5.7C Key Concepts - Rooster 5
advertisement

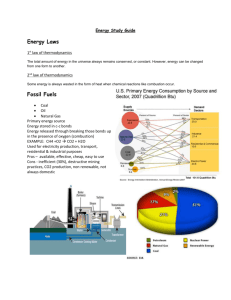
5.7C Alternative Energy Key Concept 1: Alternative energy resources rely on natural processes and can be used to produce energy. Alternative energy is any energy that does not come from nonrenewable resources, such as coal, oil, or natural gas (fossil fuels). For a resource to be considered “green” (environmentally friendly), the energy source must be renewable and “clean.” This means the supply must be continually available, have few or zero carbon emissions, and produce few toxic byproducts. Nonrenewable resources are materials of which there is a finite or fixed amount, and once they are consumed, they cannot be replaced by the Earth in any reasonable time. Fossil fuels, such as oil, coal, and natural gas, are irreplaceable once they are burned or manufactured into a human-made product (like gasoline). For many years, humans have relied on nonrenewable energy resources, which unfortunately have produced hydrocarbon pollutants that harm our environment. Overdependence on nonrenewable energy cannot protect future generations from running out of fuel or energy, nor reduce pollution. With a nonrenewable resource, excessive consumption only hastens the day when that resource will no longer be available. Renewable resources are materials that can be replenished by nature in a relatively short time, like lumber, which comes from trees. In the United States, for every tree felled to be made into building materials, a new seedling is planted to take its place. Although air, water, soil, plants, and animals are renewable resources, proper conservation and management policies need to be in place to insure we do not use these resources faster than they can be replenished. There are two solutions: dramatically reduce our consumption or find alternative resources. Students will explore alternative resources that are renewable, nonpolluting, come from Earth’s natural processes, and can be transformed into usable energy. Key Concept 2: Alternative energy resources include wind, solar, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biofuels. Wind Energy - Wind energy comes from changing the power of moving air into a useful form. Windmills have been used to pump water and grind grains for hundreds of years. Modern windmills sit atop 30-foot towers to harness wind energy by rotating three enormous turbine blades, which turn a shaft connected to an electric generator. When more power is needed, wind farms, consisting of hundreds of wind turbines, are connected to produce large quantities of electricity. Meteorologists help engineers identify appropriate sites with suitable wind conditions, such as hill tops, coastal areas, or offshore (to catch ocean winds). Although wind energy is renewable, cost effective, and environmentally friendly, there are limited areas in which frequent windy conditions exist. Solar Energy - Solar panels made of photovoltaic (PV) cells produce electricity directly from sunlight. Solar collectors concentrate the Sun’s rays in the form of heat, which can then be used directly or converted into electricity using a generator. Solar panels are nonpolluting, make no noise, and have no moving parts that require maintenance. Passive solar energy can be used where buildings have walls that absorb sunlight and radiate that heat instead of burning fuel in a furnace. The disadvantages of solar energy are: the high cost of producing and installing solar panels, the limited areas of use at Earth latitudes where sufficient hours of sunlight can be captured, and overcast weather days that block sunlight. Hydroelectric Energy - The force of moving water from dammed up rivers, free flowing rivers, or ocean tides can provide unlimited hydroelectric power. The gush of flowing water turns the blades of a turbine, which generates electricity. Hydroelectric energy offers the advantage of having constantly moving water. The disadvantage is the limited availability to only communities near water sources. Geothermal Energy - Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source because the heat is continuously produced inside Earth where magma deep underground heats overlying rocks and water, which creates hot spots. Geothermal power plants drill down to that heat source to make steam used to heat homes, or to turn a turbine, which generates electricity. In the United States, most geothermal reservoirs of hot water are located in California, Alaska, and Hawaii. Newer geothermal power plants use the hot water source to boil a working fluid that vaporizes and then turns a turbine. Biofuel Energy - Humans have burned wood for fuel for thousands of years. Modern technology can now convert other sources of “biomass,” organic material made from plants and animals, into usable sources of fuel. Biofuel contains stored energy from the Sun that plants absorbed. Biofuel is a renewable energy source because we can always grow more trees and crops, and waste will always exist. Biofuels, such as ethanol and methane gas, are produced from sugar cane or corn. Biodiesel is made from vegetable oil or animal fat. Other sources of biofuel are algae and animal manure. Although biofuels are renewable, some pollution is produced from biofuel engines or biofuel power plants.