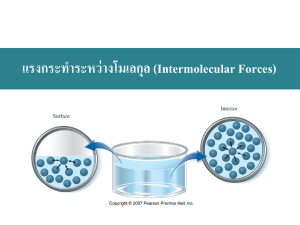
intermolecular forces
advertisement

Raba’a AL-Adawiya Secondary Girls Independent School Chemistry Student’s name: ____________________ Class : ____________________ Teacher : ____________________ Due date : _______________ Unit 1 – Chemical bonding and intermolecular forces Grade 11 Chemistry 2009- 2010 Ms. Amany Ibrahim 1 Raba’a AL-Adawiya Secondary Girls Independent School 1- This is an easy way to work out the charge on an ion: Group Charge on Ion 1 +1 2 +2 13 +3 14 No Ions 15 –3 16 –2 17 –1 18 No Ions Share 4 Now use the periodic table of elements to write the chemical formula for the following compounds: “the first one is made for you” Barium Sulphide 2 2 Ba S Ba2S2 BaS Calcium sulphide CaS Sodium oxide Na2O Lithium fluoride LiF Carbon dioxide CO2 Magnesium bromide MgBr2 Unit 1 – Chemical bonding and intermolecular forces Grade 11 Chemistry 2009- 2010 Ms. Amany Ibrahim 2 Raba’a AL-Adawiya Secondary Girls Independent School 2- Use the periodic table to find the position of the following element. Element Symbol Group Period Charge on ion Valencey Ca 2 4 +2 2 3 +1 1 1- Calcium 2- Sodium Na 1 3- Fluorine F 17 2 -1 1 4-Aluminum Al 13 3 +3 3 5-Phosphours P 15 3 -3 3 6-Chlorine Cl 17 3 -1 1 7- Nitrogen N 15 2 -3 3 8- Sulphur S 16 3 -2 2 9- Carbon C 14 2 No charge OR 4 +4 10- Helium He 18 1 Unit 1 – Chemical bonding and intermolecular forces Grade 11 Chemistry 2009- 2010 Ms. Amany Ibrahim 0 0 3 Raba’a AL-Adawiya Secondary Girls Independent School 3- Circle 5 metals and 5 nonmetals on the periodic table: 4- Write the formula of 3 covalent compounds and 3 ionic compounds. Covalent H2O, CO2, HCl, H2S, HF, SO2,NO3,… Ionic MgCl2, AgCl, NaF, NaCl, KI, KCl, MgO. … 5- Choose the correct completion for each statement: 1- When two atoms have difference in Electronegativity values great enough to separate them, the bond formed between the two atoms is likely to be, a- polar covalent b- ionic b- nonpolar covalent c- nonpolar ionic 2- When the bonding electrons make equal electron clouds around the bonded atoms, the bond formed is likely to be, a- polar covalent c- ionic Unit 1 – Chemical bonding and intermolecular forces Grade 11 Chemistry 2009- 2010 Ms. Amany Ibrahim b- nonpolar covalent d- nonpolar ionic 4 Raba’a AL-Adawiya Secondary Girls Independent School 3- When atoms share bonding electrons unequally, the bond formed is likely to be, a- polar covalent b- nonpolar covalent c- ionic d- nonpolar ionic 4- A compound in which atoms are added individually forming a compound with millions of atoms is, a- water b- potassium iodide c- carbon dioxide d- nitrogen dioxide 6- Write the suitable charge over each atoms in the compounds: 0 + + _ + + - HCl - 0 0 H2 LiCl Write the chemical formula for each of the above compounds (H2, HCl, and LiCl) Unit 1 – Chemical bonding and intermolecular forces Grade 11 Chemistry 2009- 2010 Ms. Amany Ibrahim 5 Raba’a AL-Adawiya Secondary Girls Independent School 7- Use the Electronegativity table to tell the type of bond formed in the following compounds. Compound Electronegativity difference) Bond type ZnI2 2.5 - 1.5 = 1 Weak polar ZnCl2 3- 1.5 = 1.5 Strong polar ZnF2 4 – 1.5 = 2.5 Ionic CdBr2 CdF2 MgI2 Na F CCl4 AlCl3 8- Complete the following statements using the given words: (greatest – hydrogen – fluorine – dipole – highest – lowest – strength ) 1- A molecule in which one end has a partial positive charge and the other has a partial negative charge is called a dipole 2- Fluorine is a non metal with the highest electronegativity, while hydrogen is a nonmetal with the lowest electronegativity. 3- In hydrogen fluoride molecule (HF), hydrogen. atom has a partial positive charge δ+ , but fluorine atom has a partial negative charge δ-. 