Margo-Kinzer-Couter-Finding-Academic-Success-for-all
advertisement

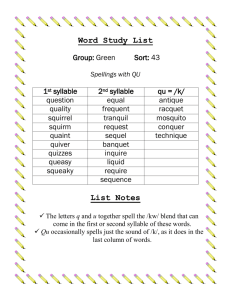
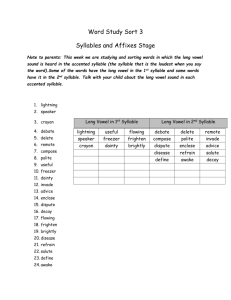
Finding Academic Success for All Students Margo Kinzer Courter, MBA, MA, CCC-SLP Courter Communications, LLC Speech, Language, & Learning courtercx@gmail.com • Defines the knowledge and skills students should have within their K-12 education • Aligns K-12 with expectations in English/language arts and math standards for college and career success • Consistent standards across all states • Determined through evidence and research based criteria Facts from The ACT Report • Needs to understand complex texts • Critical thinking is NOT enough • Complexity of college texts have not decreased • Decline in vocabulary complexity • Word difficulty in scientific journals have increased • Discrepancy in the complexity of texts from end of high school to beginning of college ACT Report continued The clearest differentiator was students’ ability to answer questions associated with complex texts through understanding complex sentence structure - NOT critical thinking skills. In 2004-2005, only 51% of students taking the ACT scored at the benchmark (C equivalency) for understanding complex text needed for college readiness. Learning to Read PreK K 1 2 Reading to Learn 3 4 5 6 infinity Children’s phonological awareness ability at preschool is a powerful predictor of later reading and writing success (Bradley and Bryant, 1980; Lundberg, Olofsson, and Wall, 1983; Torgesen, Wagner, & Rashotte, 1994). Strong phonological awareness base: – Phonemic awareness – Rhyming – Onset and Rime – Segmenting – Blending – Manipulating Great activities: www.phonological awarness.org Visual Phonics Explicit instruction in the six common spelling patterns, prefixes, suffixes, roots, and word origins makes decoding and figuring out meaning of words and sentences easier for students. (JustReadFlorida.com) Six Syllable Patterns C = closed syllable as in "cat" (C) L = consonant -le syllable as in "ta/ble" (L) O = open syllable as in "we" (O) V = vowel team syllable as in "read" (V) E = vowel-consonant-e syllable as in "cake" (V_E) R = r-controlled syllable as in "barn" and "bird" (R) 3rd Grade through High School • • • • • Relevance Preteach/Prelearn Peak Curiosity and Creativity Multimodality Learning Use consistent strategies across teachers and grade levels • Link to what the student knows • Students who used visual aids outperformed those using conventional reading techniques on a reading comprehension test. • The benefit of using organizers does not diminish based on the grade level. Kim, A., & Vaughn, S. (2004). Graphic Organizers and Their Effects on the Reading Comprehension of Students with LD: A Synthesis of Research. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 37(2), 105-118. Retrieved December 6, 2010, from www.asha.org • Fountas and Pinnell (2001) cite that when content is illustrated with diagrams, the information can be maintained by students over a period of time. • Students with learning difficulties need strategies to help them achieve success in academics. (Gagnon & Maccini, 2000). What Strategy Will You Use? Highlighting key words in assignments Highlighting tape or erasable highlighters in textbooks Webs Cornell Notes Venn Diagrams Graph paper for math Checklist for math story problems Vocabulary strategy Book report format Following Written Directions or Reading Paragraphs • Highlighting (highlighter tape) – Key words in directions – Supporting detail for paragraphs and chapters Example Read each sentence below. Circle the subject and underline the verb. Then write a prepositional phrase on the line to complete the sentence. or Read each sentence below. Circle the subject and underline the verb. Then write a prepositional phrase on the line to complete the sentence. Vocabulary • Introduce Vocabulary – Provide students with a description, explanation, or example as opposed to a formal definition. – Access Prior Knowledge: Build on Prior Knowledge – Make the vocabulary relevant to the students *** This is important for young students as well as they are learning high frequency words. This will aid in reading comprehension and retrieval*** Great Resource: Tennessee Department of Education Tennessee.gov/education/ci/doc/VOCABULARY.pdf Vocabulary Cards Outside top: 1 Number in the right upper corner that corresponds to the number on the vocabulary word Outside bottom: Vocabulary word Example: saw 1 Inside top: Use this space to draw a picture that represents the meaning of the word or use word finding template Inside bottom: Definitions of the word. All definitions to multimeaning words should be written. Example: 1. A tool used to cut 2. past tense of to see Diane German (1998) and Dockrell (1998) state that the prevalence word finding difficulties are high among learners with specific language impairment and learning disabilities. _Species______________ Syllables: __Spe___ __cies___ _____ ____ Speed Cheese _Species___ _Species______Species____ Sentence: Lions are a species. Relationship Building – Concept Circles doors windows house roof chimney Connection: Curriculum Based Meaning Common Language Usage Term/Phrase/Word Factor Common Use of the Word Curriculum Based Use A fact that contributes to a result Numbers that divide evenly into another number Sentence Using Terms General Use The rain was a factor in mom’s decision to not go. Curriculum Use 2 is a factor of 4 Meaning Same X Different Book Report Format Plot Setting Main Characters Conflict or Central Problem Main Idea and 3 Details from Each Chapter Resolution of the Conflict Conclusion Your Thoughts Venn Diagrams Subject 1 Subject 2 Compare and Contrast Making an Apple Pie to Making a Mud Pie Cornell Main Idea Vocabulary Questions Summary Supporting Details Webs for Organization & Prewriting Detail 1 Detail 2 Main idea Conclusion Detail 3 Math Story Problems Read the story problem Reread and highlight key words Match numbers to words What are you solving for? Solve Recheck Example: Math Story Problem Sam bought 8 ball caps, one for each of her eight friends, for $8.95 each. The cashier charged her an additional $12.07 in sales tax. She left the store with a measly $6.28. How much money did Sam start with? Caps = 8 8.95 Cost= 8.95 x 8 Sales Tax = 12.07 71.60 $ Left = 6.28 + 12.07 83.67 Answer: $89.95 + 6.28 $89.95 • Ebooks On line Textbooks – Audio, reading help, companion materials, study skills, test taking strategies, self tests, quizzes, additional practice • • • • • • Audio Downloads Reading help Textbook companion Study skills & Test taking strategies Self tests & Quizzes Additional Practice Learning is a treasure that will follow its owner everywhere. ~Chinese Proverb How lucky we are, as educators, to have the opportunity to instill the love of learning for every student! Margo Kinzer Courter, MBA, MA www.courtercommunications.com courtercx@gmail.com