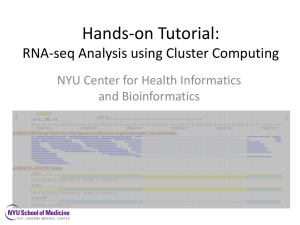
Supplementary Data Fig S1 MED25 gene and protein structure. A
advertisement

Supplementary Data Fig S1 MED25 gene and protein structure. A. MED25 gene’s evolutionary conservation, as presented by Evolutionary Conserved Regions (ECR) browser. Gene conservation is shown by pairwise alignments between human and 4 other representative species (from bottom: rhesus, mouse, rat and zebrafish). Sequence conservation of coding exons (blue) and introns (orange) as well as transposons and repeats (green) can be visualized. Layer height presents the percentage identity of sequence pairwise alignment. Pink lines above the region represent ECR conserved regions. The location of MED25 (Y39C) mutation in the first exon is shown via blue arrow. B. Comparative demonstration of the MED25 Pfam, SUPERFAMILY domains and LRSLL motif in human, rhesus, mouse, rat and zebrafish (from the bottom). Most of the domains are conserved in all 5 organisms. Table S1: MED25 Oligonucleotides Sequence Name Product Sequence Number 5' d FAM- pdCAAGpdCApdCpdUApdCpdCpdUGpdCpdUpdC- MED25 c. 116 A>G_P1 SS316498-01 MED25 c. 116 A>G_P2 SS316387-01 MED25 c. 116 A>G_F SS316328-09 5' d GCCAACCTGGGACCCTACTT 3' MED25 c. 116 A>G_R SS316328-10 5' d GTCGGAGTCAGGCAAGAAAC 3' BHQ-1 plus 3' 5' d CAL Flour Gold 540AAGpdCApdCpdUGpdCpdCpdUGpdCpdUpdC -BHQ-1 plus 3' List S1: genes that are located within the homozygotic area of chr19: 450000000550000000 (399 genes, hg19): ACPT, AKT1S1, ALDH16A1, AP2A1, AP2S1, APOC1, APOC1P1, APOC2, APOC4, APOE, ASPDH, ATF5, BAX, BBC3, BCAM, BCAT2, BCL2L12, BCL3, BIRC8, BLOC1S3, BSPH1, C19orf41, C19orf48, C19orf63, C19orf73, C19orf75, C19orf76, C5AR1, CA11, CABP5, CACNG6, CACNG7, CACNG8, CALM3, CARD8, CBLC, CCDC114, CCDC155, CCDC61, CCDC8, CCDC9, CD33, CD37, CD3EAP, CDC42EP5, CEACAM16, CEACAM18, CEACAM19, CEACAM20, CGB, CGB1, CGB2, CGB5, CGB7, CGB8, CKM, CLDND2, CLEC11A, CLPTM1, CNOT3, CPT1C, CRX, CTU1, CYTH2, DACT3, DBP, DHDH, DHX34, DKFZp434J0226, DKKL1, DMPK, DMWD, DPRX, EHD2, ELSPBP1, EML2, EMP3, ERCC1, ERCC2, ETFB, EXOC3L2, FAM71E1, FAM83E, FBXO46, FCGRT, FGF21, FKRP, FLJ26850, FLJ40125, FLJ41856, FLT3LG, FOSB, FOXA3, FPR1, FPR2, FPR3, FTL, FUT1, FUT2, FUZ, GEMIN7, GIPR, GLTSCR1, GLTSCR2, GNG8, GPR32, GPR4, GPR77, GRIN2D, GRLF1, GRWD1, GYS1, HAS1, HIF3A, HRC, HSD17B14, IGFL1, IGFL2, IGFL3, IGFL4, IGLON5, IL4I1, IRF2BP1, IRF3, IZUMO1, JOSD2, KCNA7, KCNC3, KCNJ14, KDELR1, KLC3, KLK1, KLK10, KLK11, KLK12, KLK13, KLK14, KLK15, KLK2, KLK3, KLK4, KLK5, KLK6, KLK7, KLK8, KLK9, KLKP1, KPTN, LAIR1, LENG1, LENG8, LENG9, LHB, LIG1, LILRA3, LILRA4, LILRA5, LILRA6, LILRB2, LILRB3, LILRB5, LIM2, LIN7B, LMTK3, LOC147804, LOC284379, LRRC4B, MAMSTR, MARK4, MBOAT7, MED25, MEIS3, MIR125A, MIR150, MIR371, MIR372, MIR373, MIR498, MIR512-2, MIR516A1, MIR516A2, MIR516B1, MIR516B2, MIR517A, MIR517B, MIR517C, MIR518A1, MIR518A2, MIR518B, MIR518C, MIR518D, MIR518E, MIR518F, MIR519A1, MIR519A2, MIR519B, MIR519C, 1 