102 BIOLOGY GENETICS REVIEW
advertisement

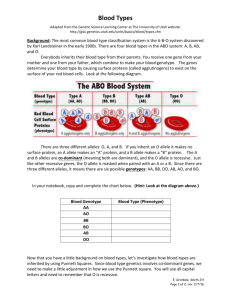
Biology Genetics Review Name ___________________________ 1. Who is the “Father of Genetics”? ________________________________ Match the definition with the appropriate Mendelian Law: 2. Pairs of alleles separate in meiosis, and each gamete A. Rule of Dominance receives one allele of each pair B. Law of Segregation 3. One trait is dominant over another, if the dominant trait C. Law of Independent Assortment is present the other will be hidden 4. Sometimes traits disappear then reappear in a new generation showing chromosomes are separated independently of one another MONOHYBRID CROSSES In mice, Brown fur (B) is dominant to white fur (b). 5. What is the genotype of a homozygous dominant mouse? _________ 6. What is the genotype of a homozygous recessive mouse? _________ 7. What is the genotype of a heterozygous mouse? ____________ 8. Which genotypes could represent a brown mouse? BB Bb bb 9. Which genotype must represent a white mouse? BB Bb bb 10. Cross a white mouse with a heterozygous brown mouse. What is the white mouse’s genotype: ___________ What is the heterozygous brown mouse’s genotype: ____________ Now, create the punnett that shows the crossing of these two mice and show genotype and phenotype percentage possibilities for their offspring. Genotypes: BB: ___________ Bb: ___________ bb: ____________ Phenotypes: Brown: ___________ White: ____________ 11. Cross two heterozygous brown mice. What is the genotype of the heterozygous female: ___________ What is the genotype of the heterozygous male: _____________ Now, create the punnett that shows the crossing of these two mice and show genotype and phenotype percentage possibilities for their offspring. Genotypes: BB: ___________ Bb: ___________ bb: ____________ Phenotypes: Brown: ___________ White: ____________ 12. If I flip a coin, what are my chances of getting heads? _________ Tails? ___________ 13. If a woman gives birth to a child, what are the chances she will have a boy? ________ Girl? _______ 14. Mrs. Davis’ grandparents gave birth to 6 daughters. If they were still having kids, what is the chance that their next child would have been a girl? (Be careful about this…) ____________ DIHYBRID CROSSES Some genes are inherited together and can be shown in a dihybrid cross. 15. In plants green peas (G) are dominant to yellow (g), and rough texture (R) is dominant to smooth (r). If a male parent plant has the genotype GgRr, what possible allele mixtures could be in the sperm of the parent for these two genes? Complete the Punnett below then fill in the sperm with allele combinations. Transfer the genotype from the punnett to the sperm picture and write underneath the sperm the phenotype of the genes it is carrying. The first one has been done for you. G R g GR GR Green, rough r 16. In apple trees, having apples (A) is dominant to not having apples (a) and having branches (B) is dominant to not having branches (b). Look at the dihybrid cross below. What are the genotypes and phenotypes of the squares labeled? The first one has been done for you as an example. Genotypes: a. AABb b. _____________ c. _____________ d. _____________ Phenotypes: A. Apples, Branches B. __________________________________ C. __________________________________ D. __________________________________ A B C D 18. Jane has red hair (h) but her parents have brown hair (H). What must her parent’s genotypes be in order for her to have red hair? 19. A mouse has 8 babies. 4 of the babies are black and 4 are white. What must the parent’s genotypes be in order to produce this litter of babies? PEDIGREES Use the pedigree below to answer the questions. This pedigree is for red hair which is recessive and is NOT sex-linked. Brown hair (H) is dominant to red hair (h). 20. What is the gender of person II-1? ___________________ 21. What is the gender of person II-2? ____________________ 22. How many children did II-2 and II-3 have? ____________ 23. How many sons did I-1 & 1-2 have? ____________________ 24. What is the genotype of person labeled I-2? ___________ 25. What is the genotype of the person labeled I-4? ___________ 26. What is the genotype of person II-2? ______ (You must look at the person’s children to figure this out) 27. What is the genotype of person II-3? ______ (You must look at the person’s children to figure this out) 28. If person III-3 marries a person who is heterozygous for hair color, what are the possible hair colors seen in their kids? What is person III-3’s genotype? ________ What is a heterozygous person’s genotype? __________ Put these two genotypes around the Punnett to determine hair color possibilities for their kids. INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE In flowers, red petal color (RR) is incompletely dominant to white petal color (R’R’) producing a new phenotype of pink petal color (RR’). 29. Cross a red flower with a white flower and show genotypes and phenotypes of offspring. Genotypes: RR _________ RR’ ________ R’R’ ________ Phenotypes: Red- ____________ Pink- ___________ White- __________ 30. Cross two pink flowers and show genotypes and phenotypes of offspring. Genotypes: RR _________ RR’ ________ R’R’ ________ Phenotypes: Red- ____________ Pink- ___________ White- __________ CODOMINANCE In chickens, black feathers (BB) is codominant to white feathers (WW) creating a new phenotype of Black and White Checkered feathers (BW). 