4- The greater the electronegativity difference, the greatest the polarity of that bond. 5- As the bond becomes more polar its strength becomes greater. Unit 1 – Chemical bonding and intermolecular forces Grade 11 Chemistry 2009- 2010 Ms. Amany Ibrahim 6 Raba’a AL-Adawiya Secondary Girls Independent School 9- Define each of the following: Intermolecular forces ….……………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………................ Intramolecular forces ….……………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………................ Dipole ………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………… Electronegativity ……………………………………………………………………………….............. ………………………………………………………………………………………… Induced dipole ……………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………… Van der Waal’s forces ……………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………… 10- Give reasons: - Intramolecular forces are much stronger than intermolecular forces. Because, in case of intra molecular bonding, there is an electron cloud among the whole molecule due to electron sharing of valence electrons, but intermolecular forces are forces of attraction between opposite poles. Unit 1 – Chemical bonding and intermolecular forces Grade 11 Chemistry 2009- 2010 Ms. Amany Ibrahim 7 Raba’a AL-Adawiya Secondary Girls Independent School - There are no intermolecular forces in ionic compounds. Because in ionic compounds, ions are added individually to make a giant structure of milliond of atoms, so there are no separate molecules. - Water “H2O” is liquid at room temperature while CO2 is gas. Because in case of water, hydrogen bonds are formed between O in one molecule and hydrogen in another. 11- label the opposite diagram of HCl dipole Dipole-dipole OR Van der Waal’s force Unit 1 – Chemical bonding and intermolecular forces Grade 11 Chemistry 2009- 2010 Ms. Amany Ibrahim 8 Raba’a AL-Adawiya Secondary Girls Independent School 12- Determine the EN and bond type for: HF……………………………………………………….. HI……………………………………………………….. HBr……………………………………………………….. HCl……………………………………………………….. Which of the above compounds have the lowest boiling point? HCl 13- Complete the following table: Covalent compound Symbol Boiling point State at room temperature Sulphur dioxide SO2 -10°C gas Carbon dioxide CO2 -78 °C Gas Water H2O 100°C liquid 14- What are the physical properties of liquid water at room temperature? 1- Liquid 2- High boiling point 3- Has surface tension Unit 1 – Chemical bonding and intermolecular forces Grade 11 Chemistry 2009- 2010 Ms. Amany Ibrahim 9 Raba’a AL-Adawiya Secondary Girls Independent School 15- Look at the following diagrams for a sheet of protein and DNA then answer the questions below: Strands - What holds the strands in a protein sheet and in a DNA macro molecule? Hydrogen bonding What is the importance of hydrogen bonding to the structure of protein and nucleic acid DNA? Holds the strands od DNA or amino acid molecules to form giant structures Unit 1 – Chemical bonding and intermolecular forces Grade 11 Chemistry 2009- 2010 Ms. Amany Ibrahim 10 Raba’a AL-Adawiya Secondary Girls Independent School Electron pair repulsion of in small compounds lone pair nitrogen atom Nitrogen tri fluoride NF3 trigonal pyramidal ammonia NH3 These are the stereo shapes of water molecule according to the repulsion of the 2 lone pairs of electrons. Assignment: lone pairs. make a stereo model for one of the small compounds showing the repulsion of the (5 marks) Unit 1 – Chemical bonding and intermolecular forces Grade 11 Chemistry 2009- 2010 Ms. Amany Ibrahim 11 Raba’a AL-Adawiya Secondary Girls Independent School Complete the mind map: Van der Waal's forces (intermolecular forces) Permanent Instantaneous .........dipole-dipole......... induced dipole Example Example HCl, HF, hydrogen bonding I2, F2, Cl2, He Example H2O / HF / HCl Unit 1 – Chemical bonding and intermolecular forces Grade 11 Chemistry 2009- 2010 Ms. Amany Ibrahim 12