PowerQuiz_iClicker-QaFor5674
advertisement

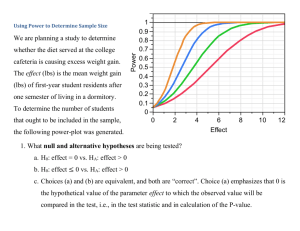
Using Power to Determine Sample Size whether the diet served at the college cafeteria is causing excess weight gain. The effect (lbs) is the mean weight gain (lbs) of first-year student residents after one semester of living in a dormitory. To determine the number of students that ought to be included in the sample, Power We are planning a study to determine 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 2 the following power-plot was generated. 4 6 Effect 8 10 12 1. What null and alternative hypotheses are being tested? a. H0: effect = 0 vs. HA: effect > 0 b. H0: effect ≤ 0 vs. HA: effect > 0 c. Choices (a) and (b) are equivalent, and both are “correct”. Choice (a) emphasizes that 0 is the hypothetical value of the parameter effect to which the observed value will be compared in the test, i.e., in the test statistic and in calculation of the P-value. 2. What is the effect (lbs), is true? a. 0 b. 2 c. 4 d. 6 e. 8 Power numerically, if the null hypothesis 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 2 4 6 Effect 8 10 12 3. What is the probability (numerically) of rejecting the hypothesis is true. a. 0.01 b. 0.05 c. 0.10 d. 0.90 e. 0.95 Power null hypothesis if the null 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 2 4 6 Effect 8 10 12 4. What (numerically) is the Type 1 a. 0.01 b. 0.05 c. 0.10 d. 0.90 e. 0.95 Power error rate shown in the plot? 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 2 4 6 Effect 8 10 12 5. What significance level is shown in the plot? b. 0.05 c. 0.10 d. All of the above e. None of the above Power a. 0.01 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 2 4 6 Effect 8 10 12 6. The sample sizes used in the graph are 32, 64, 128, and 256 students. their sample size. Which curve is based on the least sample size of 32? a. orange b. blue c. green d. red e. not enough information is given Power Label each of the four curves with 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 2 4 6 Effect 8 10 12 7. For the sample of 32 students (the red curve), what (numerically) is alternative that that the effect is 6 lbs? a. 0.05 b. 0.20 c. 0.40 d. 0.60 e. 0.80 Power the power of the test against the 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 2 4 6 Effect 8 10 12 8. For the sample of 32 students (the red curve), what (numerically) is against the alternative that that the effect is 8 lbs? a. 0.05 b. 0.20 c. 0.40 d. 0.60 e. 0.80 Power the Type 2 error rate of the test 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 2 4 6 Effect 8 10 12 For detecting an effect of 6 lbs, if the maximum acceptable Type 2 error rate is 0.15 (i.e., 15%), why would a sample size of 32 (red curve) be too small? a. Type 2 error rate would be 0.40, too big, larger than 0.15 b. Type 2 error rate would be 0.60, too big, larger than 0.15 c. Type 2 error rate would be Power 9. 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 2 4 0.0.05, too small, less than 0.15 d. Type 2 error rate would be 0.10, too small, less than 0.15 6 Effect 8 10 12 10. For detecting an effect of 6 lbs, if the maximum acceptable Type 2 would a sample size of 256 (orange) be too large? a. A sample of size 64 (green) would be sufficient, with power = 0.85 and Type 2 error rate = 0.15 b. A sample of size 256 would Power error rate is 0.15 (i.e., 15%), why 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 2 4 be wasting resources, because the power would be greater than 0.99, far more than required. c. Both of the above d. None of the above 6 Effect 8 10 12