Plate Tectonics Diagrams with Notes
advertisement

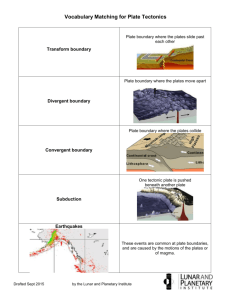
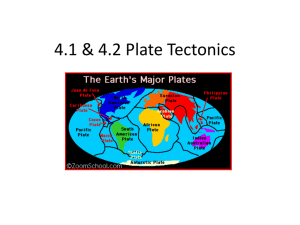
Plate Tectonics – Boundaries Lithospheric Plates– the layer of crust that is made of rocks Earth’s crust is broken up into 13 plates which move because of activity at the plate boundaries.(7 major, 6 minor) Convection cells– provide the energy for plate tectonics to occur. Heat from the hot magma causes the plates to move like they are on a conveyor belt. Plate Movement Convection Cell The Core Types of Crust Why does the oceanic crust sit below the continental crust? Continental Crust Oceanic Crust Types of Boundaries 1. Convergent – plates move towards each other 2. Divergent – plates move away from each other 3. Transform Fault – plates move in sideways against each other Divergent Plate Boundary – Oceanic Also known as Seafloor Spreading Example – Mid-Atlantic Ridge Picture – Ridges Oceanic Plate 1 Effects – Plate Movement Rift Valley Ridges Oceanic Plate 2 Magma 1. Plates spread apart and create an opening (rift valley) 2. Magma is released to the surface 3. Creates underwater mountains (ridges) – birthplace of “new oceanic rocks” 4. “Ridge Push” occurs from the thickening of the lithosphere when moving away from the ridge. a. This creates a slope of the asthenosphere underneath leading to the sliding down of the lithosphere away from the ridge b. Causes earthquakes Divergent Plate Boundary – Continental Example – East African Rift (Ethiopian Mountains) Picture – Effects – 1. Plates spread apart and create an opening (rift valley) 2. Magma is released to the surface 3. Creates mountains (ridges) around the valley – birthplace of “new continental rocks” CONVERGENT PLATE BOUNDARY – OCEANIC/CONTINENTAL Example – Mariana Trench (South Asian Coast) & Peru-Chile Trench (western coast of S. America) Picture – Volcano Mountain Range Continental Plate Oceanic Plate Ocean Trench Effects – 1. 2. 3. 4. Two plates collide together – ocean plate subducts (sinks) under the continental plate Oceanic plate melts back into magma creating a volcano on the continental plate Creates an ocean trench and continental mountains from the 2 plates colliding “Slab Pull” occurs when the lithosphere becomes denser after cooling and when moving away from the ocean ridge. a. The weight of the lithosphere causes the lithosphere to sink at a subduction zone and help pull the remaining plate down with it. CONVERGENT PLATE BOUNDARY – OCEANIC/OCEANIC Example – Aleutian Islands (Island Chain off of Alaska) Picture – Oceanic Plate 1 Ocean Trench Effects – 1. Denser oceanic plate sinks below the less dense oceanic plate 2. Subducting plate melts into magma, creating volcanoes & mountains Oceanic Plate 2 CONVERGENT PLATE BOUNDARY – CONTINENTAL /CONTINENTAL Example – Himalayan Mountains (between the Indian and Asian continents) Picture – Effects – 1. Plates collide together 2. Plates get pushed upward 3. Creates mountains Transform Fault Boundary Example – San Andreas Fault (California) Picture – Effects – 1. Land is being pulled in opposite directions 2. Earthquakes produced from plates rubbing together Questions – Name Period Answer Key 1 2 3 4 Grade ________% February 25, 2014 Score _______/24 1. How many types of boundaries are there for each category? a. Convergent 3 b. Divergent 2 c. Transform Fault 1 2. Why are mountains created by oceanic/oceanic and oceanic/continental boundaries even though one plate is subducting under the other plate? The subduction of the ocean plate pushes upward on the other plate creating the mountains 3. Why are ocean trenches formed by oceanic/oceanic and oceanic/continental boundaries? There is a gap created where the 2 plates meet. The trench is formed because the subducting plate is being bent down and the other plate is being pushed up 4. What forms the ridges (mountains) at a divergent plate boundary? Pressure from rising magma on the end of each plate 5. What will eventually happen to the West Coast of California? It will break off of California and move out into the Pacific Ocean 6. What is happening to the size of the Atlantic Ocean? It is getting bigger 7. What is happening to the size of the Pacific Ocean? It is getting smaller 8. Look at the map below. What do you notice about the locations of earthquakes/volcanoes and plate boundaries? Earthquakes and volcanoes are created mostly at plate boundaries 9. Why is the Pacific Plate (under most of the Pacific Ocean) referred to as the “Ring of Fire”? The Pacific Ocean is surrounded by plate boundaries that create volcanoes (referred to as the “ring”). These erupting volcanoes are referred to as the “fire”. 10. How are the Hawaiian Islands different from other volcanic island chains? Hawaii is located over a hot spot under the middle of the plate; it is not located at a plate boundary like other volcanic island chains. 11. Create a chart (see below) that contrasts the differences between each type of plate boundary. Differences: (Come up with at least 3 differences for each Boundary Type) Divergent Plate Boundaries Convergent Plate Boundaries Transform Fault Boundaries 1. Moving apart 1. Moving together 2. Creates new rocks 1. Moving side by side 2. Creates volcanoes 3. Creates mountain chains 2. Causes most earthquakes 3. Creates trenches 3. Creates a fault zone under water Similarities: (Come up with at least 3 similarities for the boundaries) 1. Involves plate movements 2. Involve at least 2 plates 3. Slow, constant movements