Chapter 2
advertisement

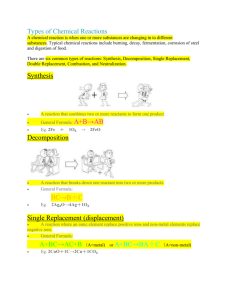
Chem I Ch. 9/17 Test Review and Study Guide The following guide is intended to be a study aid for the upcoming Test on Ch. 9 and 17 in Chem. If you work to know the topic areas listed below you will be well prepared for this test. The test will cover the topics listed below, although all information we went over in class may potentially be on the test. Good luck with your studies. Know the definitions of: Chapter 9 – Chemical Reactions Chemical reaction Reactant Product Chemical equation Coefficient Precipitate Solute Solvent Aqueous Solution Types of Reaction Synthesis Decomposition reaction Single-Replacement reaction Double-Replacement reaction Combustion Reaction Oxidation & Reduction Complete ionic equation Net ionic equation Spectator ion Chapter 17 – Chemical Equilibrium Equilibrium Le Chatelier’s Law Reversible Reaction Chapter 7 – Ionic Compounds & Chapter 8 – Covalent bonding Know how to: Read the ion chart to identify elemental ions like oxide (O2-) and polyatomic ions like carbonate (CO32-) Know how to write proper chemical formulas, both ionic and covalent compounds Page 1 of 2 Chem I Ch. 9/17 Test Review and Study Guide Chapter 9 – Chemical Reactions Know how to: Balance simple reactions Identify simple reactions as decomposition, synthesis, single replacement, double replacement or combustion. In a single replacement reaction, be able to identify what was oxidized and what was reduced. Recall the seven diatomic elements (H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2) Decomposition of carbonates yields a metal oxide and carbon dioxide (eg. CaCO3 CaO(s) + CO2(g)) Decomposition of chlorates yields a metal chloride and oxygen gas (eg. 2Al(ClO3)3 2AlCl3(s) + 9O2(g)) Identify the physical states of reactants and products (s= solid, aq=aqueous, l=liquid, g=gas) Write the reaction using formulas if you are given the names and states of the compounds Identify the precipitate and aqueous compounds using the solubility table in a double replacement reaction. Write the complete ionic equation and net ionic equation given the complete chemical equation Chapter 17 – Equilibrium Know how to: Apply Le Chatelier’s law, e.g. CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g) If we remove CO2 from a vessel, the reaction will shift to the right to create more CO2. If we add CO2 the reaction will shift left. For this test, I will give you: a periodic table a list of ions and oxidation numbers the prefixes and numbers (ex. mono- is one, di- is two, etc.) the metal and halogen activity chart the solubility table It is your responsibility to know how to use them. Page 2 of 2