Worksheet 4-4 - Iowa State University
advertisement

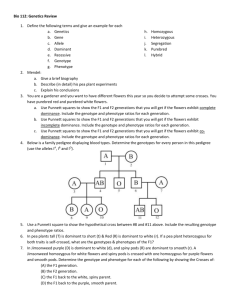
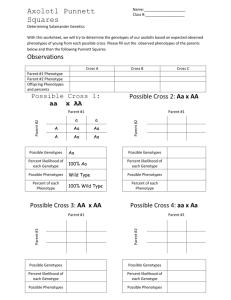
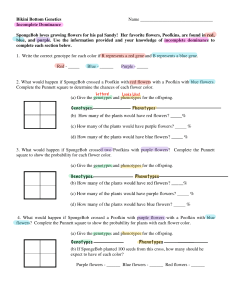
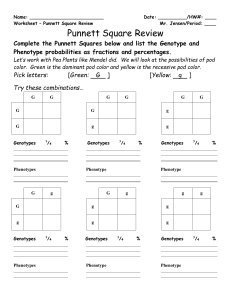
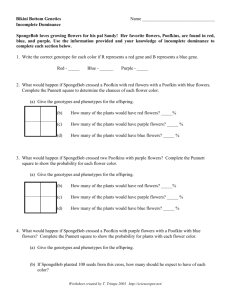
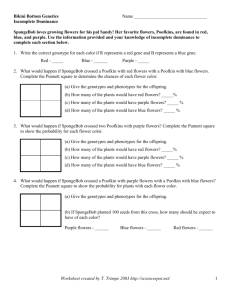
Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Date: Leader: Raelyn Course: Biology 211 Instructor: Dr. Raich 1. Describe the genotype and phenotype and list the ratios and percentages for each. a. 2. Jerry has a pea plant that has a phenotype that is green (G), but he wants to find out the genotype of the plant. You know that green tends to be a dominant trait. Show your work of the possible outcome(s). a. How will Jerry do this? Describe the process. 3. You have a dog that is homozygous recessive at locus (A) and has light fur. She has 8 puppies that all express dark fur color. What is most likely the genotype of the father? Show the Punnett Square to support your answer. a. What are the parental genotypes: Are they hetero/homozygous? b. How many different gametes can each parent produce: 4. Describe each of the following. a. Law of Independent Assortment b. Law of Segregation 5. Explain how independent dominance is different from what we previously discussed. a. Provide examples of characteristics that have use dominance. 6. SpongeBob loves growing flowers for his pal Sandy! Her favorite flowers, Poofkins, are found in red, blue, and purple. Use the information provided and your knowledge of incomplete dominance to complete each section below. a. Write the correct genotype for each color if R represents a red gene and B represents a blue gene. b. What would happen if SpongeBob crossed a Poofkin with red flowers with a Poofkin with blue flowers? Complete the Punnett Square to determine the chances of each flower color. List the genotypes, phenotypes, and percentages of each phenotype. c. What would happen if SpongeBob crossed two Poofkins with purple flowers? Complete the Punnett Square to show the probability for each flower color. List the genotypes, phenotypes, and percentages of each phenotype. d. What would happen if SpongeBob crossed a Poofkin with purple flowers with a Poofkin with blue flowers? Complete the Punnett Square to show the probability for plants with each flower color. List the genotypes, phenotypes, and percentages of each phenotype.