Type of Infectious Agent Disease Examples Modes of Transmission
advertisement
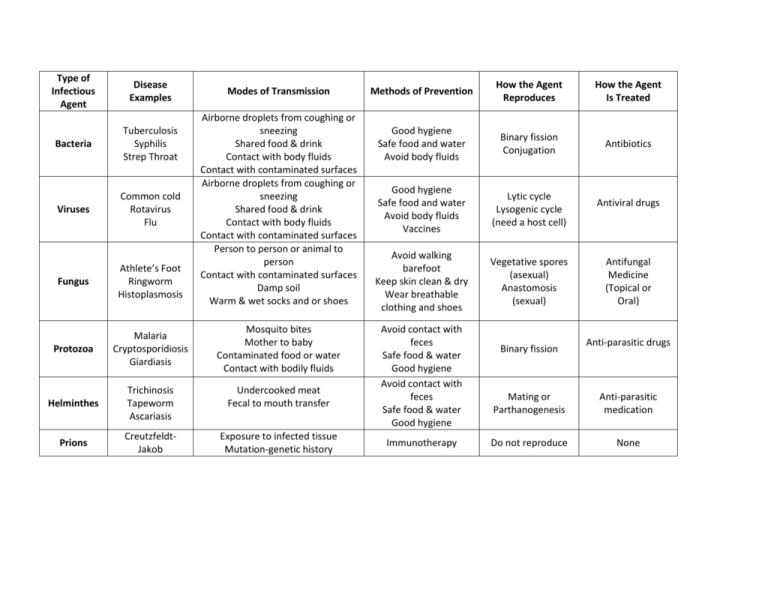
Type of Infectious Agent Disease Examples Bacteria Tuberculosis Syphilis Strep Throat Viruses Common cold Rotavirus Flu Modes of Transmission Airborne droplets from coughing or sneezing Shared food & drink Contact with body fluids Contact with contaminated surfaces Airborne droplets from coughing or sneezing Shared food & drink Contact with body fluids Contact with contaminated surfaces Person to person or animal to person Contact with contaminated surfaces Damp soil Warm & wet socks and or shoes Fungus Athlete’s Foot Ringworm Histoplasmosis Protozoa Malaria Cryptosporidiosis Giardiasis Helminthes Trichinosis Tapeworm Ascariasis Undercooked meat Fecal to mouth transfer Prions CreutzfeldtJakob Exposure to infected tissue Mutation-genetic history Mosquito bites Mother to baby Contaminated food or water Contact with bodily fluids Methods of Prevention How the Agent Reproduces How the Agent Is Treated Good hygiene Safe food and water Avoid body fluids Binary fission Conjugation Antibiotics Good hygiene Safe food and water Avoid body fluids Vaccines Lytic cycle Lysogenic cycle (need a host cell) Avoid walking barefoot Keep skin clean & dry Wear breathable clothing and shoes Vegetative spores (asexual) Anastomosis (sexual) Avoid contact with feces Safe food & water Good hygiene Avoid contact with feces Safe food & water Good hygiene Immunotherapy Binary fission Antiviral drugs Antifungal Medicine (Topical or Oral) Anti-parasitic drugs Mating or Parthanogenesis Anti-parasitic medication Do not reproduce None