Theoretical & Experimental Probability Worksheet
advertisement

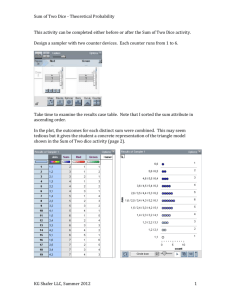
Theoretical and Experimental Probability Theoretical Probability A ratio that compares the number of possible successful outcomes to the total number of possible outcomes. Determined by reason or calculation. Activity Determine the theoretical probability of obtaining each of the possible sums when rolling two dice. Total of Two Dice Number of Combinations 2 1 3 2 Theoretical Probability Fraction of the Percent of the Total Number of Total (to the Combinations nearest percent) 2 1 = 36 18 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 ***Make sure you write all fractions /36 and in lowest possible terms*** Theoretical Probability – Reflection Questions 1) Two dice are rolled 100 times. How many times should the total of the dice be 2? Explain why. 2) How many times would you expect to roll a total of 8 with 1000 rolls of two dice? 3) The theoretical probability of rolling a total of 7 with two dice equals the sum of the probabilities of rolling which other numbers? Theoretical and Experimental Probability Experimental Probability A ratio that compares the number of times an event occurs to the total number of trials or tests. Determined by experiment. Activity Determine experimental probability by rolling two dice 50 times. Record your results in the table below. Total of Two Dice 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tally Number of Times Rolled Experimental Probability Fraction of the Percent of the Total Number Total Number of Rolls (in of Rolls lowest terms) Experimental Probability – Reflection Questions 1) How many times did you roll a 5? 2) What is the experimental probability of rolling a total of 5, as a percent? 3) What is the theoretical probability of rolling a total of 5, as a percent? 4) Does your experimental probability match your theoretical probability for rolling a total of 5?