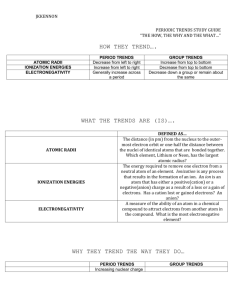
Periodic Trends
Quiz 7
Name__________________________________
1. Electronegativity is
A. how strongly an atom pulls electrons to itself when it is bonded to other atoms
B. how much energy is needed to take an electron away from an atom
C. how large an atom is
D. the total negative charge of the electrons in an atom
2. Ionization energy (or ionization potential) is
A. how strongly an atom pulls electrons to itself when it is bonded to other atoms
B. how much energy is needed to take an electron away from an atom
C. how large an atom is
D. the energy needed to add an electron to an atom
3. Which of the following elements has the largest atomic radius?
A. carbon (C) B. silicon (Si) C. germanium (Ge) D. tin (Sn)
4. Which of the following elements has the largest atomic radius?
A. nitrogen B. oxygen C. fluorine D. neon
5. Which has the largest atomic radius?
A. K
B. K+ C. Rb
D. Rb+
6. Which has the largest atomic radius?
A. fluorine
B. chlorine
C. bromine
D. a bromine anion with a charge of 1-
7. Which has the lowest ionization energy?
A. beryllium (Be) B. strontium (Sr) C. calcium (Ca)
D. magnesium (Mg)
8. Which has the highest ionization energy?
A. phosphorus B. sulfur C. chlorine
D. argon
9. Overall, the group with the lowest ionization energy on the periodic table is the
A. the noble gases (group 18) B. the halogens (group 17)
C. alkali metals (group 1)
D. alkaline earth metals (group 2)
10. Which has the highest electronegativity?
A. Na B. Al C. S D. Cl
11. Which has the lowest electronegativity?
A. F
B. I
C. Br
D. Cl
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
12. As you go from left to right across the periodic table, what happens to the shielding
effect, which happens because the inner levels of electrons block the pulling force of the
positive protons on the outer electrons?
A. The shielding effect increases. B The shielding effect decreases. C. The shielding effect
stays the same
13. What charge will oxygen have after it has gained a full set of valence electrons (in its
outer energy level)?
A. 8 B. 16 C. -2 D. +2 E. none of the above
14. Which element will react most quickly with chlorine? A. Na B. Mg
15. Which element is most reactive? A. Li
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
B. Rb
C. K
C. Al
D. Na
D. Si
Periodic Trends Awesomeness
Name___________________________________________
1. Define atomic radius.
2. What is the trend for atomic radius as you go from left to right in period?
3. Explain the reason for your answer to number 2 above.
In other words, why does it change this way as you go from left to right?
4. What is the trend in atomic radius as you go from top to bottom in a group.
It increases.
5. Explain the reason for your answer to number 4 above.
In other words, why does it change the way you said as you go from top to bottom?
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
6. Which atom on the whole periodic table would require the most energy to take its electron?
(Hint: It also has the smallest atomic radius.)
7. Why is the periodic table called the periodic table? (Think about your graphing activity.)
8. Why do the halogens (group 17) react quickly and easily with the alkali metals (group 1) to
form salts?
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
Periodic Trends
Quiz 7
Name____________________________________
1. Electronegativity is
A. how strongly an atom pulls electrons to itself when it is bonded to other atoms
B. how much energy is needed to take an electron away from an atom
C. how large an atom is
D. the total negative charge of the electrons in an atom
2. Ionization energy (or ionization potential) is
A. how strongly an atom pulls electrons to itself when it is bonded to other atoms
B. how much energy is needed to take an electron away from an atom
C. how large an atom is
D. the energy needed to add an electron to an atom
3. Which of the following elements has the largest atomic radius?
A. carbon (C) B. silicon (Si) C. germanium (Ge) D. tin (Sn)
4. Which of the following elements has the largest atomic radius?
A. nitrogen B. oxygen C. fluorine D. neon
5. Which has the largest atomic radius?
A. K
B. K+
C. Rb
D. Rb+
6. Which has the largest atomic radius?
A. fluorine
B. chlorine
C. bromine
D. a bromine anion with a charge of 1-
7. Which has the lowest ionization energy?
A. beryllium (Be) B. strontium (Sr) C. calcium (Ca)
D. magnesium (Mg)
8. Which has the highest ionization energy?
A. phosphorus B. sulfur C. chlorine
D. argon
9. Overall, the group with the lowest ionization energy on the periodic table is the
A. the noble gases (group 18) B. the halogens (group 17)
C. alkali metals (group 1)
D. alkaline earth metals (group 2)
10. Which has the highest electronegativity?
A. Na B. Al C. S D. Cl
11. Which has the lowest electronegativity?
A. F
B. I
C. Br
D. Cl
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
12. As you go from left to right across the periodic table, what happens to the shielding
effect, which happens because the inner levels of electrons block the pulling force of the
positive protons on the outer electrons?
A. The shielding effect increases. B The shielding effect decreases. C. The shielding effect
stays the same.
13. What charge will oxygen have after it has gained a full set of valence electrons (in its
outer energy level)?
A. 8 B. 16 C. -2 D. +2 E. none of the above
14. Which element will react most quickly with chlorine? A. Na B. Mg
C. Al
D. Si
15. Which element is most reactive? A. Li
B. Rb
C. K
D. Na
Quiz 7 Short answer
Name___________________________________________
1. Define atomic radius.
Size of the atom from center of nucleus to outer edge of electron cloud
2. What is the trend for atomic radius as you go from left to right in period?
Atomic radius decreases. The atoms get smaller.
3. Explain the reason for your answer to number 2 above.
In other words, why does it change this way as you go from left to right?
Protons are being added as you move across but no more orbital “rings”or energy level of
electrons are being added. Therefore, the pulling power of the positive nucleus on the
negative electrons increases because there are no more inner rings of electrons have been
added to shield or block that power of attraction.
4. What is the trend in atomic radius as you go from top to bottom in a group.
It increases.
5. Explain the reason for your answer to number 4 above.
In other words, why does it change the way you said as you go from top to bottom?
You are adding more energy levels of electrons which are further away from the nucleus.
6. Which atom on the whole periodic table would require the most energy to take its electron?
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
(Hint: It also has the smallest atomic radius.)
Helium furthest to the right and at the top of its column
7. Why is the periodic table called the periodic table? (Think about your graphing activity.)
The properties we studied seem to repeat in a regular, predictable pattern.
Things that happen in a regular, predictable pattern are called periodic.
With each new row (or period) of the table, the pattern repeats (almost like the days of
each week).
8. Why do the halogens (group 17) react quickly and easily with the alkali metals (group 1) to
form salts?
The halogens need one electron to have 8 in their outer shell (stable noble gas configuration)
and the alkali metals need to lose one to have full outermost energy levels.
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org