label the following structures on the diagram:
mRNA 1
tRNA 5
codon – any set of 3 bases
amino acid 3
ribosome 2
polypeptide (protein) 4
Multiple choice:
24. DNA replication results in a. 2 completely new DNA molecules b.
2 DNA molecules that each contain a strand of the original c.
2 old DNA molecules d.
1 new molecule of RNA
25. What are the units that form a DNA molecule?
A. amino acids b . nucleotides c. nitrogen bases
26. Which is used in DNA replication AND in protein synthesis?
A. DNA b.tRNA c. mRNA
27. Which mutation is being illustrated below?
Normal: GUG-UGA-CGC-UGU-CCA
Mutated: GGG-UGA-CGC-UGU-CCA a.
Substitution b. insertion c. deletion
28. In the sequence TAC GGA, what do the letters represent?
A. amino acids b. nitrogenous bases c.sugars
29. Describe what happens at each stage of the diagram
I.
DNA will unwind
II.
mRNA is made from the DNA template in the nucleus
III.
DNA helix zips back up; mRNA leaves the nucleus
IV.
tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome to pair with mRNA codons to make a complete protein
30. Label #2, #3, and #4 on the diagram
2=sugar 3=phosphate
31. Describe what is happening in each stage of the diagram:
4=nucleotide
transcription=mRNA made from DNA template
Translation= mRNA codons pair with tRNA to assemble amino acids into a protein
32. Which of the following shows a mutation that will not change the nature of the protein that is made (so it will function normally)? a.
UCC to GAC b.
GAG to UAG c . GAA to GAG- still Glu d. GAG to CAG