Period 3: 600-1450 CE: Islam bursts on the scene, End of the Post
advertisement

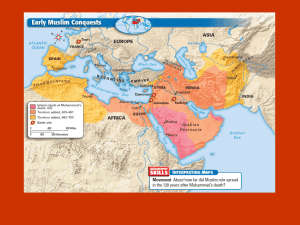
Period 3: 600-1450 CE: Islam bursts on the scene, End of the Post Classical Era, Trade dramatically increases Big Picture snapshots of this time period Trade increases on the Silk Road, Indian Ocean and Trans Saharan Trade impacts new cities (Swahili City States, Timbuktu) Islam dramatically effects history Mongols Western Europe turns feudal and is compared to feudal Japan Byzantine Empire China and its second golden age (Sui, Tang, Song dynasties) Aztec and Inca comparison in the Americas Mali in Africa Catalysts of Change during this time period o Islam o Schism in Christianity o Manufacturing in Song China o Chinese and Middle Eastern technology o Mongols o Camels o Black Death Period 3 Islam Monotheistic religion like Judaism and Christianity Accepts Abraham, Moses and Jesus as prophets Joins Buddhism and Christianity as a universalizing religion (easily adapted to other cultures) By 711, Islam reaches both India and Spain Spread by merchants, missionaries and conquering due to weaker surrounding areas Dar Al Islam House of Islam Territory of Islam includes the Middle East, North Africa and Spain Indonesia is the most populated Muslim country in the world today Umayyad Dynasty (661-750 CE) Jizya is a tax on non-Muslims used in Islamic empires Al-Andalus Abbasid Caliphate (750-1258 CE) Accomplishments include: Arabic numerals, advancements in algebra, geometry and trigonometry, perfection of the astrolabe, astronomical observatories, optic surgery, medical encyclopedias, and literature like the Arabian Nights. Arabesques Mosques use of geometric patterns Women in Islam Better treatment under the Quran Harem, 4 wives, testimony and veiling show patriarchal society Byzantine Empire What are they known for (4-5 things)? Western Europe: Feudalism, Franks, Charlemagne Women in Europe mainly midwives and healers Gothic Architecture o Tall spires, flying buttresses, stained glass Vikings Crusades Black Death Nation states develop o England: William the Conqueror -1066 , Magna Carta -1215 and Parliament o France: 100 Year War o Spain: Ferdinand and Isabella, Reconquista and their use of Catholicism o Russia: Mongol Horde eventually lose power, Moscow emerges Reasons why Europe is lifted from the Middle Ages into the Renaissance o Gunpowder, longbow, Crusades, Marco Polo’s Travels, Black Death and the Printing press. Spread of Buddhism from India to China, Korea and then to Japan China Sui Dynasty (Grand Canal) Tang Dynasty (618-907 CE) Expands Chinese territory Kowtow shows Chinese dominance over places like Korea Second Golden Age of the Silk Road Letters of Credit (Flying money) Gunpowder developed Champa rice from Vietnam fuels population surge Song Dynasty Iron manufacturing makes China manufacturing giant of the world at this time Largest cities in the world Golden Age of innovation with the compass and printing Neo-Confucianism combines both Buddhism and Confucianism Foot binding shows patriarchal society Yuan Dynasty Mongol rule in China (prejudice towards the Chinese ) Ming Dynasty (1368-1644 CE) Kicked out the Mongols and Chinese culture reemerges Japan: Shinto, Fuedalism, Shoguns India Delhi Sultanate Islamic rule in Northern India Hinduism remains a constant especially in Southern India Mongol Must Know Information: o Largest continuous land empire in world history o Facilitated the 3rd Golden Age of the Silk Road (Pax Mongolica) o Religiously tolerant o Never took Japan, Egypt and India Mongol Khanates o Golden Horde- Russia o Chagatai- Central Asia o Persian Ilkhanate o China- Yuan dynasty Forbade the Chinese from marrying Mongols and learning the Mongol language Two areas where Christianity remained in Africa was Egypt and Ethiopia Remember gold and salt as the major products of Africa Africa East Africa Swahili, The Salt Gold Trade Trans Saharan trade o Camel saddle in the 300’s CE and the motivation of gold accelerated trade Sub Saharan Africa o Bantu migrations Iron technology, farming techniques, influence of language o Stateless societies (kinship groups) o Diffusion of bananas from Malaysia increases population o Ghana: Islam and Gold o Mali: Sundiata, Mansa Musa, Mosque at Jenne o Songhai: Sonni Ali Sonni Ali Americas Llama: only large domesticated beast of burden Maya Aztec Incas Oceania o Polynesian migrations (600 CE) Fiji, Tahiti, Hawaii and New Zealand Regional kingdoms established Trade explodes in this time period o Trans Saharan, Silk Road and Indian Ocean Reasons for trade expansion: o Technological advancements (astrolabe, compass, lateen sail, camel saddle) o Monetary systems (credit) Results of trade: o Diffusion of goods (salt, spices, precious metals, silk), religions, language, technologies and disease o Growth of cities like Swahili city states (Kilwa), Constantinople, Venice, Cairo, Chang’an How do the civilizations of this time compare to one another? What patterns can use see across this period? What traditions and changes occur? Include maps and visuals of: o Byzantine empire, feudal Europe, Mongol empire, Dar Al Islam, spread of the Black Death