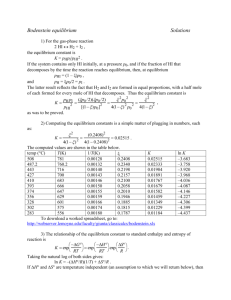
+ H 2 O (g)
advertisement

Name:___________________ CP Acids and Equilibrium Review Date:________________ 1. Using collision theory, explain how the following affect the rate of a reaction. Surface Area Concentration Temperature 2. Using the information below, determine [H+] and [OH][H+] I. [OH-] pH of 3.29 II. pOH of 7.87 III. pOH of 10.07 IV. pH of 4.39 3. With the given the concentration, find the pH and pOH I. A solution with an H+ concentration of 0.0252 mol/L pH: pOH: II. A solution with an H+ concentration of 5.4x10-4 mol/L pH: pOH: III. A solution with an OH- concentration of 0.086 mol/L pH: pOH: 4. Describe what the term equilibrium means in a chemical reaction. Describe a real life situation involving the concept of equilibrium. 5. Write the equilibrium expression for the following: 2H2(g) + O2(g) ⇄ 2H2O(g) 2NO(g) + Br2(g) ⇄ 2NOBr(g) FeO(s) + CO(g) ⇄ Fe(s) + CO2(g) 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) ⇄ N2(g) + 2H2O(l) 2C2H6(g) + 7O2(g) ⇄ 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(g) FeO(s) + CO(g) ⇄ Fe(s) + CO2(g) 6. Initial concentrations of H2(g) and Cl2 (g) in a flask were 0.576 mol/L The mixture was allowed to reach equilibrium at 45°C. The equilibrium concentration of HCl(g) was found to be 0.356 mol/L Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of the reactants ___H2(g) + __Cl2(g) ⇄ __HCl(g) 7. Initially 0.463 mol of HI(g) is placed in a 1.50 L reaction vessel. The temperature is raised to 300°C and maintained until equilibrium is established. At equilibrium, the vessel contains 0.119mol of hydrogen gas and 0.119 mol iodine gas. Calculate Keq for the reaction. Are the products or reactants favored? ___HI(g) ⇄ __H2(g) + __I2(g) 8. What would happen to the position of the equilibrium if the following were to occur? A) Reaction: CH4 (g) + H2O (g) ↔ CO(g) + 3H2 (g) H = 206.5 KJ Temperature is increased CO is removed CH4 is added Volume is decreased Pressure is decreased H2 is added B) CS2(g) + 4H2(g) ↔ CH4(g) + 2H2S(g) ∆ H= -21.3 kJ Temperature is increased CH4 is removed Pressure is increased Volume is decreased H2 is added H2S is added 9. What is the pH of a solution of 0.004M HNO3? 10. Find the pH of a 0.62 M solution of propanoic acid, HC3H4O2, ( Ka= 1.32x10-5) 11. It takes 38 mL of 0.75 M NaOH solution to completely neutralize 155 mL of a sulfuric acid solution (H2SO4). What is the concentration of the H2SO4 solution? 12. 30.0 mL of 0.500 M hydrobromic acid is added to 38.0 mL of strontium hydroxide of unknown concentration. What is the concentration off the base? Use this space for any scratch work, notes, or equations used to help you solve acid and/or equilibrium problems.