Enzymes - SchoolWorld an Edline Solution
Name_______________________Hour: _____
Enzymes—Quiz next day!!!!!
Reactions
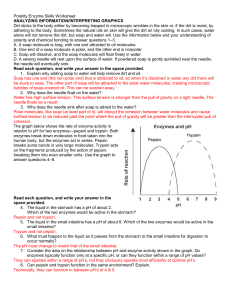
Sucrose is a sweetener found in many candies. It is a carbohydrate made up of glucose and another sugar called fructose. When we eat sucrose, it must be digested or broken down into smaller substances, which our cells can absorb. An enzyme (specialized protein) called sucrase speeds up this chemical reaction. Sucrase breaks the chemical bond in sucrose, which is the reactant, or substrate, in this chemical reaction. High heat and strong acids or bases cause the enzyme shape to unravel, call denaturing, and this stops its ability to catalyze the chemical reaction. On the other hand, the only way to make the reaction go faster is to add more enzymes. Scientists support the “lock and key” model below for how an enzyme speeds up chemical reactions. The letters “ase” at the end of words help us identify enzymes.
1.
Label A-E directly on the picture above with these words: active site, substrate, enzyme, glucose and fructose
2.
All enzymes are _________________.
3.
What is the substrate in the picture above?_____________________
4.
Write the chemical reaction that is occurring below with the proper reactants and products:
_______________________ ___________________ + ____________________
5.
What is the name of the enzyme?________________________
6.
What 3 letters in the enzyme’s name tells that it is an enzyme?_______________
7.
How can you tell from the diagram that sucrase is not used up during the chemical reaction?
8.
How are protein shapes destroyed, or denatured?
pH and enzyme activity
Experiments were designed to study the effect of pH on the rate of enzyme action for 2 different enzymes found in animals, pepsin and trypsin.
Pepsin is found in the stomach and digests proteins like meats. Typsin is found in the intestine and digests lipids (fats). Use the graph to answer the following questions.
9.
At what pH is pepsin working at its maximum rate?_____________Is this an acidic or basic pH?____________
10.
Since pepsin is found in the stomach, what is the probable pH of the stomach?____________
11.
At what pH levels does pepsin not work at all?____________________________________
12.
At what pH is typsin working at its maximum rate?____________Is this an acidic or basic pH?_____________
13.
Since trypsin is found in the intestine, what is the probable pH of the intestine?_______________
14.
If pepsin were produced in the intestine, would this enzyme still carry out its usual functions? ______Explain.
15.
The diagram to the right represents a beaker containing a solution of various molecules involved in digestion.
Use logic and your knowledge of enzymes to determine which structures represent products of this digestion reaction? a.
A and D b. B and E c. B and C d. D and E
16.
Which is the reactant, or substrate in this digestion reaction? a.
A b. B c. C d. D
17.
An enzyme and four different molecules are shown in the diagram to the right.
The enzyme would most likely affect reactions involving a.
molecule A, only b. molecule C, only c. molecules B and D d. molecules A and C Use