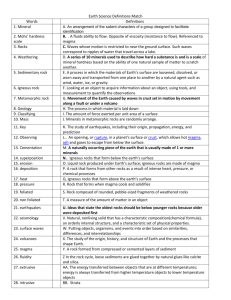
Rocky`s Journey Slide Guide: Illustrate and label the rock cycle Hi
advertisement

Rocky’s Journey Slide Guide: 1. Illustrate and label the rock cycle 2. Hi, My name is rocky, I’m a rock sitting on the surface I am your guide on the journey around the rock cycle. The rock cycle is a _______ ______ that occurs over _______ of years. It makes new rock, destroys old rock, and recycles the ingredients of the Earth's crust over and over again! 3. Oh no! I'm breaking up...That's right, it doesn't look good - I'm weathering away fast All rocks on the Earth's surface ________ - though some weather faster than others. Three different forces work together to break up rocks into smaller pieces. 1. _______ _______ - cycles of hot and cold temperatures make rocks expand and contract, and rain may freeze and expand in cracks in the rock. These processes eventually lead to rocks cracking and breaking up. 2. ________ ______ - different chemicals can dissolve rock, helping to break it up; even water can dissolve some rocks. Polluted 'acid rain' causes chemical weathering. 3. _________ ______ - tree roots can force themselves into small cracks in rocks and eventually break the rocks apart. 4. Describe the following as it would look in nature: Physical Weathering Chemical Weathering Biological weathering 4. I'm being swept off my feet! Yep - now that I have weathered into small pieces, it is easy for me to be moved around. As rocks weather, they are _____ ______ into small, easily transportable pieces or particles. The movement of these particles is called ________. There are four major ways erosion can occur: 1. ____ ______ - broken pieces of rock fall to the ground, and roll or slide down slopes. 2. ____ ______ - rivers and streams can transport all sizes of particles. 3. ____ ______ - small grains of sand can be picked up and moved by the wind in dust storms. 4. ____ ______ - ice rivers, called glaciers, can transport very large pieces of stone. 6. I've got a sinking feeling... The river that has carried me along has now reached the _____ - I think I'm being dumped. Particles of rock cannot be ___________ forever. Rivers reach the ______, the wind stops _______ and ________ melt - they dump the load of __________ they were carrying. This process is called ________. During deposition particles of rock are laid _______ ____ _______. Heavier particles are normally dumped _______ and then covered by _______ ________. Layers of sediment build up over time. These layers form a ___________ __________. 7. Oh no, what's happening now? This might not be so bad after all - I'm feeling whole again As the layers of ________ build up, the ___________ on the lower layers __________. The layers are __________ together and any _______ mixed in with the sediments is forced out. This process is called __________. At the same time the particles of sediment begin to ______ to each other - they are cemented together by ________, or by ________ like ______ or ________. After compaction and cementation the sedimentary sequence has changed into a sedimentary rock. Sedimentary rocks like _________ , ______ and _________ differ from other rocks in that they: 1. Are formed from _______ of sediment built up over _______ years. 2. Are ________ of sediment _________ together by various minerals. 3. May contain ________ - remains of plants and animals that were _________ up in the sediment. 8. Up, up and away... What - light at the end of the tunnel? The Earth's crust can be put under a lot of _________. Sometimes ________ act to ______ sections of the Earth's crust apart. At other times they are ________ together. All this movement can cause rocks that were once underground to be __________ ____ to the Earth's surface. This process is called _______. Once exposed to the elements the rock on the Earth's surface begins to _______ and _______. The _____ ______ begins all over again. 9. The pressure's mounting... I'm getting all hot under the collar now that the pressure is on. Deep within the Earth's _______ rocks can be put under huge _________ and __________ are very high. These conditions can cause the minerals in the rock to change. This process is called metamorphism. All rocks can be ____________, and there are many different types of metamorphic rock. __________ can change into marble, _________ and mudstones into slate, and igneous rocks like _________ can turn into gneiss. The extent to which the rocks are changed depends on: 1. Whether they are exposed to ________, _________ or both. 2. Whether they are _________ to change shape. 3. The ________ they are exposed to these conditions. 10. Up, up and away... What - light at the end of the tunnel? Just like sedimentary rocks, ___________ rocks can be forced to the Earth's surface too. Sometimes forces act to _____ sections of the Earth's crust apart. At other times they are forced together. All this movement can cause rocks that were once ____________ to be brought up to the Earth's surface. This process is called _______. Once exposed to the elements the rock on the Earth's surface begins to _________ and _______. The rock cycle begins all over again. 11. It's getting very hot down here! Oh no - I'm melting, I'm melting... It can get quite hot deep in the Earth's _______. In fact, it can get so hot that the rocks that make up the crust can actually _______ __ _______. This molten material is called _________. It is _______ _______ than the surrounding rock so it tends to move _________ through the crust. Magma also comes from material below the Earth's crust - the ________. This new material rises up from the mantle and adds to the magma _________ from the molten crust. 12. I'm cooling down... But I think I'll take my time about it... Molten rock can sometimes form huge _________ called magma chambers within the Earth's crust. Left ___________ over many hundreds of thousands of years this magma will cool and _________ to form intrusive ________________ rocks. ______________ igneous rocks like granite and gabbro have some things in common. They: 1. Are large __________ - magma cools very slowly beneath the Earth's surface so the ________ in the rock have a long time to grow. 2. Are made up of _________ interlocking crystals 13. Intrusive rock I'm now an ________ igneous rock and can be __________ at the Earth's surface through uplift. But what would have happened if I had moved up to the Earth's surface as ________ rock? 14. This is my chance... I'm free Sometimes ________ can force itself through a crack or ________ in the rock at the Earth's surface. It pours out over the Earth's surface in a _________ eruption. This process is called extrusion. The rocks that form from _________ magma are called extrusive igneous rocks. _______ and _______ are extrusive igneous rocks. The type of rock that forms depends on the magma it came from, but generally extrusive igneous rocks: 1. Are very _____ _______ - magma cools very _______ when it erupts onto the Earth's surface and the ________ in the rock _______ have much time to grow. 2. May contain _____ bubbles 15. Extrusive rock I'm now an __________ igneous rock and I’m exposed at the Earth's surface. But what would have happened if I had stayed deep in the Earth's crust?