File - 4th Grade Standards
advertisement
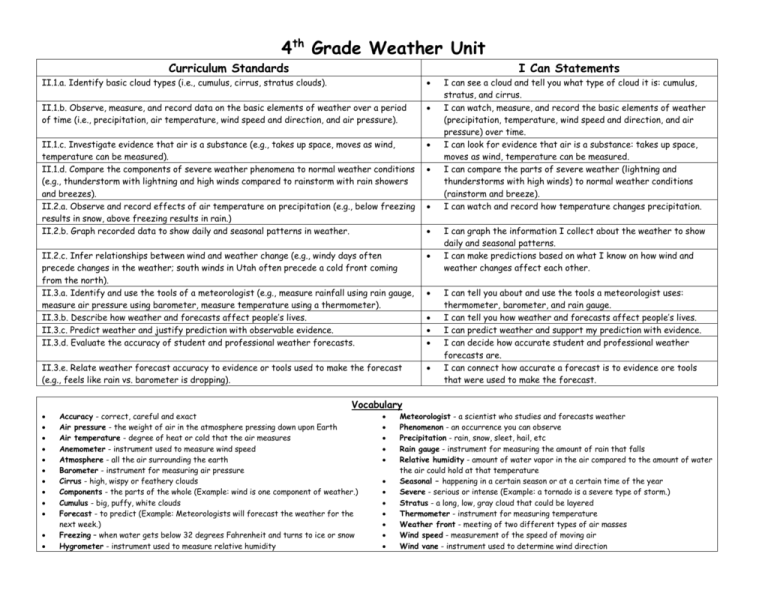
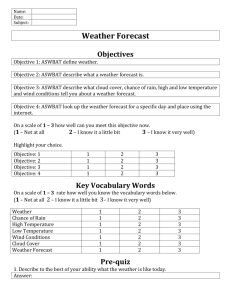
4th Grade Weather Unit Curriculum Standards I Can Statements II.1.a. Identify basic cloud types (i.e., cumulus, cirrus, stratus clouds). II.1.b. Observe, measure, and record data on the basic elements of weather over a period of time (i.e., precipitation, air temperature, wind speed and direction, and air pressure). II.1.c. Investigate evidence that air is a substance (e.g., takes up space, moves as wind, temperature can be measured). II.1.d. Compare the components of severe weather phenomena to normal weather conditions (e.g., thunderstorm with lightning and high winds compared to rainstorm with rain showers and breezes). II.2.a. Observe and record effects of air temperature on precipitation (e.g., below freezing results in snow, above freezing results in rain.) II.2.b. Graph recorded data to show daily and seasonal patterns in weather. II.2.c. Infer relationships between wind and weather change (e.g., windy days often precede changes in the weather; south winds in Utah often precede a cold front coming from the north). II.3.a. Identify and use the tools of a meteorologist (e.g., measure rainfall using rain gauge, measure air pressure using barometer, measure temperature using a thermometer). II.3.b. Describe how weather and forecasts affect people’s lives. II.3.c. Predict weather and justify prediction with observable evidence. II.3.d. Evaluate the accuracy of student and professional weather forecasts. II.3.e. Relate weather forecast accuracy to evidence or tools used to make the forecast (e.g., feels like rain vs. barometer is dropping). Vocabulary Accuracy - correct, careful and exact Air pressure - the weight of air in the atmosphere pressing down upon Earth Air temperature - degree of heat or cold that the air measures Anemometer - instrument used to measure wind speed Atmosphere - all the air surrounding the earth Barometer - instrument for measuring air pressure Cirrus - high, wispy or feathery clouds Components - the parts of the whole (Example: wind is one component of weather.) Cumulus - big, puffy, white clouds Forecast - to predict (Example: Meteorologists will forecast the weather for the next week.) Freezing – when water gets below 32 degrees Fahrenheit and turns to ice or snow Hygrometer - instrument used to measure relative humidity I can see a cloud and tell you what type of cloud it is: cumulus, stratus, and cirrus. I can watch, measure, and record the basic elements of weather (precipitation, temperature, wind speed and direction, and air pressure) over time. I can look for evidence that air is a substance: takes up space, moves as wind, temperature can be measured. I can compare the parts of severe weather (lightning and thunderstorms with high winds) to normal weather conditions (rainstorm and breeze). I can watch and record how temperature changes precipitation. I can graph the information I collect about the weather to show daily and seasonal patterns. I can make predictions based on what I know on how wind and weather changes affect each other. I can tell you about and use the tools a meteorologist uses: thermometer, barometer, and rain gauge. I can tell you how weather and forecasts affect people’s lives. I can predict weather and support my prediction with evidence. I can decide how accurate student and