Thermochemistry and Rates Review Test
advertisement

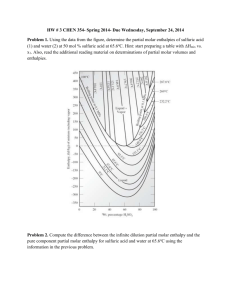
SCH 4UI – Thermochemistry and Rates of Reaction Unit Review Test Name: _______________________________________ A. Date: ____________________________________ Multiple Choice 1. A chemical system in which both energy and matter can flow into or out of a system is described as a. a closed system d. a chemical system b. an open system e. none of the above c. an isolated system 2. a. b. c. d. e. Which of the following is not a form of kinetic energy in a chemical system? moving electrons within an atom the vibration of atoms connected by chemical bonds the rotation of molecules that make up the chemical system the translation of molecules within the chemical system the energy of protons and neutrons in atomic nuclei 3. The molar heat of vaporization of water is 42 kJ/mol. How much energy is released by the condensation of 3.0 g of water? a. 0.88 kJ d. 250 kJ b. 7.0 kJ e. 0.07 kJ c. 130 kJ 4. Which statement concerning the accompanying diagram is true? a. b. c. d. e. H is positive the system is endothermic the system releases heat to the surroundings the heat content of the reactants is less than the heat content of the products the enthalpy of the products is greater than the enthalpy of reactants 5. a. b. c. d. e. A rate of reaction is usually obtained by measuring the rate at which products are consumed the rate at which reactants are produced the rate at which reactants are consumed the temperature of the solution the mass and volume of the products 6. In the reaction, , if the concentration changes from 0.45 mol/L to 1.00 mol/L in 2 minutes, what is the overall rate of production of nitrogen dioxide in the system? a. 3.64 mol/(L·min) d. 12.6 mol/(L·min) b. 0.275 mol/(L·min) e. 0.333 mol/(L·min) c. 0.137 mol/(L·min) 7. a. b. c. d. e. The presence of a catalyst is thought to increase the rate of a reaction by changing the products that are formed in the reaction decreasing the enthalpy change of the reaction increasing the enthalpy change of the reaction decreasing the activation energy of the reaction increasing the activation energy of the reaction 8. The activated complex a. is an unstable molecule b. has the maximum potential energy possible c. may continue on to produce products d. e. may revert to reactants all of the above B. Short Answer 1. What are two rules that can be applied to chemical equations and enthalpy changes when using Hess's Law? 2. 3. 4. Why is a certain amount of energy required within an effective collision? C. Problems 1. Consider the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide reaction. If the rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide at a particular temperature is determined to be 0.098 mol/(L·s), what are the rates of reaction with respect to the products of the decomposition reaction? 2. Pyruvic acid is a molecule involved as an intermediate in metabolic reactions such as cellular respiration. Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is converted into acetic acid and carbon monoxide in the reaction: What is meant by the activation energy of the reaction? If the reaction of H2 and O2 to produce water vapour releases 285.4 kJ of energy to the surroundings; write four different methods that can be used to communicate this information. CH3COCOOH CH3COOH + CO If the molar enthalpies of combustion of these substances are, respectively –1275 kJ/mol, 875 kJ/mol, and 282.7 kJ/mol, use Hess’s law to calculate the enthalpy of change for the given reaction. 3. Given the following elementary steps determine the rate law and the overall reaction equation? 2B E A + E F + C A + F D Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 (slow) (fast) (fast) If the initial concentration of is [A] = 2.0 M, and [B] = 4.0 M and the rate of the reaction was 1.5 M/s, determine the specific rate constant for the above reaction. (1 mark) 4. 5. Use the following data to calculate the reaction rate law for the system (be sure to solve for k) Experiment NO (mol/L) H2 (mol/L) Initial Rate of Reaction (mol/(L·s)) 1 2 3 4 5 6 0.001 0.002 0.003 0.004 0.004 0.004 0.004 0.004 0.004 0.001 0.002 0.003 0.002 0.008 0.018 0.008 0.016 0.024 Calculate Ho for the following reaction. C6H6(l) + O2 (g) C(s) + H2O(l) State whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic.