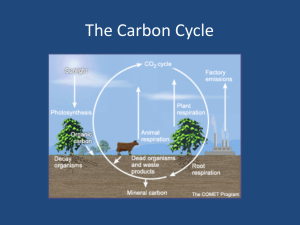
Background: All living things undergo cellular respiration
advertisement

Biology Common Lab 11-12 Name____________________________ Observing Cellular Respiration LS2–4aa: Students demonstrate an understanding of matter flow in an ecosystem by explaining the transfer using cellular respiration as a model. Background: All living things undergo cellular respiration. In this investigation you will observe the release of CO2 in humans. You will also perform an experiment to determine whether plants release CO2 as a product of respiration. Note: Bromothymol Blue/Purple Cabbage* is an acid indicator – What does this mean?_________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Carbonic acid is formed when carbon dioxide is mixed with water Safety: Wear safety goggles and aprons. Do not eat or drink anything in the lab. Problem Question: Part A: How can the release of CO2 by humans be observed? Part B: Do plants release CO2 as a product of cellular respiration? Hypothesis for Part A: Hypothesis for Part B: * Your class will use one of these two indicators. Biology Common Lab 11-12 Name____________________________ Observing Cellular Respiration LS2–4aa: Students demonstrate an understanding of matter flow in an ecosystem by explaining the transfer using cellular respiration as a model. Materials: Bunsen burner 4 test tubes Beaker Cotton Ball Purple cabbage Ring stand Striker Aluminum Foil Wire mesh 10 radish seedlings Straws Wax pencil Procedure - If using purple cabbage indicator: 1. Collect materials for the lab. 2. Label the test tubes 1, 2, 3, 4 with wax pencil. 3. Set up a ring stand, Bunsen burner and wire mesh. 4. Measure about 100mL of water into a beaker. 5. Tear purple cabbage leaves into small pieces. Add to water in beaker. 6. Light Bunsen burner and allow water to heat until it boils. 7. When beaker has cooled pour cabbage liquid (not the leaves) into the four test tubes until two are ½ full (1 and 2) and two are ¼ full (3 and 4). 8. Discard any remaining liquid in the sink. Discard cabbage in trash and rinse beaker. 9. If solution will not be used until the next day, cover each test tube with Parafilm. PART A: 1. Use a straw to blow a few times into test tube 1. Compare the color of test tube 1 with test tube 2. Record observations in the data table below. 2. Pour solution down the drain. Rinse test tubes. PART B: 1. Place a cotton ball and 10 radish seedlings in test tube 3. Cotton ball should just be touching cabbage liquid. 2. Cover test tubes with Parafilm and set aside for 24 hours. 3. After 24 hours compare the color of test tubes 3 and 4. Record observations in the data table below. Biology Common Lab 11-12 Name____________________________ Observing Cellular Respiration LS2–4aa: Students demonstrate an understanding of matter flow in an ecosystem by explaining the transfer using cellular respiration as a model. Data: Table 1: Title = _______________________________________________________________ Test Tube Description Color of Cabbage Indicator 1 2 3 4 Analysis Questions: Use notes, textbook and internet. These questions must be woven into your conclusion in COMPLETE SENTENCES and MUST BE RICH IN DETAIL AND EVIDENCE!!! Write in paragraph form and include all other components of a proficient lab report conclusion! No cutting and pasting at all!!! Work that has been copied from another source will earn no credit = 0% for the lab report. 1. In Part A and Part B, why is nothing added to one of the test tubes? 2. Explain why the purple cabbage indicator changed color when a person blew into it through a straw. 3. Explain why there was a change in the test tubes with seeds. 4. Why was it necessary for seedlings to be used in Part B instead of green leaves? (HINT: Explain the process that occurs in green leaves that does not occur in seedlings.) 5. Is there any other plant part that could have been used in the experiment in place of seeds that would have given you the same results? Explain. Biology Common Lab 11-12 Name____________________________ Observing Cellular Respiration LS2–4aa: Students demonstrate an understanding of matter flow in an ecosystem by explaining the transfer using cellular respiration as a model. 6. Use the internet to find out how a CO2 probe works. If we had used a CO2 probe instead of an acid indicator in what way(s) would our results have been the same? What additional information would we have obtained? 7. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere contributes to global warming. Planting large numbers of trees is one method for decreasing global warming. Why? 8. Adding limiting nutrients to the ocean is another method for decreasing global warming. Why? 9. What will be the effect of increasing CO2 levels on the pH of ocean waters? What long-term effects might this have on the ocean ecosystem? Explain. 10. During cellular respiration do plants produce more or less CO2 than they use during photosynthesis? a. To answer this fully consider the following: i. What would happen to the plants and animals on Earth if plants produced more CO2 than they used? ii. What would happen to the plants and animals on Earth if plants produced less CO2 than they used? Submit: Double spaced typed formal lab report. Introduction Purpose of lab Background information on cell respiration and on the use of an acid indicator in the experiment Hypotheses for the lab – your hypotheses must be testable and must be supported by your background information. Your hypotheses should specifically address what you expect to observe in the experiment. Data Table Rewritten and typed. If you do not know how to make a table on a computer, then you may use graph paper and a ruler to make the table. Conclusions Paragraph 1 – restate (briefly) your hypotheses. Were your hypotheses correct? Support your assertions by referring to your data. Paragraph 2 – Analyses questions (see above) 1-6 Paragraph 3 – Analyses questions 7 - 10. Paragraph 4 - Sources of error identified Discuss applications and or extensions of experiment