MIR519D, MIR519E, MIR520A, MIR520B, MIR520C, MIR520D, MIR520E, MIR520F, MIR520G, MIR520H, MIR521-1, MIR521-2, MIR522, MIR523, MIR524, MIR525, MIR526A1, MIR526A2, MIR526B, MIR527, MIR642, MIR643, MIR769, MIR99B, MIRLET7E, MYADM, MYBPC2, MYH14, MYPOP, NANOS2, NAPA, NAPSA, NAPSB, NCRNA00085, NDUFA3, NKG7, NKPD1, NLRP12, NOSIP, NOVA2, NPAS1, NR1H2, NTF4, NTN5, NUCB1, NUP62, NUP62_ATF5, OLT-2, OPA3, OSCAR, PGLYRP1, PIH1D1, PLA2G4C, PLEKHA4, PNKP, PNMAL1, PNMAL2, POLD1, PPFIA3, PPP1R13L, PPP1R15A, PPP2R1A, PPP5C, PRKCG, PRKD2, PRMT1, PRPF31, PRR12, PRR24, PRRG2, PTGIR, PTH2, PTOV1, PVR, PVRL2, QPCTL, RASIP1, RCN3, RELB, RPL18, RPS11, RPS9, RRAS, RSHL1, RTN2, RUVBL2, SAE1, SCAF1, SEC1, SEPW1, SFRS16, SHANK1, SIGLEC10, SIGLEC11, SIGLEC12, SIGLEC14, SIGLEC16, SIGLEC5, SIGLEC6, SIGLEC7, SIGLEC8, SIGLEC9, SIGLECP3, SIX5, SLC17A7, SLC1A5, SLC6A16, SLC8A2, SNAR-C3, SNAR-C4, SNAR-D, SNAR-E, SNAR-F, SNAR-G1, SNAR-G2, SNORD23, SNORD32A, SNORD33, SNORD34, SNORD35A, SNORD35B, SNORD88A, SNORD88B, SNORD88C, SNRNP70, SNRPD2, SPACA4, SPHK2, SPIB, STRN4, SULT2A1, SULT2B1, SYMPK, SYNGR4, SYT3, TBC1D17, TEAD2, TFPT, TMC4, TMEM143, TMEM160, TOMM40, TPRX1, TRAPPC6A, TRPM4, TSEN34, TSKS, TTYH1, TULP2, VASP, VN1R2, VN1R4, VRK3, VSIG10L, VSTM1, ZC3H4, ZNF114, ZNF137, ZNF160, ZNF175, ZNF180, ZNF28, ZNF296, ZNF320, ZNF321, ZNF331, ZNF347, ZNF350, ZNF415, ZNF432, ZNF468, ZNF473, ZNF480, ZNF525, ZNF528, ZNF534, ZNF541, ZNF577, ZNF578, ZNF600, ZNF610, ZNF611, ZNF613, ZNF614, ZNF615, ZNF616, ZNF649, ZNF665, ZNF677, ZNF701, ZNF702P, ZNF761, ZNF765, ZNF766, ZNF808, ZNF813, ZNF816A, ZNF83, ZNF836, ZNF841, ZNF845, ZNF880. *The homozygotic genomic area (chr19: 450000000-550000000) in the families contains 2600 targeted regions (787Kbp sequenced in total) in 399 genes (based on the coordinates of Trusec enrichment kit). The average coverage of regions per sample was >100x. 2 Table S2. List of candidate variants that are located within the homozygotic area of chr19: 450000000-550000000 (399 genes, hg19): Gene Position (hg19) REF ALT Protein change rs# Family Segregation Allele count, Homozygote count in ExAC database1 NPAS1 chr19:47544375 C T p.(Arg212Cys) . doesn’t follow 3,0 DHDH chr19:49442849 TGGGGGGG TGGGGGGGG p.(Ala173Glyfs) rs3830420 not checked 25794, 3607 TRPM4 chr19:49686146 G A p.(Trp171*) rs71352737 not checked 151,2 MED25 chr19:50321714 A G p.(Tyr39Cys) . Follows 0,0 MYH14 chr19:50735262 G A p.(Arg342Gln) . Follows 11,0 SIGLEC8 chr19:51961605 C G p.(Gly13Arg) rs142744819 not checked 21,1 SIGLEC12 chr19:52000150 C T p.(Arg528Lys) rs114249698 not checked 14,0 ZNF880 chr19:52887145 TAAAAA TAAAA p.(Asn106Ilefs) rs34470614 not checked 17984 ,3620 ZNF525 chr19:53884101 T C p.(Ile54Thr) . doesn’t follow 1,0 LOC284379 chr19:54103610 G A p.(Thr131Ile) . doesn’t follow Gene Not Available LILRB3 chr19:54726237 C G p.(Glu90Gln) rs138323850 not checked 608,98 LILRA6 chr19:54742965 G A p.(Ala420Val) rs148424804 not checked 15,0 Remarks also listed as pseudo also listed as pseudo leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor, homozygote LoF count in the gene=1 Table S2: The 12 variants that were found in the homozygotic region in the family. The top five candidates were examined for disease segregation in the family (see more information in the main text). The ExAC database spans 60,706 unrelated individuals sequenced as part of various disease-specific and population genetic studies and therefore is highly useful to estimate the abundance of alleles in the population. 1 Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC), Cambridge, MA (URL: http://exac.broadinstitute.org) [date (February, 2015) accessed]. 3