Practice Test 4
advertisement

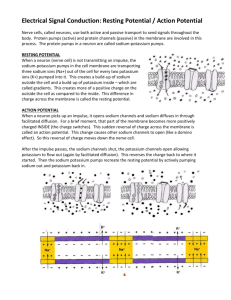
Bio 212 Practice Test 4 1. An action potential is _____. a. a traveling wave of depolarization in the neuron membrane b. a brief neutralization of the charges on sodium and potassium ions c. a sudden increase in speed by the sodium-potassium pump d. a sudden reversal of the sodium-potassium pump e. none of the above 2. If we stand up too quickly, blood pressure and, hence, blood flow to the brain will decrease. Which receptors will respond to this decrease in blood pressure? a. chemoreceptors b. thermoreceptors c. photoreceptors d. mechanoreceptors e. electromagnetic receptors 3. Schwann cells make up the _____. a. neurons b. nodes of Ranvier c. myelin sheath d. radial glia e. neurotransmitter secretory vesicles 4. Which one of the following statements is not true about the resting potential? a. The neuron's plasma membrane is much more permeable to potassium than to sodium. b. The concentration of sodium is much higher inside the cell than outside. c. The sodium-potassium pump plays a role in maintaining the resting potential. d. Inside the cell, the concentration of potassium is much higher than the concentration of sodium. e. All of these are true statements. 5. A type of cell that makes immunizations effective is the _____. a. red blood cell b. killer T cell c. killer B cell d. macrophage e. memory B cell 6. Once you have been exposed to an antigen, you develop immunity against the same antigen because _____. a. antibodies against the disease are constantly circulating in your blood b. certain lymphocytes are able to make the proper antibodies quickly c. your innate defenses are strengthened d. B cells are stimulated to quickly engulf invaders e. antigens are altered so that the invaders can no longer attack your tissues 7. A macromolecule produced in the body, which recognizes another molecule as "foreign" to the body, is a(n) _____. a. platelet b. antibody c. antigen d. lymphocyte e. macrophage 8. Neurosecretory cells can be found in the _____. a. hypothalamus b. anterior pituitary c. hypothalamus and anterior pituitary d. anterior and posterior pituitary e. adrenal glands 9. Since most chemical signals are unable to pass through the plasma membrane, the cellular action they initiate results from _____. a. ligand binding b. the activation of a signal transduction pathway c. direct stimulation of the cell's DNA d. the enzymatic behavior of the signal molecule e. binding to intracellular receptors 10. From a single cell, oogenesis in a mammal will produce _____. a. four ova (eggs) b. four spermatozoa c. an ovum and three polar bodies d. a primary oocyte e. four polar bodies 11. After a sperm penetrates an egg, a fertilization envelope forms. This envelope _____. a. secretes important hormones b. enables the fertilized egg to implant itself in the wall of the uterus c. prevents more than one sperm from entering the egg d. attracts additional sperm to the egg e. is responsible for the fast block to polyspermy 12. What is the embryonic origin of the lining of the digestive tube? a. endoderm b. ectoderm c. mesoderm d. both endoderm and mesoderm e. all three germ layers 13. a. b. c. d. e. What is the resting potential of a neuron axon? -70 mV -50 mV -100 mV +50 mV +70 mV 14. a. b. c. d. e. When a neuron is hyperpolarized... Na+ channels are open Cell is more positive than resting potential The signal reaches the threshold K+ channels are closed Cell is more negative than resting potential 15 The axon……. a. receives stimuli b. send impulses c. regulates cell processes d. all of the above 16. What is a major role for calcium ions in animal fertilization? A. calcium ion influx triggers cortical granule fusion with the egg plasma membrane B. nuclear fusion requires calcium ions C. sperm flagella action requires calcium ion transport D. fusion of the egg and sperm plasma membranes requires calcium ions E. sperm cells recognize the egg cell because of calcium ion binding 17. Inositol triphosphate (IP3) stimulates Ca2+ entry into the cytoplasm from a. Extra cellular fluid b. Endoplasmic reticulum c. Mitochondria d. Nucleus e. None of the above 18. An advantage of sexual reproduction is that a. it is easier than asexual reproduction b. offspring have a better start when produced from a union of egg and sperm than when simply budded off a parent c. it produces diploid off spring d. it produces variation in the offspring e. it requires male and female members of a population and have behavioral interactions 