professional weather forecasts are. I can connect how accurate a forecast is to evidence ore tools that were used to make the forecast. Meteorologist - a scientist who studies and forecasts weather Phenomenon - an occurrence you can observe Precipitation - rain, snow, sleet, hail, etc Rain gauge - instrument for measuring the amount of rain that falls Relative humidity - amount of water vapor in the air compared to the amount of water the air could hold at that temperature Seasonal – happening in a certain season or at a certain time of the year Severe - serious or intense (Example: a tornado is a severe type of storm.) Stratus - a long, low, gray cloud that could be layered Thermometer - instrument for measuring temperature Weather front - meeting of two different types of air masses Wind speed - measurement of the speed of moving air Wind vane - instrument used to determine wind direction Weather Unit Plan Day Obj. Lesson/Activity 1 II.3.b II.1.d 2 II.1.c 3 II.1.a 4-5 II.3.a 6-7 II.2.a II.2.c Weather Pre-Assessment Question to investigate: What is weather? Think about words they use to describe weather – make a list to get them thinking Why do we study weather or have weather forecasts? **Main reason is to save lives. How does weather affect our lives? **Throughout this unit, read books and study the difference between severe and normal weather during reading time. Components of Weather: Air o Air is a substance o Moves – wind (fan & Jason’s thing) o Gets hotter/colder – temperature o Has moisture in it – humidity (bag on hand) o Presses on us – air pressure (blow up balloon, paper towel and water, newspaper & ruler, water bottles, etc.) Components of Weather: Precipitation & Clouds o Cloud Book by Tomie dePaola o Cloud Finder o Cloud Picture Sort o 4 types of precipitation Tools of Meteorologists o Introduce all 6 – show as you introduce o Make Tools Cards – can use as flashcards to quiz each other Intro. Utah Weather Rules o Rules 2/3 – give them the Beaufort Wind Scale chart and briefly go over it o Rule 5 - Complete the thermometer paper with freezing point, the average range for seasons and months in Utah, etc. Notes/Assessment/Grading Copy pre-assessment. Use severe weather books. Need: Jason’s air thing, fan, ziplock bags, balloon, paper towel, jar, water, newspaper, ruler, water bottle, etc. Cloud Book by Tomie dePaola Copy Cloud Finder Get cloud picture sort bags Copy weather tools cards (add snow to ruler one) Weather Tools from bucket Copy Utah Weather Rules, blank thermometer, and Beaufort Wind Scale chart. 8+ II.1.b II.2.b II.3.c II.3.d II.3.e 8+ Introduce the weather graphs o Use KSL or Fox 13 websites at the same time each day to get the information o Model how to graph each component o Go through the Utah Weather Rules sheet each day and decide what a reasonable forecast would be o Record your class forecast, then check the “official” forecast on the website o Each day review how accurate your predictions were Throughout the rest of the unit, students will work together or as a class to complete the Weather Cards and learn to read and answer questions about weather data. Weather Post Assessment Throughout the rest of the year, have a daily weather routine where you post the data for the day and students graph it. Briefly discuss forecasts, accuracy, etc. Copy weather graphs and forecast page(s) Copy Weather Cards for students Copy post assessment