Prehistory Notes: Paleolithic & Neolithic Societies
advertisement

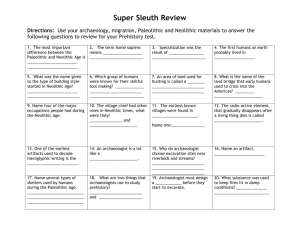
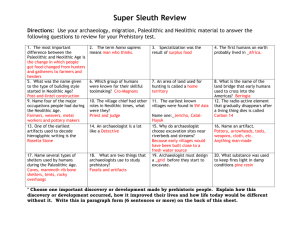
NAME ___________________________________ Unit 2 Prehistory Notes BLOCK____ 5 Minutes-pre-lesson (Your answers here): __________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Exploring Prehistory What is Prehistory? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 1. The Role of Archaeology in Prehistory Since we have no written records for prehistoric times, how does archaeology provide knowledge of early human life and its changes? Archaeologists study past cultures by locating and analyzing human ____________________________, ____________________________, ____________________________and ____________________________. A fossil is any remain, impression, or trace of a ____________________________ thing of a former geologic age, as a skeleton, footprint, etc. An artifact is any object _________________ by human beings, especially one found in excavation. They use scientific tests such as ________________________________________________ to analyze fossils and artifacts. They also use stratigraphy, the idea that ___________________ items will be found in _______________________ layers of earth, to help date artifacts. 2. Prehistoric Peoples How did physical geography determine the lives of early humans? Homo sapiens, or modern humans emerged in Africa between ____________________________ years ago. Homo sapiens migrated from ___________________ to Europe, Asia, Australia, and the Americas. 3. Paleolithic Society (Old Stone Age)=Hunter-gatherer societies Early humans were ________________________________________________________ whose survival depended on the availability of wild plants and animals. Imagine a life where your daily tasks were to find, and kill, your food. Hunter-gatherers had to be ____________________________ (migrating in search of food, water and shelter) or they would not survive. This is how the first people groups spread from Africa to Europe, Asia and Australia. Usually the men would hunt animals and women would gather nuts, berries and grains. Why? 4. Early Paleolithic Culture Early human societies began the process of overcoming the limits set by the physical environment through the development of ____________________________ (go back to pre-lesson). What limits were there in their environment? ____________________________________________________________________________________ Paleolithic people invented the first _______________, including simple weapons, mostly made of stone (hence, the Old Stone Age). They learned how to make and use __________. Why would this benefit them? They lived in ____________(extended family groups). Why? They developed early _____________________________. They created “_____________________________.” 5. It’s a REVOLUTION! The beginning of ___________________________________________________ (including permanent settlements) was a major step in the advancement of civilization. For the first time, people were able to stay in one place and not have to be nomadic, all because of the _____________________________ REVOLUTION. How did the beginning of agriculture and the domestication of animals (and plants) promote the rise of settled communities? The Neolithic Agricultural Revolution—Answer: The shift from food gathering to food producing revolutionized human life. Farming created a surplus of food which meant that humans no longer needed to be _________________________. Settlements of farming families eventually developed into the first villages, and then into even more _____________________________. People learned that the items they were __________________________________________________________ back in the ground and would return the following year. Thus, agriculture was developed, also known as _____________________________of plants. Animals, too, could be trained to stay alongside people and work for them. Do you know what animal was the first to be domesticated? The _____________! Historians believe _________ were domesticated earlier for hunting purposes. As people learned to domesticate animals and plants, they needed to develop better, more advanced, _______________. These were still made of ________________, mostly, so the time became called, the Neolithic Age (New Stone Age). Many crops they grew could be made into fabrics so _____________________________ developed. This meant that clothing was easier to come by… They made _____________________________, too. Many archaeologists believe early humans always knew how to make pottery, but not worth the effort. Why do you think this is so? List 5 characteristics of Neolithic societies: How did humans make it from Africa, Asia, Europe and Australia to the Americas? _____________________ 6. Accomplishments of the Stone Age _____________________________ is an example of an archaeological site in _____________________________ that was begun during the _____________________________ and completed during the _____________________________ Age. _____________________________ continue to find and interpret evidence of early humans and their lives. __________________________________________________________ are examples of early cities in the _____________________________ studied by archaeologists. _____________________________ is an example of a Neolithic settlements currently under excavation in Anatolia (_____________________________). Aleppo (______________________) Jericho (_____________________________, “Israel”) Settled Communities…. …grew into ______________________! Artifact Analysis: P/N Use? 1 2 3 4 Material? Explanation? Directions: Fill in the chart by matching the characteristics below with Paleolithic man or Neolithic man. Draw a picture to illustrate each characteristic. Fire Pottery Cave Art Temporary Settlements Weaving Hunting & Gathering Houses Tents/Caves Paleolithic Man Domesticated Animals Wild Plants & Animals Permanent Settlements Agriculture (domesticated plants) Neolithic Man