DNA Day Project
advertisement

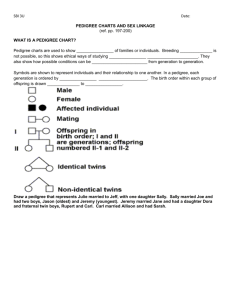
The Role of Genetics in Addiction Methamphetamine 1.) 2.) 3.) Parts of brain affected by methamphetamines: - Occipital Lobe (Vision) - Cerebellum (coordination) - Parietal Lobe (sensation) - Frontal Lobe (Movement, Judgement, Memory, Reward Pathway) I could not find any chromosomes linked to addiction to methamphetamine. General Information on Meth: Meth is made from just any typical everyday home ingredients. Some common meth ingredients are very common, but very flammable and dangerous, such as: - Methanol - Methylene Chloride - Ether - Trichloroe Thane - Benzene - Toluene - Muriatic Acid - Sodium Hydroxide - Table Salt - Ammonia Effects on the body: Meth doesn’t have many short-term effects, but it does have long term effects such as: - Violent and psychotic behavior - Hallucinations - Delusions and paranoia - Suicidal and Homicidal thoughts Meth is a very addicting drug because when someone is high off of the drug, they get a great pleasurable feeling. When the person is no longer high, the person quickly gets depressed, has anxiety and gets very irritable. When the person gets to feeling this way, they feel like they should take the drug again so they can get the good high feeling they had when they were on the drug. Meth is also known as crank, crystal, Ice and speed. Meth can be taken by shots, orally or snorting. http://alcoholism.about.com/od/meth/a/effects.-Lx6.htm Alcohol 1.) Parts of the brain effected: - Striatum - Frontal Lobe (movement, intelligence, reasoning, behavior, memory, personality) - Hippocampus - Medulla - Reticular Activating System - Cerebellum (Balance, Coordination, Fine Muscle Control) 2.) Chromosomes containing genes linked to addiction: - 2, 3, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 13 3.) General Info: Taken by drinking. long term: - Stretching of muscles - Heart problems - High blood pressure - Stroke - Steatosis of the liver - Alcoholic Hepatitis - Fibrosis - Cirrhosis Short term: - Causes loss of motor coordination - Impairs reasoning - Balance - Speech - Reaction - Time - Judgment http://niaaa.nih.gov/alcohol-health/alcohols-effects-body Marijuana 1.) Parts of the brain affected: Hippocampus (Memory) Cerebal Cortex (concentration) Sensory portions of the Cerebal Cortex (concentration) Cerebellum, substania nigra, and globus palidis (movement) 2.) Chromosomes containing genes linked to addiction: - Chromosomes 4 and 11 3.) General Info Chemical Makeup: - Chemicals from Marijuana are stored in fat cells for a long time. - THC is one of the most known “ingredients” in marijuana. THC stands for Tetrohydrocannabinol) - THC passes into the blood stream from the lungs, then to the brain and other organs. Cannabis has been directly linked to miscarriage. Marijuana can be smoked, or baked into foods like cookies or brownies, it can also be made into tea. Short term effects: - Difficulty thinking properly - Problems with memory and understanding information - Distorted knowledge or perception - Coordination that is not good Long term effects: - Change in how the brian acts - Fertility problems- women have problems during ovulation and males have problems making sperm. - Respiratory problems - Blood pressure problems - Depression/ anxiety, or emotional problems https://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/mari.html http:// kidshealth.org/teen/drug-alcohol/drugs/marijuana.html http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/addiction/ritalin Pedigree investigator: The pedigree investigator was on the Marshall Family where some of the family members were addicted to nicotine, and had been for most of their lives. The program starts off by interviewing the oldest alive member of the family Wally Marshall. Wally is 80 years old, never done tobacco before. He takes prescription medicine for High Blood Pressure Problems and for Arthritis. Since Wally doesn’t use any tobacco products, he went on the pedigree as an unaffected male. The next person is Wally’s wife Trudy. Trudy was 70 years old when she died. She smoked cigarettes since she was in her teens. She smoked almost two packs a day. When she tried to quit she got very nervous and had withdrawals. She was