Chemistry Balancing Reactions Vocab
advertisement
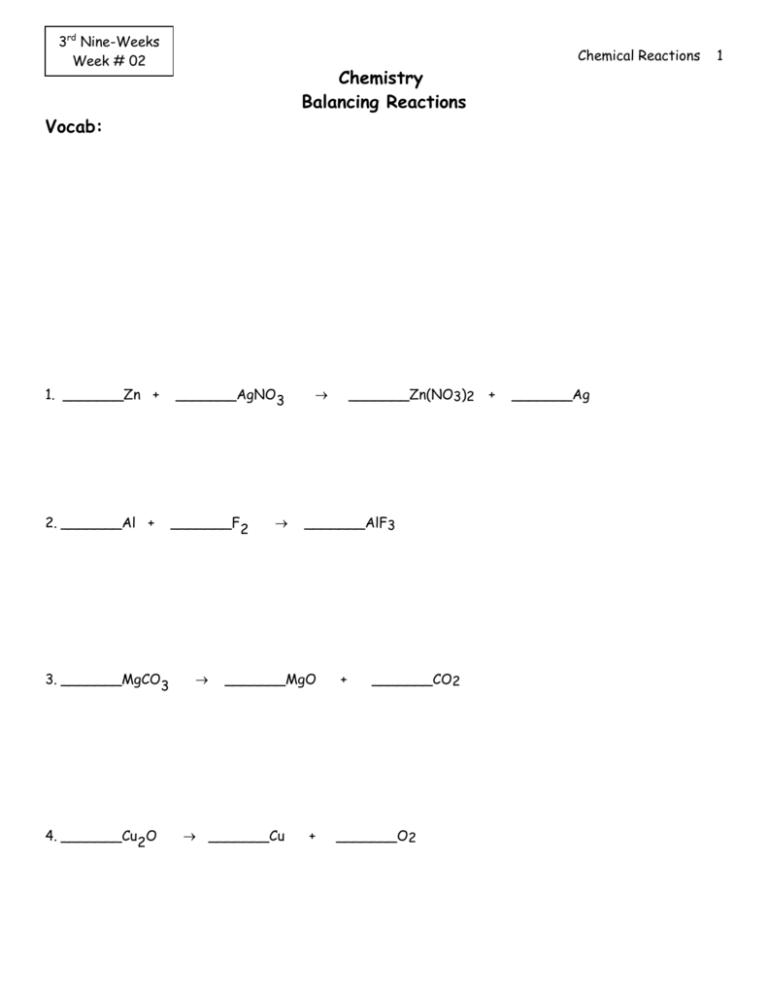
3rd Nine-Weeks Week # 02 Chemical Reactions Chemistry Balancing Reactions Vocab: 1. _______Zn + 2. _______Al + 3. _______MgCO3 4. _______Cu2O _______AgNO3 _______F2 _______AlF3 _______MgO _______Cu _______Zn(NO3)2 + + _______CO2 _______O2 + _______Ag 1 Chemical Reactions 5. _______Cl2 + _______LiI 6. ______Ca(NO3)2 + 7. _______C2H6 + ______Na2SO4 _______O2 8. _______NaClO3 9. ______C3H8 _______O2 + 10. ______ Mg(OH)2 _______LiCl _______NaCl + _______I2 ______CaSO4 _______CO2 + + + ______NaNO3 _______H2O _______O2 _______CO ______ MgO + + _______H2O ______ H2O 2 Chemical Reactions I. EVIDENCES OF CHEMICAL REACTION 1. bubbling or fizzing, evolution of a gas 2. color change 3. cloudy, formation of a precipitate (an insoluble solid) 4. production of heat and light (does not have to have both) 5. a cloudy solution becomes clear II. UNDERSTANDING the PARTS of a CHEMICAL REACTION ___ NaCl (aq) +___ H2SO4 (aq) + ___ MnO2 (s) (g) [A] [B] [C] ___ Na2SO4 (aq) + ___ MnCl2 (aq) +___H2O (l) + ___ Cl2 [D] [E] [F] ______________________1. List the reactants. ______________________2. List the products. ______________________3. List the solids. ______________________4. List the gases. ______________________5. List the liquids. ______________________6. List the aqueous (dissolved in water) solutions. ______________________7. What is the mole ratio of sulfuric acid to sodium sulfate? ______________________8. What is the mole ratio of chlorine gas to manganese (IV) oxide? ______________________9. What is the mole ratio of sodium chloride to chlorine gas? [G] 3 Chemical Reactions III. Predicting Products Diatomic Molecules: Synthesis: H2, O2, N2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 (HON & Halogens) X + Y = XY 1. Barium metal reacts with nitrogen gas 2. Aluminum reacts with sulfur (S8) 3. Chlorine gas and oxygen gas react to produce dichlorine heptoxide. Decomposition: XY = X + Y 4. An electric current is applied to molten sodium nitride. 5. An electric current is applied to aluminum oxide. Combustion: (a) complete combustion (sufficient oxygen) (b) incomplete combustion (limited oxygen) CxHy + O2 CO2 CxHy + O2 CO + + H2 O H2 O 6. Butane burns in the presence of sufficient oxygen. 7. Heptane burns in the presence of limited oxygen. Single Replacement: metals will take the place of the cation in the compound halogens will take the place of the halogen in the compound [remember to use the activity series to determine if the reaction actually works] Reaction: X + YZ = Y + XZ 4 Chemical Reactions 8. A small piece of potassium metal is dropped into a container of water. 9. A piece of aluminum metal is dropped into a solution of sulfuric acid. 10. A piece of silver metal is dropped into a solution of hydrochloric acid. 11. A piece of magnesium metal is mixed with a solution of aluminum nitrate. 12. A piece of aluminum metal is mixed with a solution of magnesium nitrate. 13. Fluorine gas is bubbled through a solution of lithium iodide. 14. Iodine crystals are dropped into a solution of aluminum chloride. Double Replacement. AB + CD AD + CB 15. A solution of potassium iodide is mixed with a solution of lead (II) nitrate. 16. A solution of aluminum acetate is mixed with a solution of ammonium sulfate. 17. A solution of barium hydroxide is mixed with a solution of phosphoric acid. 5 Chemical Reactions 18. A solution of sodium hydroxide is mixed with a solution of phosphoric acid. G. Redox Reactions Definition – 1) To be oxidized mean to have an increase in your oxidation number 2) To be reduced means to have your oxidation number decrease 3) To solve each reaction you must first determine the oxidation number of each element A. Determining oxidation numbers rules: 1. The oxidation number of an element in its elemental state is ZERO. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to the charge of the ion. 3. The oxidation numbers of Groups 1 and group 2 in compounds are +1 and +2 respectively 4. The oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 unless it is combined with a metal, in which case it is -1. 5. The oxidation number of oxygen is -2 in most oxygen containing compounds 6. For a compound, the sum of the individual oxidation numbers is zero; for a polyatomic the charge is equal to the sum of the ion Ex: (PO4) -3 Ex: O = -8 FeO + CO P = +5 Fe + CO2 Find: A. The substance oxidized Ex: 3MnO2 + 4Al B. The substance reduced 2Al2O3 + 3Mn Find: A. The substance oxidized B. The substance reduced 6











