Physical & Life Science Test – Classification & Ecosystems
advertisement

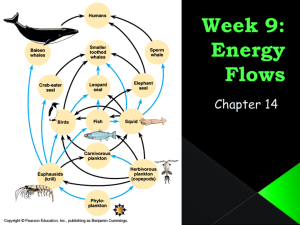
Physical & Life Science Test – Classification & Ecosystems - Answer Key Section A – MCQ 1. Which of the following is NOT a Taxonomic rank? (a) Phylum Consumer = is a name usually given to a trophic level. E.g. (b) Order Primary Consumer or Secondary consumer. The Taxonomic (c) Consumer Ranks include: Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, (d) Kingdom Genus, Species. Try remembering with this mnemonic device: (e) Genus (King Philip Came Over For Good Spaghetti) Answer = C 2. In a community of organisms living on a plains ecosystem (large grassland area). The population with the greatest biomass would be: Answer: Grasses. – Grasses would be the Producer in (a) Hawks this ecosystem. Typically in a balanced successful (b) Foxes ecosystem the Biomass of the producer will be greater (c) Prairie dogs than the other trophic levels. (In order to support the (d) Grasses flow of energy through trophic levels). (e) Beetles Answer = D 3. Fig1: Grassland Pyramid of Biomass example The flow of energy within an ecosystem always begins with: (a) Producer (b) Primary Consumer Producer: “produces” the energy in the ecosystem – (c) Indicator species typically captures the Suns energy. Primary (d) Secondary consumer Consumer then typically feeds on producer. (e) Parasites Parasites may be found feeding off any trophic level. (Usually does harm to its host”) Answer = A 4. Which of the following is NOT a reason for causing a species’ status to change from “vulnerable” to “endangered” All of the options may cause the decrease in a (a) Disease species numbers due to: overkilling, competition (b) Poaching for resources, environment becoming inhabitable (c) Conservation (cannot live there anymore). A Conservation (d) Natural disasters program aims to protect species. (e) Competition with species Answer = C 5. Data that shows the direction of energy flow through an ecosystem is called: (a) Biodiversity Survey A Food Chain shows (using arrows) the flow of energy from (b) Food Chain producers to consumers or higher order trophic levels, (c) Pyramid of Biomass Biodiversity survey is essentially a count of the amount of (d) Trophic levels organisms in an ecosystem. Pyramid of numbers and (e) Pyramid of numbers Biomass represent the total number / total Biomass of particular species in an ecosystem. Answer = B Fig 2: Energy Flow in Food Chain example (Note a lot of energy is lost as it moves through trophic levels) 6. An organism that has cold blood and dry scaly skin is most likely to belong to the class: (a) Bird (b) Fish (c) Amphibian (d) Mammal (e) Reptile Answer = E (From Arkive.org) : Reptiles are cold blooded, scaly-skinned vertebrates of which which most lay leathery cased eggs. Examples include: Crocodiles, and Turtles Lizards, 7. Each species’ scientific name is given in two parts. This two part name is given by:\ (a) Species Genus Answer = Genus Species: examples (b) Genus Species include: (c) Kingdom Class Ailuropoda melanoleuca (Panda). (d) Class Species Remember to type scientific names (e) Class Genus using italics. Homo Sapians (Human), Answer = B 8. Taxonomy splits all living things into how many different kingdoms? (a) 4 I accepted both answers 5 or 6 to this question. The amount of kingdoms of life (b) 3 is often debated about by scientists. The most common answer given is 5: (c) 7 Animals, Plants, Protists, Fungi and Monera (Bacteria). There is evidence to (d) 5 argue that the Kingdom Monera can be divided into Eubacteria and (e) 6 Arcahebacteria making 6 kingdoms. Interestingly there are also those who believe we should have 8 Kingdoms. This is a great example of how science is Answer = D or E 9. constantly changing. Its important for us to keep reading as much as we can Organisms in the Kingdom Animalia who possess a backbone would be placed in the phylum: (a) Arthropoda Chordata is the only Phylum mentioned here that has a backbone. (b) Mollusca (think spine, then spinal Chord – Chordata). Artropoda is the phylum (c) Cnidaria containing insects (Invertebrates), Mollusca contains the octopuses and (d) Chordata snails (invertebrates) Cnidaria contains the Jellyfish (invertebrate), and (e) Annelida Annelida contains the worms (invertebrates). These are all soft bodied with no backbone. Answer = D 10. Two organisms in the same class must also be in the same (A) order. (B) species. (C) genus. Because of the taxonomy ranking system: (Kingdom, Phylum, (D) family. Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species) - Organisms in the same (E) phylum. class can ONLY be guaranteed to be in the same PHYUMUM or KINGDOM. (e.g. Panthera tigris & Balenoptera musculus are in the same class & Phylum but are in different Orders, Families and Answer = E Geneses. Section B – Data Analysis Pyramid of Numbers: total 5 points. Points awarded for: (3 points) For accurate representation of the ecosystem. E.g. 1 square = 1 organism. The scale used must be consistent for each different species. E.g. if: 12 pieces of grass = 12 boxes then 6 insects = 6 boxes, 3 frogs = 3 boxes & 1 fox = 1 square, if 12 grass = 24 boxes then 6 insects = 12 boxes etc. (2 points) awarded for correct labeling of each section on the pyramid. Also there must be clear differentiation between the levels (using different colors or shading is a good idea). Example: Fox (Key or labels = 2 points) Frog Insect Grass Use the information below to make your own pyramid of biomass. (Total = 10 points) Organism Desiccated weight per organism Number of organisms/100m2 Tomato Plant 10 g 100 Aphid 0.1 g 1000 Ladybird 1g 50 Thrush (small bird) 9g 5 Pyramid of Biomass: Representation of the total mass (in kg or g) of the TOTAL number of a particular species in an ecosystem. 2 Points awarded for correct calculation of the Total Biomass of each species. E.g. Tomato Plant: 100 organisms each with mass = 10g. Total Biomass = 10g x 100 = 1000g (1 kg). Aphid: 1000 each 0.1 g. Total Biomass = 0.1g x 1000 = 100g. Ladybird – (1g x 50) = 50g & Thrush = (9g x 5) = 45g (3 points) for correct representation of Biomass. E.g. each species must be represented by a proportionate section of the chart. (Tomato plant has largest Biomass – largest section of the chart). Each block must be conatant for the whole chart. (1 point) for clearly stating the scale you used. E.g. if 1 block = 100g the Tomato plant biomass has 10 blocks, aphid biomass is 1 block, ladybird biomass is 0.5 of a block and Thrush biomass = 0.45 of a block. (1 point for clearly stating the scale you used. (3 points) for correct labeling of the Biomass pyramid (including te Biomass of each section). + (1 point) for having clear differentiation between levels. Thrush (45g) Example: Ladybird (50g) Aphid (100g) T. Plant (1 kg) Scale: 100g = In the space provided draw a cladogram for the following organisms in the kingdom Animalia. FOR FULL MARKS YOU MUST USE THE SCIENTIFIC NAME OF EACH ORGANISM. (Total = 5 points) Organism 1 (species- tigris) Organism 2 (Species - musculus) Organism 3 Organism 4 (Species – Lupus) (Species – arachnoides) (3 points) awarded for correct representation of evolutionary relationship between the organisms using a cladogram. (2 points) awarded for using the scientific name of each organism. (Genus Species). Panthera tigris Example: Canis Lupus Balaenoptera musculus Pyxis arachnoides