Quantitative Genetics - Iowa State University
advertisement

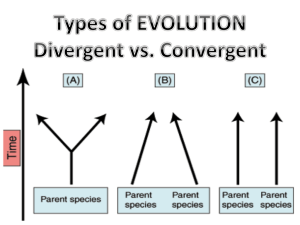
Quantitative Genetics Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Lilli Howard BIOL/GEN 313 Dr. Vollbrecht 04/28/14 Define 1. Continuous variation:______________________________________________________ 2. Discontinuous variation: ___________________________________________________ 3. Quantitative traits: ________________________________________________________ 4. Qualitative traits: _________________________________________________________ 5. For each of the four terms described above give an example. 6. Why might a trait controlled by a single gene act like a quantitative trait? Define: 7. Meristic traits: ___________________________________________________________ 8. Threshold traits:__________________________________________________________ 9. Mean: __________________________________________________________________ 10. Variance: _______________________________________________________________ 11. Standard deviation: _______________________________________________________ 12. The measurements of a distribution with a higher ____ will be more spread out. a. b. c. d. Mean Variance Standard deviation Standard deviation and variance 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 sistaff@iastate.edu http://www.si.iastate.edu 13. A geneticist is interested in whether asthma is caused by a mutation in the DS112 gene. The geneticist collects DNA from 120 people with asthma and 100 healthy people and sequences the DNA. She finds that 35 people with asthma and non of the healthy people have a mutation in the DS112 gene. What is the population in this study? a. The 120 people with asthma b. The 100 healthy people c. The 35 people with a mutation in their gene d. All people with asthma 14. Explain the relationship between a population and a sample. What characteristics should a sample have to be representative of the population? 15. List all the components that contribute to the phenotypic variance and define each component. 16. For each of the following characteristics, indicate whether it would be considered a discontinuous or a quantitative characteristic. Justify your answer. a. Kernel color in a strain of wheat in which two co-dominant alleles segregating at a single locus determine the color. Thus, there are three phenotypes present in this strain: White, light red, and medium red. b. Body weight in a family of Labrador retrievers. An autosomal recessive allele that causes dwarfism is present in this family. Two phenotypes are recognized: dwarf and normal. c. Presence or absences of leprosy. Susceptibility to leprosy is determined by multiple genes and numerous environmental factors. d. Number of toes in guinea pigs, which is influences by genes at many loci. e. Number of fingers in humans. Extra fingers are caused by the presences of an autosomal dominant allele. 17. The following data are the numbers of digits per foot in 25 guinea pigs. Construct a frequency distribution for the data: 4, 4, 4, 5, 3, 4, 3, 4, 4, 5, 4, 4, 3, 2, 4, 4, 5, 6, 4, 4, 3, 4, 4, 4, 5 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 sistaff@iastate.edu http://www.si.iastate.edu