Cell Nucleus - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

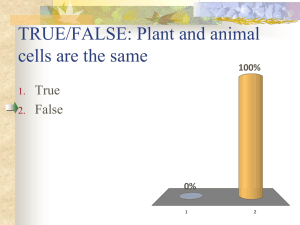
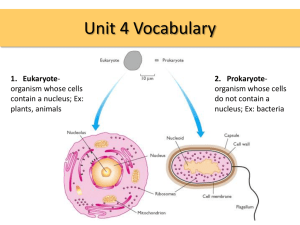
Read the information about the nucleus and DNA. Then follow the directions for drawing below the diagram. Cell Nucleus - Commanding the Cell The cell nucleus acts like the brain of the cell. It helps control eating, movement, and reproduction. If it happens in a cell, chances are the nucleus knows about it. The nucleus is not always in the center of the cell. It will be a big dark spot somewhere in the middle of all of the cytoplasm (cytosol). You probably won't find it near the edge of a cell because that might be a dangerous place for the nucleus to be. If you don't remember, the cytoplasm is the fluid that fills cells. Life Before a Nucleus Not all cells have a nucleus. Biology breaks cell types into eukaryotic (those with a defined nucleus) and prokaryotic (those with no defined nucleus). You may have heard of chromatin and DNA. You don't need a nucleus to have DNA. If you don't have a defined nucleus, your DNA is probably floating around the cell in a region called the nucleoid. A defined nucleus that holds the genetic code is an advanced feature in a cell. Important Materials in the Envelope The things that make a eukaryotic cell are a defined nucleus and other organelles. The nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus and all of its contents. The nuclear envelope is a membrane similar to the cell membrane around the whole cell. There are pores and spaces for RNA and proteins to pass through while the nuclear envelope keeps all of the chromatin and nucleolus inside. When the cell is in a resting state there is something called chromatin in the nucleus. Chromatin is made of DNA, RNA, and nuclear proteins. DNA and RNA are the nucleic acids inside of the cell. When the cell is going to divide, the chromatin becomes very compact. It condenses. When the chromatin comes together, you can see the chromosomes. You will also find the nucleolus inside of the nucleus. When you look through a microscope, it looks like a nucleus inside of the nucleus. It is made of RNA and protein. It does not have much DNA at all. DNA consists of two long, twisted chains made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains one base, one phosphate molecule and the sugar molecule deoxyribose. The bases in DNA nucleotides are adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine. Draw, label and color the DNA strand using the same colors you see here. This will go in your journal – page number is on the board. Chromosomes and DNA Chromosomes are DNA wrapped around proteins to form an X-shaped structure. The diagram will help you see the relationship. 1. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus 2. Chromosomes are made of DNA 3. Sections of chromosomes are called genes DNA - deoxyribonucleic acid (it is the genetic code that contains all the information needed to build and maintain an organism) • DNA guides the cell in making new proteins that biological traits. • DNA gets passed from one generation to the next. • DNA is one of the nucleic acids, information-containing molecules in the cell. • DNA is found in the nucleus of almost every cell – prokaryotes usually have RNA instead of DNA. Two Types of Cell Division 1. Mitosis- Occurs in body cells (somatic cells) - In mitosis you start with one cell and end up with two cells that have the same number of chromosomes as the first cell. 2. Meiosis- Occurs in sex cells (reproductive cells) - In meiosis you start with one cell and end with four cells that have one-half the number of chromosomes of the first cell. Division to Multiply – Mitosis Vocabulary cell = the basic unit of a living thing cell division = the dividing of a cell following mitosis chromosome = the stringlike structure in a cell nucleus that carries information controlling all the cell's activities DNA = the molecule in each cell that directs the cell's activities mitosis = the process by which a cell produces two new identical nuclei The Cell Cycle - Mitosis