August 29, 2007
advertisement

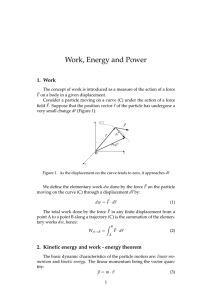
Tuesday, February 16th, 2010 TA: Tomoyuki Nakayama PHY 2048: Physic 1, Discussion Section 3695 Quiz 4 (Homework Set #6) Name: UFID: Formula sheets are not allowed. Calculators are allowed. Do not store equations in your calculator. You need to show all of your work for full credit. ________________________________________________________________________________ The figure below right shows a plot of potential energy U versus position x of a 0.400-kg particle that can travel only along an x axis under the influence of a conservative force. The graph has these values: UA = 10.0 J, UC = 22.0 J and UD = 27.0 J. The particle is released at the point where U forms a “potential hill” of “height” UB = 14.0 J, with kinetic energy of 5.00 J. a) What is the speed of the particle at x = 3.5 m? The initial mechanical energy of the particle is Ei = Ki + Ui = 5 + 14 = 19.0 J Since only a conservative force is exerted on the particle, its mechanical energy is conserved. At x = 3.5 m, the potential energy is UA = 10 J. Thus the kinetic energy is E = K + U ⇒ K (x = 3.5) = E – UA = 19 – 10 = 9.00 J The definition of kinetic energy yields K = (1/2)mv2 ⇒ v = √(2K/m) = 6.71 m/s b) What is the position of the turning point on the right side? The particle turns around when its kinetic energy is zero. The kinetic energy is zero when the potential energy equals the mechanical energy. The potential energy function between x = 7 m and x = 8 m is given by U = [(UD – 0) /(7-6)] × (x-7) = 27(x-7) The function takes the value of E = 19 J at 19 = 27(x-7) ⇒ x = 19/27 + 7 = 7.70 m c) What is the position of the turning point on the left side? The potential energy function between x = 1 m and x = 3 m is expressed as U = [(UA - UC)/(3-1)]×(x-1) + UC ⇒ U = -6(x - 1) + 22 The function takes the value of E = 19 J at 19 = -6(x-1) + 22 ⇒ x = (19 - 22)/(- 6) +1 = 1.50 m