put on an oxygen tank and that was when she quit smoking. She took medicine for asthma. She went on the pedigree as a deceased affected female. The next person is Ken, Trudy and Wally’s son Ken. He died at age 55 from metastic nonsmall cell lung cancer from smoking cigarettes. He went on the pedigree as a deceased affected male. Now to be interviewed is Elizabeth, Ken’s widow. She is 53 years old, and does not smoke cigarettes. She takes medication for arthritis. She went on the pedigree as an unaffected female. Their daughter Allison is 32 years old, does not smoke cigarettes and takes prescription medicine for asthma. She went on the pedigree as an unaffected female. Their twin sons Todd and Alex are 31 and smoke cigarettes. Todd smokes a pack a day and Alex smokes about half a pack a day. They are both trying to get off with nicotine gum. Both took Ritalin around the ages of 11-12 for ADHD. They went on the pedigree as special affected males because they both smoke cigarettes and took Ritalin as kids, which is a risk factor. Their daughter Jennifer is 28 years old, and doesn’t smoke cigarettes. She went on the pedigree as an unaffected female. Her sister Joy smokes cigarettes, 2 or more packs a day and started around age thirteen. Might be on antidepressants. She went on the pedigree as a Asterisk because her sister says she is engaged in risky behavior, and she smokes and might take anti depressants. Next is Wally and Trudy’s daughter Vanessa, and her little family. Vanessa is 45 years old, smokes cigarettes, but only two a day, She used to smoke two packs a day. She started in highschool and takes medicine for high cholesterol. She went on the pedigree as an effected female. Her husband Jason is 48 years old, and smokes cigarettes. He is currently in the hospital recovering from bypass surgery. He went on the pedigree as an effected male. Their son Michael is 22 years old and doesn’t smoke. He went on the pedigree as an unaffected male. Their daughter Tina is 20 years old and smokes a lot. She went on the pedigree as an unaffected female. Wally and Trudy’s son Victor is 54 and does not smoke cigarettes. He went on the pedigree as an unaffected male. Lily, his wife, is 42 and does not smoke cigarettes because she has a past of lung cancer in her family. Their son Brian is 20 years old and doesn’t smoke cigarettes. He went on the pedigree as an unaffected male. Brian’s brother Peter is 20 and doesn’t smoke. He also went on the pedigree as an unaffected male. Next is Wally and Trudy’s son James. He smokes about 2 packs a day and takes antidepressants. He went on the pedigree as an affected male. His wife Linda is 35 years old and doesn’t smoke. She went on the pedigree as an unaffected female. Their daughter Tess is 16 years old, smokes cigarettes (about a pack a day). She went on the pedigree as a special affected female because her friends are a risk for her trying new things. Why are adolescents who take Ritalin more prone to cocaine addiction as adults? Ritalin and cocaine are very alike in many ways such as how they act in the body. They both increase alertness and productivity. So as an adult, they get taken off of Ritalin. If they tried cocaine one time, they would see that it gave them the same calming affect that Ritalin did, and then they would be hooked. Mouse Party: Methamphetamine: Dopamine transporters get confused by meth. Meth goes in the transporters and make them work backwards. Meth goes into dopamine cells, forcing the dopamine molecules out, then the transporters pump dopamine into the synapse, which causes the cell to over work itself. Alcohol: GABA receptors are inhibitory nuerotranmitters that work in the brain and stay active. When alchol enters the brain, it messes with the GABA receptors, making them even more inhibitory. Then it attaches to glutamate receptors, refusing the glutamate to get inside of the cells. Marijuana: Nuerotransmitters are active in the synapse letting dopamine be released in the brain. When activated by the body’s cannabanoid, cannabanoid receptors turn off the release of inhibitory receptors, letting dopamine be released. THC mimics anandamide and binds to cannaboid receptors causing dopamine to be released into the synapse again. Meth Mouse: