Genomes/Proteosomes - Iowa State University
advertisement

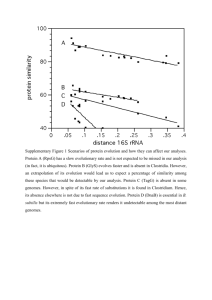
Genomes/Proteosomes Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Lilli Howard BIOL/GEN 313 Dr. Vollbrecht 04/22/14 1. Define: Comparative Genomics: _____________________________________________ 2. What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes? 3. Define: Co-linearity: ______________________________________________________ 4. T/F: Humans have relatively short introns 5. T/F: Most of the human genome encodes proteins 6. What is the goal of proteomics? What two processes are used to accomplish this? 7. What is the relation between genome size and gene number in prokaryotes? 8. Eukaryotic genomes are typically much larger than prokaryotic genomes. What accounts for the increased amount of DNA in eukaryotic genomes? 9. What makes up most of the human genome? 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 sistaff@iastate.edu http://www.si.iastate.edu 10. What is the average total length of a human gene? a. 270 bp b. 2,700 bp c. 27,000 bp d. 270,000 bp 11. A scientist determines the complete genomes and proteomes of a live cell and a muscle cell from the same person. Would you expect bigger differences in the genomes or proteomes of these two cell types? Explain your answer. 12. Why is knowledge of a protein’s structure important? 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 sistaff@iastate.edu http://www.si.iastate.edu