Key Terms and Vocab
advertisement

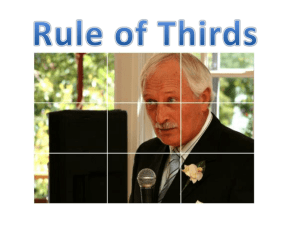
KEY TERMS and VOCABULARY of PHOTO I Photography – “light writing”; the creation of images through the exposure of light on a surface. The art of making photographs for fine art or commercial purposes. Composition – the way the elements and principles of art are visually arranged into a harmonious and unified whole. Relies on successful use of the Elements and Principles of art. Abstraction – to distort; to take a small part of a larger image to create a new image not immediately recognizable as being from its original source. Rule of thirds – a compositional format that divides a composition into 3 equal parts, placing main subjects on or near dividing lines. Nine zone grid - a compositional format that divides a composition into 9 sections (rule of thirds drawn overlapping horizontally and vertically), placing main subjects on or near intersecting lines. Harsh light – an intense light quality that creates bright highlights and dark shadows without a very wide transitional value range. Soft light – a subtle light quality that creates soft edges and a wide transitional range of values. Diffused light – light that has been “spread out”, for example through frosted glass or sheer curtains ELEMENTS of ART: Elements of Art are the basic building blocks of composition; the basic structural pieces that go together toward creating unity in a composition. Line – one of the basic elements of art, literal or implied. Shape – one of the basic elements of art, geometric (circle, square, triangle, etc.) or organic. Texture - one of the basic elements of art, refers to the visual and/or tactile quality of a surface. Pattern - one of the basic elements of art, refers to regular or geometric repetition of a shape. Repetition of elements or combinations of elements in a recognizable organization. Form - one of the basic elements of art, refers to three-dimensionality of shapes. Value – an element of art concerned with the degree of lightness or darkness of a color. In photography, the range of light and dark (shades of grey) on a spectrum with white on one end and black on the other. Space – an element of art that indicates areas between, around, above, below or within something. Can refer to background, foreground, middle-ground. Can refer to positive or negative space. PRINCIPLES of ART: The way the Elements of Art are used and combined in a composition. Contrast – principle of art that refers to differences between elements such as color, texture, value, shape and scale. In photography it can also refer to the degree of light to dark value in an image. Emphasis – one of the principles of art, refers to a center of interest in a composition; where the viewer’s attention is drawn to first, it tends to stand out in some way and creates a focal point in the composition. Movement - one of the principles of art, refers to the way a viewer’s eye is drawn throughout a composition from one area to the next. Associated with rhythm and how the compositional arrangement of the parts move the viewer’s eye through the work. Rhythm – a principle of art that refers to ways of combining elements to produce the appearance of movement in a composition. Can be achieved through repetition, alternation or progression of an element. Variety – a principle of design concerned with the inclusion of differences in the elements of a composition to offset unity and add visual interest. Balance – a principle of art that refers to the arrangement of visual elements to create stability in an artwork. Can be symmetrical, asymmetrical, modified symmetry, and radial. Can refer to placement of subjects, light and dark, etc. Unity - one of the principles of art, refers to all of the sense of wholeness that results from the successful combination of the elements of art in a composition. Symmetry – compositional balance that is the same on both sides if split down the middle. (symmetry, asymmetry / modified symmetry, radial)