31. Cross a white feathered chicken with a black and white checkered chicken and show genotypes and phenotypes. Genotypes: BB _________ BW ________ WW ________ Phenotypes: Black ____________ Black & White- ___________ White- __________ 32. Cross two black and white checkered chickens and show genotype and phenotypes. Genotypes: BB _________ BW ________ WW ________ Phenotypes: Black ____________ Black & White- ___________ White- __________ MULTIPLE ALLELES 33. Fill in the chart below with the possible genotypes of the blood types listed. PHENOTYPES Blood Type A Blood Type B Blood Type AB Blood Type O GENOTYPES 34. Would you say a person with a genotype of AA is homozygous or heterozygous? ______________ 35. Would you say a person with a genotype of AO is homozygous or heterozygous? _______________ 36. Is blood type AB an example of incomplete dominance or codominance? ______________________ 37. Which blood type seems to be more recessive- A, B, or O? _________________________________ 38. Cross a parent with O blood with a parent with AB. What are the possible blood types for their kids? Blood Phenotypes: _____________________ _____________________ 39. Cross a parent with BB blood with a parent with OO blood. What are the possible blood types for their kids? Blood Phenotypes: _____________________ 40. Cross a parent with BO blood with a parent with OO blood. What are the possible blood types for their kids? Blood Phenotypes: _____________________ _____________________ 41. Suppose a mother with A blood produced a child with O blood. (The father is OO), what genotype must the mother be to produce a child with O blood? A Mom ? O Dad O OO child A SEX-LINKED TRAITS Sex linked traits are found on the X chromosome. Look at the chromosomes shown to the right. 42. Which pair belongs to a girl? _________ 43. What is a girl’s genotype? ___________ 44. Which pair belongs to a boy? ________ 45. What is a boy’s genotype? ___________ 46. The band across the tall chromosomes in both pictures represents an allele for a sex-linked trait. What is different about the bands on the boy’s chromosomes? _______________________________________________ 47. Can a boy be a carrier of a sex-linked trait? ______________ Why or why not? __________________________________Look at the Punnett to the right. Do boys get their X’s from their moms or dads? ______________________________________________________ B 48. Who gives a boy his sex-linked trait/disorder- his mom or dad? ______________________________ Hemophilia (h) is a recessive sex-linked blood disorder. Answer the following questions based on this information. The first one has been done for you. 49. What is the genotype of a homozygous normal female? XHXH 50. What is the genotype of a heterozygous female? _____________ 51. What is another name for a heterozygous female? ___________________________ 52. What is the genotype of a homozygous recessive female that has hemophilia? ______________ 53. What is the genotype of a normal male? _______________________ 54. What is the genotype of a hemophiliac male? ______________ 55. Cross a homozygous dominant female with a hemophiliac male. Answer the questions below a. What are the chances of getting a CHILD with hemophilia? _____________ b. What are the chances of getting a GIRL that is a carrier? ________________ (remember, you have to cover up the boys boxes, to answer questions about girls only) 56. Choose a male and female offspring from the Punnett Square above in question 52 and mate them. Use a Punnett square to show the results of their offspring. Answer the questions that follow. a. What are the chances of getting a CHILD with hemophilia? _____________ b. What are your chances of getting a BOY with hemophilia? _______________ (remember, you have to cover up the girls boxes, to answer questions about boys only) c. What are the chances of getting a GIRL that is a carrier? ________________ 57. What is the genotype of person I-1? ______________ 58. What is the chance of person I-1 passing the disease to their offspring? ______________ 59. Suppose person II-2 and II-3 have another child. What is the chance they will have a GIRL with hemophilia? (Do a Punnett) _____________ 60. What is the chance they will have a CHILD with hemophilia? ____________ 61. Other than looking at the title of the picture, how else would you have known this pedigree was for a sex-linked disorder? MUTATIONS & DISORDERS Match the mutation name with the picture. 62. Insertion 63. Deletion 64. Duplication 65. Inversion Match the type of mutation to the picture. 66. Point mutation 67. Frameshift 68. nondisjunction B A C Match the disorder to its description. 69. Child cannot drink milk b/c he can’t break down phenylalanine 70. Person has abnormal shaped red blood cells, severe pain & clots 71. Person’s sex chromosomes are XXy 72. Person has mucus build up in lungs and digestive system A. B. C. D. Klinefelters Cystic fibrosis Sickle Cell PKU Match the disorder to its description. 73. Child has fat build up in nerve cells, loses ability to function, dies before age 8 74. Adult male loses feeling in arms legs, dies before age 40 75. Child born with shortened arms and legs, normal head & chest region 76. Female has sex chromosomes XO, webbed neck, mild mental deficiency A. B. C. D. Turners Achondroplasia Huntington’s Tay Sachs Disease Use the karyotype picture to the right to answer the following questions: 77. Is this person a boy or girl? __________ 78. Circle the sex chromosomes. 79. What are all the other chromosomes called? ___________________ 80. Is the person in the karyotype to the right a boy or girl? ________________ 81. This person is not normal. Look over the chromosomes and find the abnormality. What genetic disorder does this person have? ___________________________________ 82. What type of mutation causes this genetic disorder? a. Point mutation b. Frameshift mutation c. Nondisjunction