Practicum Lesson Plan 7
advertisement

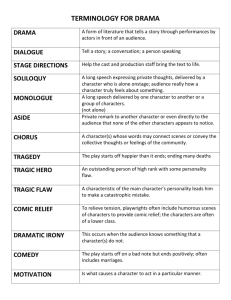
LESSON PLAN 7 Grammar Focus: The future tense with be going to, will, and the present continuous. Also review present continuous vs. simple present; want and need. Vocabulary: Continuing education classes. Review vocational words and vocabulary related to a course catalog, future tense words and phrases Reading: Reading a course catalog Pronunciation: concept of syllable, strong syllables Student Proficiency Level: Multi-level (Levels 1, 2, and 3 combined) Ethnographic composition: Vietnamese, Laotian, Thai Objectives: Students will learn to use be going to, will, and the present continuous to talk about the future, especially pertaining to their personal and vocational goals. They will learn to read and comprehend a course catalog. They will learn the concept of syllables and be able to decipher strong syllables in English words. Materials: dry erase board, markers, flashcards, magnetic board and magnets, picture dictionary, outlines from a college course catalog, textbook, audio CD Warm up and Review: (10 minutes) Write today’s lesson focus on the board. The future tense with be going to, will, and present continuous. Read a course catalog. Pronounce strong syllables. - Books closed. Review language for describing people (hair and eye color, age, clothing, etc.) Ask individual Ss: What are you wearing today? What color is Lo’s hair? What do you do during the weekend? What do you want to do in the future? What will you do after class? Practice: (15 minutes) Reading, listening, speaking, and writing Books open to Pg. 30. Direct Ss attention to Exercise 1 and read the instructions aloud. Read the question and the answer choices in 1 and point to the right answer b which has been circled. Example: Q 1. How old is Fernando? A. (B). 35. Ask individual Ss to read aloud the remaining questions and answers. Say: Now, listen to the CD about Fernando and circle the correct answers.(Class audio Cd1 track 17). Repeat the audio program as needed. Check answers by calling on individual students. Read aloud the second part of the instructions for exercise 1: Talk with a partner. Ask and answer the questions using complete sentences (Fernando is 35 years old). Ss complete this part in pairs. Walk around and help as needed. Practice: Reading and writing (10 minutes) - Direct Ss’ attention to Exercise 2A pg.30.. Ask Ss: What is the title of the story? (An important Day). The story is written in a cloze-gap format with blanks where Ss have to write the verb indicated under each blank in its correct tense. Example: Nguyen __(1. Be) 45 years old. (Nguyen is 45 years old). Encourage Ss to think about the main idea as they are skimming the story. Read aloud the instructions for 2B.Ss read the answers provided and complete the question about it. Example: 1B(A). Tan is 45 years old. 1A.(Q). How old ____ (is Tan)? Ss complete the exercise individually. Provide help as needed. Presentation: (10 minutes) There are three ways to talk about future events. Be going to: Martin is going to make dinner after class. Will. He will make dinner after class. The present continuous. He’s making dinner after class. Tell Ss that all the sentences have the same basic meaning: some future event. -Write time phrases or time-related words on the board that talk about the future. After class, tomorrow, next week/ weekend/month/year/ semester, or in the future, on your next vacation. These are signals that we are talking about the future and need to use one of the future tenses. Practice: Pair group activity: Talking and writing ( 8 minutes) - Direct Ss’ attention to P. 29. Each S writes his/her name on the blank lines on the top row. Have three Ss read the example questions and answers aloud. Example: A. What are you going to do after class? B. I’m going to make dinner. A. What are you doing tomorrow? B. I’m going shopping. Ss ask each other questions and complete the chart under correct names. Presentation: (8 minutes): Go over the course catalog (pg.28) homework assigned last week. Explain related vocabulary ( instructor,fee,GED, TSI, Campus, Computer technology vs. Computer repair, Prerequisite, Course numbers, sections, assessment, requirements, etc.) by writing them on the board. . Ss may make their own flashcards as they have each word introduced. Practice(10 minutes): pass out paper slips containing cut and paste selections of course outlines from real college catalogs of both credit and continuing education courses. Each slip will also contain questions to check for comprehension. Write the questions on the board, read aloud for comprehension, and ask Ss to look for answers in the catalog. Examples: How long does it take to finish the software User program? What are the prerequisites for enrolling in Catering? When can the practicum/capstone be taken during the course? Ss work individually, and then check answers with a partner, followed by whole group checking. Warm up and Presentation: (5 minutes): Write the word syllable on the board. Point to the word. Say it aloud. Ask Ss to repeat. Underline the syllables in the word syllable( syl-la-ble), clapping with each syllable. Say: These are syllables. Next, draw a circle around the first syllable of the word syllable (syl) . Say the word again and clap each syllable again, but this time, put extra emphasis on the first syllable. - Direct Ss’ attention to Exercise 3A on Pg. 31.Play the audio program which sounds out the syllables in the words pá per, reś tau-rant, and com-pú- ter. Ss just listen. Practice: Whole group: Listening and clapping (15 minutes) Tell Ss that they will listen to each word (3B, pg. 31) and clap as they hear the syllables in each word. Model with the words ‘neck-lace’ and ‘nur-sing’ with a S by clapping. Show them how to clap louder for the strong syllable (neck in neck-lace; nur in nursing) -Play class audio CD1 track 19. Ss listen to the words, repeat and clap the syllables (correct pronunciation as needed), working with a partner (Exercise 3B). - Class audio CD 1 track 20. Before playing the CD, say the word ins-truć-tor, the first word on the audio program. Ask: Which syllable is strong? (the second one). Point to the dot over the second syllable in the word. Direct Ss to listen to each word in the CD, and then put a dot over the strong syllable in each word. Repeat the program as needed. Check answers. Homework: For homework, students write eight words from unit 1 and unit 2.They put a dot over the strong syllable in each word. Also change the bold words in the following text to make conversations. Example: A. What will you do in the next five years? B. Maybe I’ll open a business. A. That’s great. Answer choices: 2. Probably/ take a vocational course. 3. Most likely/ start business school. 4. Hopefully/go to college. 5. Maybe/learn a new language. Reflections: I had my regular three students. This time, I had planned for the prioritization of topics, since I always plan extra activities. I had also drawn three vertical lines down the whiteboard to keep my writings on the board organized. There was one section for the vocabulary, one for the example sentences, and one for the syllables. I was also partially successful in coaxing some of my students to make their own flashcards while I introduced new vocabulary words, even though they were used to taking notes in their notebooks. I could see that they were excited to learn about reading a course catalog, and it seemed like an extremely viable topic that held considerable practical interest to them. Same can be said of the syllabification practice, since pronunciation is an area that frequently gets to be overlooked in ESL classes. Overall, it was a productive lesson.