19. cytoplasmic determines…… a. unevenly disturbed egg components that influence the developmental fates of cells b. are involved in regulation of gene expression c. usually included in materal mRNA d. are often separated in first few cleavage divisions e. all of the above 20. Movement of action potential is one direction of the neuron is a function of ….. a. salutatory conditions b. pathway from dendrite to axon c. refractory period when sodium inactivation gates are still closed d. delocalized depolarization of surround membrane e. reaching of a threshold 21. After reaching deplorization of an action potential, the fall of membrane potential occurs due to the a. closing of sodium gates b. closing of potassium and sodium gates c. refractory period where membrane is hyperpolarized d. delay in action of sodium-potassium pump e. opening of voltage gated potassium channels and the closing of sodium inactivation gates 22. The absorption of light by rhodopsin in a rod cell leads to a. an increase in the release of neurotransmitter b. a hyperpolarized membrane and a decrease in the release of neurotransmitter c. the bleaching of rhodopsin, which increases the sensitivity of rod cell cells to light. d. the closing of sodium channels and the release of a neurotransmitter 23. MHC complexs molecules a. are involved in the ability to distinguish self from nonself b. are a collection of cell surface proteins c. may trigger T cell response after transplant operations d. present antigen fragments on infected cells e. all of the above 24 A transfusion of type B blood given to a person who has type A blood would result in…… a. The recipient's anti-B antibodies reacting with the donated red blood cells b. The recipient’s B antigens reacting with the donated anti-B antibodies c. The recipient forming both anti-A and anti-B antibodies d. No reaction, because B is a universal donor type of blood 25. Which hormone stimulates ovulation and the development of the corpus luteum? a. FSH b. hCG c. Progesterone d. LH 26. Which hormone is produced by the developing follicle? a. LH b. Progesterone c. Estradiol d. FSH 27. Which one of the following is part of the inflammatory response? (Concept 43.1) a. constriction of the arterioles b. clonal selection of B and T lymphocytes followed by the production of effector cells c. dilation of the capillaries d. production of antibodies e. production of memory cells 28. A type of cell that makes immunizations effective is the _____. (Concept 43.3) a. red blood cell b. killer T cell c. killer B cell d. macrophage e. memory B cell 29. In males, FSH _____. a. is not produced; it is a female hormone b. is directly responsible for facial hair growth beginning at puberty c. is produced by the hypothalamus d. stimulates development of sperm cells in the testes 30. How does calcium affect muscle contractions ? a. It is release from the T-0tubles in response to an action potential to initiate contractions b. The binding of acetylcholine opens Ca channels in the plasma membrane, creating an action potential that travels down the T- Tubule c. It binds to tropomyosin and helps stabilize formation of cross bridges d. It binds to tronin which causes tropomyosin to move away from the myosin binding sites on the actin filament e. Its release from the sacroplasmic reticulum changes the membrane potential of a muscle cell so that contraction can occur. Short answer questions to know 1. What is the benefits of asexual and sexual reproduction 2. How does Spermatogenesis differs from oogenesis? 3. What is the role of FSH and LH in males 4. Be able to explain the diagram below 5. Explain in a step by step manner the process of Fertilization? What is the fast block and slow block? (be sure to mention the role of calcium, the cortical reaction, and Acrosomal reaction) 6. Explain the Two general strategies for cell differations occur 7. Explain the Transplant experiments talked about in class 8. Explain the formation of the neural tube 9. Explain the mechanism of muscle concretion. ( be sure to include the role of ATP and Calcium) 10. How does inflammation occur? 11. How do we obtain Acquired immunity, or adaptive immunity? 12. Be able to explain the diagram below in term of what is happening in a neuron (generation of the Action diagram below) 13. Be sure to look over the learning objectives and bring questions Answer Key 1. A 2. D 3. C 4. B 5. E 6. B 7. B 8. A 9. B 10. C 11.C 12. A 13. A 14. E 15. B 16. A 17. B 18. D 19. E 20. C 21. E 22. B 23. E 24. D 25. D 26. C 27. C 28. E 29 D 30 D