Study Guide Geography - Henry County Schools
advertisement

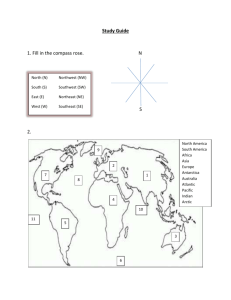
Study Guide Geography Standards: SS3G1 The student will locate major topographical features. a. Identify major rivers of the United States of America: Mississippi, Ohio, Rio Grande, Colorado, Hudson. b. Identify major mountain ranges of the United States of America: Appalachian, Rocky. c. Locate the Equator, Prime Meridian, and lines of latitude and longitude on a globe. d. Locate Greece on a world map. SS3G2 The student will describe the cultural and geographic systems associated with the historical figures in SS3H2a. a. Identify on a political map specific locations significant to the life and times of these historical figures. b. Describe how place (physical and human characteristics) had an impact on the lives of these historical figures. c. Describe how each of these historical figures adapted to and was influenced by his/her environment. d. Trace examples of travel and movement of these historical figures and their ideas across time. e. Describe how the regions in which these historical figures lived affected their lives and had an impact on their cultural identification. By the end of this unit you should be able to: Locate the major rivers of the U.S.A on a map (see above). Locate the major mountain ranges of the U.S.A. on a map (see above). Locate the equator, the prime meridian, and lines of latitude and longitude on a globe. Locate a country given lines of latitude and longitude on a globe. Locate Greece on a world map. Match the concepts related to the 5 Themes of geography to example of each. Describe how these themes influenced the lives of specific Americans (Paul Revere). Vocabularygeography – the study of people, places and the earth. landform – a shape or feature of the earth’s surface. Vocabulary continued – latitude – lines that cross the globe from east to west. longitude – lines that cross the globe from north to south. Prime Meridian – a line of longitude that passes through Greenwich, England. Equator – a lone of latitude that circles the globe exactly halfway between the North and South poles. coast – the land next to the ocean. Appalachian Mountains – a mountain range west of the Atlantic Coastal Plain that stretches up the eastern United States from Georgia to Main. Colorado River – a river in the United States that flows through the Rocky Mountains and carved much of the Grand Canyon. Hudson River – A river in the United States that flows through the state of New York to the Atlantic Ocean. Mississippi River – a large river in the United States that beings in northern Minnesota and flows to the Gulf of Mexico. Ohio River – a river in the United States that flow from Pennsylvania to the Mississippi River. Rocky Mountains – a mountain region in the western United States. Rio Grande – a river in the United states that forms part of the border between Texas and Mexico. Use this map to locate the following: Appalachian Mountains Rocky Mountains Hudson River Ohio River Mississippi River Rio Grande River Colorado River The Mediterranean country of Greece has influenced our country in many ways, particularly related to our democratic form of government. The map below shows where Greece is located. The 5 Themes of Geography Location Place Where is it? Absolute: A location can be absolute (specific) as in coordinates of a map using longitude and latitude Relative: A location can be relative - examples: next door, nearby, a short drive, down the road a ways. Or, it can be in the same general location as another location - example: next to the post office. Movement Movement refers to the way people, products, information and ideas move from one place to another. This can be local such as how did you get to school today, or it can be global such as how did humans get to North America? A place is an area that is defined by everything in it. All places have features that give them personality and distinguish them from other places. Human/Environment Interaction Human-environment interaction looks at the relationships between people and their environment; how people adapt to the environment and how they change it. If you refer to your school as a place, then that place would include walls, windows, gym, cafeteria, classrooms, people, clothing, books, maps, mops, brooms, hallways, mice (if you have them) and everything else in the school, including the languages spoken. Region A region is an area that is defined by certain similar characteristics. Those unifying or similar characteristics can be physical, natural, human, or cultural. How do people depend on the environment? (Example: In ancient times, the annual flooding of the Nile River produced good soil for growing crops.) How to people adapt to the environment? (Example: The ancient Egyptians rebuilt their homes each year, after the annual flooding. As time went on, they built their homes above the flood plain.) How do people modify the environment? (Example: The ancient Egyptians built irrigation ditches to help water the crops. In modern times, Egypt built a dam to control the flood waters of the Nile River.) Suggested Websites: http://kids.nationalgeographic.com/kids/ http://www.kbears.com/geography.html http://www.knowledgequestmaps.com/My-Top-Geography-Websites.html