Resources: BCC pp
advertisement

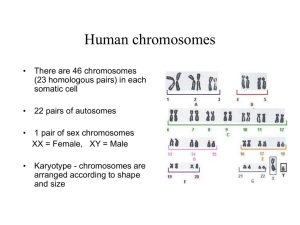
Essential Biology 4.1/4.2 Chromosomes, Genes, Alleles, Mutations/Meiosis Due Date: Student Name: Resources: Clegg pp. 91-94, 98-102 and Revision Guide pp. 23 covering Topic 4.1 .(and some review of transcription and translation!) 1. Define the following: Chromosome Gene Allele Gene locus Genome Chromatid Mutation Haploid Diploid 2. State the components of a chromosome. DNA & 3. State the number of chromosomes present in a single human diploid cell. 4. Identify structures a. and b. on the line drawing of a chromosome in prophase shown to the right. a. b. 5. Give two examples of genes and some of their possible alleles. Gene Eye colour Possible alleles Blue, brown, green, hazel 6. List factors that increase the chance of a genetic mutation. UV chemical carcinogen (tar in tobacco) certain organic solvents uncorrected mistakes in natural replication http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 4.1/4.2 Chromosomes, Genes, Alleles, Mutations/Meiosis Due Date: Student Name: 7. Compare the following types of base-substitution mutation. Silent mutation Number of bases substituted Mis-sense mutation 1 Stop codon produced early – polypeptide shortened Effect on polypeptide Example illness Nonsense mutation Sickle cell disease Resources: Clegg pp. 94-97 8. Define homologous chromosomes. 9. Explain reduction division. 10. State the function of meiosis. 11. Add chromosomes and annotate the diagram below summarizing the steps in meiosis. Identify the stage where crossing over occurs and state its effect. http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 4.1/4.2 Chromosomes, Genes, Alleles, Mutations/Meiosis Student Name: http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Due Date: Essential Biology 4.1/4.2 Chromosomes, Genes, Alleles, Mutations/Meiosis Due Date: Student Name: 12. Compare mitosis and meiosis: Mitosis Meiosis Number of divisions Number of daughter cells Chromosome number in daughter cells Functions: 13. Outline the major events and movements of chromosomes occurring at these stages of meiosis: Meiosis I Meiosis II Interphase Interphase Prophase I Prophase II Metaphase I Metaphase II Anaphase I Anaphase II Telophase I Telophase II Cytokinesis Cytokinesis No replication occurs in interphase between Meiosis I and II. 14. Deduce the answers to these questions. a. A cell with a diploid number of 12 chromosomes goes through meiosis. How many daughter cells will be produced and with how many chromosomes in each? Cells: Chromosomes: b. A gamete contains 18 chromosomes. How many chromosomes in the somatic cell? Chromosomes: http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 4.1/4.2 Chromosomes, Genes, Alleles, Mutations/Meiosis Due Date: Student Name: c. A diploid cell with 16 chromosomes undergoes meiosis. How many chromatids are present in metaphase I? Chromatids: 15. A cell with a chromosome number (n) of 3 undergoes meiosis. Draw a series of diagrams to outline the steps of meiosis. 16. Describe what you can see in this image. 17. Distinguish between chromosomes, sister chromatids and bivalents. http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 4.1/4.2 Chromosomes, Genes, Alleles, Mutations/Meiosis Due Date: Student Name: 18. Annotate the diagram below to show what happens in non-disjunction in meiosis II. 19. Describe how non-disjunction and fertilization lead to trisomy. Non-disjunction: Fertilization: 20. Distinguish between non-disjunction and trisomy. Non-disjunction: Trisomy: QUESTIONS 21-27 WILL BE COMPLETED IN CLASS! 21. Compare the outcomes of non-disjunction in anaphase I with anaphase II: Non-disjunction in… Number of normal cells Cells with extra chromosome (n+1) http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Anaphase I Anaphase II Essential Biology 4.1/4.2 Chromosomes, Genes, Alleles, Mutations/Meiosis Due Date: Student Name: Cells with chromosome missing (n-1) 22. Using information in the graph, outline the effect of maternal age on likelihood of Down Syndrome: 23. Describe the effects of Down syndrome. 24. Compare the outcomes of non-disjunction in anaphase I with anaphase II: Non-disjunction in… Number of normal cells Cells with extra chromosome (n+1) Cells with chromosome missing (n-1) http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Anaphase I Anaphase II Essential Biology 4.1/4.2 Chromosomes, Genes, Alleles, Mutations/Meiosis Due Date: Student Name: 25. A karyotype can be used to test for non-disjunction disorders. Fetal cells are taken and the number of chromosomes counted. Outline how these cells are retrieved: Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS): Amniocentesis: 26. State three visual aspects of homologous chromosomes which can be used to identify them for the purpose of a karyotype? a. Banding patterns b. c. d. 27. Analyse this karyotype: Gender: http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Condition: Essential Biology 4.1/4.2 Chromosomes, Genes, Alleles, Mutations/Meiosis Student Name: http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Due Date: Essential Biology 4.1/4.2 Chromosomes, Genes, Alleles, Mutations/Meiosis Due Date: Student Name: 28. Describe the effects of sickle cell disease on sufferers in terms of: a. Hemoglobin production b. Symptoms and mortality 29. Identify parts of the world where a single sickle cell (Hbs) allele could be beneficial Explain your answer 30. Define evolution. 31. Outline how mutations lead to evolution by natural selection. 32. Outline how the spread of the sickle cell gene is an example of natural selection in action. 33. How could this be an example of a correlation which has a strong element of causality? http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 4.1/4.2 Chromosomes, Genes, Alleles, Mutations/Meiosis Due Date: Student Name: In-class activity: Using gene databases (ICT Databases) 1. Using the NCBI gene database at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene , identify the gene locus of the HBB (hemoglobin) gene. 2. Using the same database, look for the gene related to the illness PKU (phenylketonuria) a. What is the gene name? b. What is the gene locus of this gene? c. Which enzyme is encoded by this gene? d. What is the consequence of a base-substitution (mis-sense) mutation of this gene? e. How is PKU diagnosed and why must it be diagnosed as early as possible? 3. Stem cells link: Read this article: http://notexactlyrocketscience.wordpress.com/2007/12/08/sickle-cell-micecured-by-stem-cells-reprogrammed-from-their-own-tails/ a. What is an IPS stem cell? b. Outline the use of this technology in treating the mice with sickle cell disease. http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com