Energy Laws
advertisement
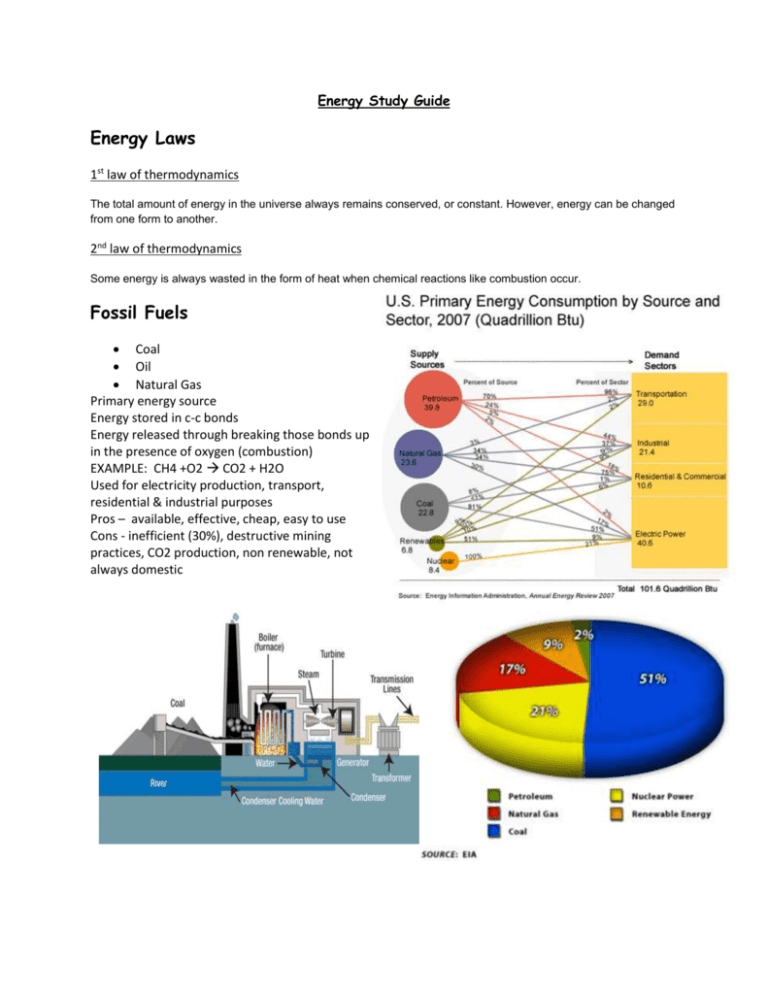
Energy Study Guide Energy Laws 1st law of thermodynamics The total amount of energy in the universe always remains conserved, or constant. However, energy can be changed from one form to another. 2nd law of thermodynamics Some energy is always wasted in the form of heat when chemical reactions like combustion occur. Fossil Fuels Coal Oil Natural Gas Primary energy source Energy stored in c-c bonds Energy released through breaking those bonds up in the presence of oxygen (combustion) EXAMPLE: CH4 +O2 CO2 + H2O Used for electricity production, transport, residential & industrial purposes Pros – available, effective, cheap, easy to use Cons - inefficient (30%), destructive mining practices, CO2 production, non renewable, not always domestic Greenhouse effect Caused by green house gasses in the air soaking up solar radiation and keeping from bouncing back out into space (this heats up the earth) Nuclear Power Fusion of Uranium 235 splitting of atoms release heat energy can be used to turn water to steam and spin steam turbines to generate electricity Accidents 3 mile island & Chernobyl Pros – less fuel needed, less waste, little to no emissions Cons – more dangerous nuclear waste, higher potential for large accidents Renewables Solar Active and passive Solar water heating Solar thermal power plants Photovoltaic cells Passive solar architecture Wind No emissions Sporadic some environmental impact on wildlife, NIMBY problem Geothermal Geothermal power plants Passive geothermal for home heating and cooling Hydro Dams generate free renewable energy but can cause heavy environmental impact Biomass Biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel Waste to energy plants Landfill recovery Know how to read one of these











