The Skull [9-29
advertisement

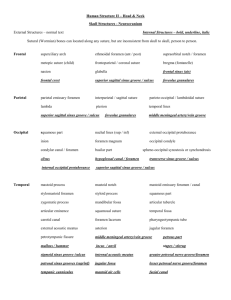
The Skull Cranium: Anterior View: includes the frontal bone, zygomatic bones, nasal bones, maxilla, and mandible Lateral View: includes lateral calvaria bones, lateral facial bones, and the mandible Superior View: includes frontal, parietal, and occipital bones Inferior View: includes maxilla, zygomatic, palatine, sphenoid, temporal, and occipital bones External Foramina: Foramen Supra-orbital foramen Infra-orbital foramen Mental foramen Zygomaticofacial foramen Parietal foramen Incisive foramen Greater palatine foramen Lesser palatine foramen Pterygoid canal Carotid canal Stylomastoid foramen Bone Frontal Maxillary Mandible Zygomatic Parietal Maxilla Palatine Palatine Sphenoid Temporal Temporal Contents Supra-orbital nerve and vessels Infra-orbital nerve and vessels Mental nerve and vessels Zygomaticofacial nerve Emissary veins Nasopalatine nerve, sphenopalatine vessels Greater palatine nerve and vessels Lesser palatine nerve and vessels pterygoid nerve and vessels Internal carotid artery and nerve plexus Facial Nerve [VII] Landmarks of the Skull: - Bregma: intersection of coronal and sagittal sutures Lambda: intersection between lambdoid and sagittal sutures Glabella: depression of frontal bone between the superciliary arches Nasion: articulation of nasal and frontal bones Pterion: junction of the frontal, parietal, temporal, and sphenoid bones. This area is of great relevance in skull fractures because the bone in this region is thin and overlies the anterior division of the middle meningeal artery Cranial Cavity: Roof of the Cranial Cavity: the calvaria - - Consists of the frontal, parietal, and occipital bones Contains sutures between bones: o Coronal suture: between frontal and parietal bones o Sagittal suture: between paired parietal bones o Lambdoid suture: between parietal and occipital bones, may contain sutural (wormian) bones Frontal Crest: midline ridge of bone on the frontal bone acts as attachment point for falx cerebri (dura mater that separates the two cerebral hemispheres) Groove for Superior Sagittal Sinus Grooves for Meningeal vessels Granular Foveolae: mark locations of arachnoid granulations (involved in CSF reabsorption) Floor of the Cranial Cavity: - - Anterior cranial fossa: parts of frontal, ethmoid, and sphenoid bones o Filled by frontal lobes of cerebral hemispheres o Crista galli: located on the ethmoid, acts as another point of attachment for the falx cerebri o Cribiform Plate: located on ethmoid, allows passage of small olfactory nerves o Anterior Clinoid Process: end of lesser wing of scaphoid that serves as attachment for the Tentorium Cerebelli (dura separating the cerebral hemispheres from the cerebellum) o Chiasmatic Sulcus serves as border between anterior and middle fossae Middle cranial fossa: parts of sphenoid and temporal bones o Sella turcica: body of sphenoid, consisting of hypophysial fossa which contains the pituitary gland o Posterior Clinoid Process: located on lateral end of dorsum sellae (on sella turcica) and serve as another attachment point for the tentorium cerebelli o Trigeminal Impression: located on the temporal bone, the location of the sensory ganglion of the Trigeminal Nerve [V] o Arcuate Eminence: rounded protrusion of temporal bone produced by the underlying anterior semicircular canal of the inner ear o Tegmen Tympani: part of temporal bone that marks the roof of the middle ear - Posterior cranial fossa: mostly temporal and occipital bones with small contributions from the sphenoid and parietal bones. o The largest and deepest of the cranial fossa o Contains the brainstem and cerebellum o Clivus: slope of sphenoid and occipital bones that extends upward from the foramen magnum o Groove for Inferior Petrosal Sinus: between basal part of occipital bone and petrous part of temporal bone o Groove for Sigmoid Sinus o Jugular Tubercle: just superior to jugular foramen o Internal Occipital Crest and Protuberance and Groove for Transverse Sinus Internal Foramina: Foramen Foramen cecum Olfactory foramina Optic canal Superior orbital fissure Foramen rotundum Bone Frontal Ethmoid Sphenoid Sphenoid Foramen ovale Sphenoid Foramen spinosum Hiatus for greater petrosal nerve Hiatus for lesser petrosal nerve Foramen lacerum Foramen magnum Sphenoid Temporal Internal acoustic meatus Temporal Sphenoid Temporal Sphenoid Occipital Hypoglossal canal Between Temporal and Occipital Occipital Condylar canal Occipital Jugular foramen Contents Emissary veins Olfactory nerves [I] Optic Nerve [II] and ophthalmic artery Oculomotor Nerve [III], Trochlear Nerve [IV], Ophthalmic nerve [V1], Abducent Nerve [VI], and ophthalmic veins Maxillary nerve [V2] Mandibular nerve [V3], lesser petrosal nerve (carrying fibers of tympanic plexus from Glossopharyngeal Nerve [IX]), accessory middle Meningeal artery Middle Meningeal artery and associated veins Greater petrosal nerve (branch of Facial Nerve [VII]) Lesser petrosal nerve (carrying fibers of tympanic plexus from Glossopharyngeal Nerve [IX]) Cartilage Spinal cord, meninges, vertebral arteries, and the spinal roots of the Accessory Nerve [XI] Facial Nerve [VII], Vestibulocochlear Nerve [VIII], and the labyrinthine artery Sigmoid sinus forming the Internal jugular vein, Glossopharyngeal Nerve [IX], Vagus Nerve [X], and the Accessory Nerve [XI] Hypoglossal Nerve [XII] leaves and Meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal artery (external carotid) enters Emissary vein