Physical Science-Radiation - Harnett County High School
advertisement

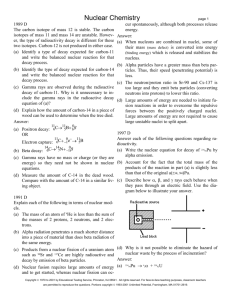
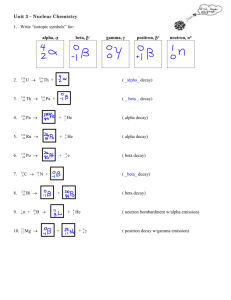
HARNETT COUNTY HIGH SCHOOLS Course: Physical Science Title of Unit: 2.3 Radioactivity Timeframe: 3 days Content Area Standard(s): PSc.2.3 Understand the role of the nucleus in radiation and radioactivity. PSc.2.3.1 Compare nuclear reactions including alpha decay, beta decay and gamma decay; nuclear fusion and nuclear fission PSc.2.3.2 Exemplify the radioactive decay of unstable nuclei using the concept of half-life. Unpack What does this standard mean a child will know, understand and be able to do? PSc.2.3.1 • Compare the characteristics of alpha and beta particles and gamma rays – composition, mass, penetrability. • Compare alpha, beta, and gamma decay processes –alpha decay reduces the mass of an atom by 4 and the atomic number by 2; beta decay increases the atomic number by 1 (a neutron decays into a proton and electron); gamma rays are electromagnetic waves released from the nucleus along with either an alpha or beta particle. • Compare the processes of fission (splitting of a very large atom) and fusion (joining of atoms) in terms of conditions required for occurrence, energy released, and the nature of products. PSc.2.3.2 • Conceptually explain half-life using models. • Perform simple half-life calculations based on an isotope’s half-life value, time of decay, and/or amount of substance. Reading Standard(s): 3. Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks, attending to special cases or exceptions defined in text. 4. Determine the meaning of symbols, key terms, and other domain-specific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context relevant to grades 9–10 texts and topics. 5. Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relationships among key terms (e.g., force, friction, reaction force, energy). Writing Standard(s): 4. Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. 6. Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products, taking advantage of technology’s capacity to link to other information and to display information flexibly and dynamically. 9. Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. Math Practice(s): 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. Model with mathematics. Use appropriate tools strategically. Attend to precision. Look for and make use of structure. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Technology Standard(s): HS.TT.1 Use technology and other resources for assigned tasks. Learning Experiences: HS.TT.1.1 Use appropriate technology tools and other resources to access information (multidatabase search engines, online primary resources, virtual interviews with content experts). *see Notes and Additional Information Project Goals and Description of Unit: Students will obtain a basic understanding of how nuclear energy is created using fusion and fission and have a working understanding of half-life. Essential Questions: 1. How is nuclear energy created, and what are its uses? 2. How is the process of half-life used in reference to the environment? 3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of nuclear energy? Vocabulary: Fusion fission half-life isotopes Uranium-235 alpha particles beta particles gamma radiation nuclear decay Parent nucleus daughter nucleus Geiger counter Instructional Resources (print materials, technology): Textbook, Power Point presentations, physical science websites, science articles from periodicals, science video clips Facilitator’s Role: Provide clear and effective explanations of concepts, provide descriptive feedback, provide visual representations of concept Formative Assessments: Ticket out the door Bell ringers White boarding Online assessments Clock buddies Think-Pair-Share Pop quizzes Parking Lot to allow students to ask questions Peer Assessment KWL Popcorn questioning Writing summary of learned concepts Summative Assessments: projects unit tests, midterm exam, quizzes lab report comprehensive final Learning Experience Examples Fission animation [B2] www.youtube.com/watch?v=o-9yt7OAYmE Half-life animation [B2] http://www.furryelephant.com/player.php?subject=physics&jumpTo=re/3Ms1 Geiger counter simulation [B2] http://www.furryelephant.com/player.php?subject=physics&jumpTo=re/11D2s1 www.pleasanton.k12.ca.us/fhsweb/.../chemlab/U238Simulation.pdf [D6] Lab isotopes of pennies (Materials needed pennies made prior and post 1982 6old and 4 new pennies are needed for each group) http://sciencenetlinks.com/student-teacher-sheets/isotopes-pennies/ Lab of radioactive decay using pennies [C4 ] http://serc.carleton.edu/quantskills/activities/PennyDecay.html Lab Half life (100 nickels and 100 pennies per group) similar to the one lab above [ C4 ] http://www.pbs.org/safarchive/4_class/45_pguides/pguide_501/4551_animals.html khanacademy.com (resource) SAS (Access via the Harnett County Schools homepage) Goal 2 PSc.2.3 Understand the role of the nucleus in radiation and radioactivity. PSc.2.3.1 Compare nuclear reactions including alpha decay, beta decay, and gamma decay; nuclear fusion and nuclear fission. SAS: Understand the role of the nucleus in radiation and radioactivity. Nuclear Reactions QL#77 Radioactivity QL#1008 Nuclear Power: The Pros & Cons, Web Lesson 268 Notes and Additional Information: To add and/or check for new materials check the following: http://harnettcountyhighschools.wikispaces.com/Science