File
Unit One EOC Review
1.
What is an organic molecule? Molecule that contains carbon and is important to life
2.
Complete the chart for the following organic molecules:
Organic
Molecule
Subunit/Building
Block/Monomer
Function Examples
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Monosaccharide
Fatty acid
Amino acid
Short term energy
Glucose, cellulose, starch, glycogen
Long term energy, plasma membrane structure, water proof covering
Support, structure, storage, transport
Phospholipids, steroid
Enzyme, hemoglobin, insulin
Nucleic Acids Nucleotide Heredity, protein synthesis DNA, RNA
3.
Classify the following molecules into one of the four main macromolecules: a.
Starch ____C______ g.
Hemoglobin__________P__________ b.
Cellulose ____C__________________ c.
Insulin_______P_________________ h.
i.
Steroids_________L_____________
Phospholipids____L_______________ d.
Glycogen_____C_________________ e.
Glucose_____C__________________ f.
Enzymes_____P_________________ j.
k.
l.
Fats_________L________________
DNA_________N________________
RNA___________N______________
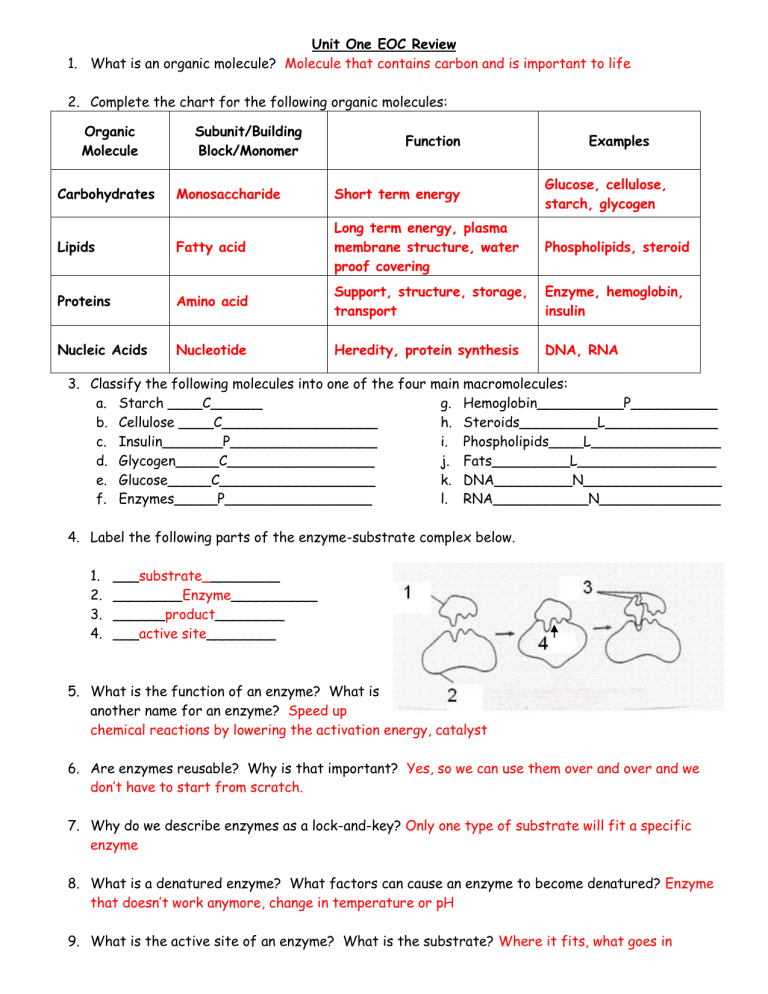
4.
Label the following parts of the enzyme-substrate complex below.
1.
___ substrate_ ________
2.
________ Enzyme __________
3.
______ product ________
4.
___ active site ________
5.
What is the function of an enzyme? What is another name for an enzyme? Speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy, catalyst
6.
Are enzymes reusable? Why is that important? Yes, so we can use them over and over and we don’t have to start from scratch.
7.
Why do we describe enzymes as a lock-and-key? Only one type of substrate will fit a specific enzyme
8.
What is a denatured enzyme? What factors can cause an enzyme to become denatured? Enzyme that doesn’t work anymore, change in temperature or pH
9.
What is the active site of an enzyme? What is the substrate? Where it fits, what goes in
10.
What can be the result of a missing or defective enzyme? The reaction will not occur
11.
Do enzymes raise or lower the activation energy? lower
12.
Check which are examples or are related to these biological molecules:
Carbohydrate
Lipid
Insulin Glucose
X
Cellulose
X
DNA Hemoglobin Steroids
X
Starch
X
Enzymes
Protein
Nucleic Acid
X
X
X X
Glycogen RNA phospholipids
Carbohydrate
Lipid
Protein
Nucleic Acid
X
X
X
Hexagon shape
X
Amino
Acids
X
Protein synthesis
X
Denature Cell membranes
X
X
Quick
Energy
X a.
Carbohydrates
1.
What is the function of glucose?______
simple sugar, energy_________________
2.
What is the function of cellulose and where is it found?__
structure, cell wall of plants
3.
What is glycogen?___
energy source in animals ___________________________ b.
Proteins
1.
What is the function of insulin?_____
regulates blood sugar ________________
2.
What is the function of enzymes?____
speed up reactions ____________
3.
What is the function of hemoglobin and where is it found _ carries oxygen in blood _ c.
Lipids
1.
What is the function of phospholipids/where are they found?_
structure in plasma membrane
2.
Why are steroids important to our bodies? _ provide communication in our body ___ d.
Nucleic Acids
1.
What is the function/purpose of DNA?___
genetic material ________
2.
What is the function/purpose of RNA?_____
help to make proteins _________
13. Explain how/why enzymes are specific. Will the enzymes that break down a cracker break down meat? They are specific and because they only fit one reaction and no it would not work on meat.
14. Please use this word bank to answer the next questions: all, lower, pH, re-usable, speed up, temperature, catalysts, specific
a. Enzymes are proteins that ___ speed up ___ chemical reactions. Because of this, enzymes are called ____ catalyst _______.
b. Enzymes __ lower_ ____ the activation energy of a reaction.
c. Enzymes are ___ specific ____ and ____ reusable ______.
d. Enzymes are affected by factors such as __ temperture __ and_____ pH _________.
e. Enzymes are necessary for ___ all ___ biochemical reactions!