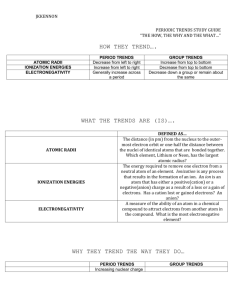
Study guide for periodic table trends. A. By referring to electron
advertisement

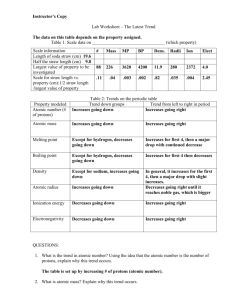
Study guide for periodic table trends. 1. A. By referring to electron arrangements and using information from Table 8 of the Data booklet, explain the difference in radius for each of the following pairs: (i) Na and Na+ Na=2,8,1 > Na+= 2,8 Na+ because only 2 energy levels and the outer level is full so greater nuclear charge (ii) Na+ and F- Na+= 11P and 10e so great nuclear charge so smaller radius< F- 9p and 10e so less charge attractions same number of electrons. B. By referring to atomic structure and using information from table 6 of the data booklet, explain the difference in melting point for each of the following pairs: (i) Na and Mg Mg> na more protons so greater attractions Mg 2+ more delocalized electrons than Na+ so has greater nuclear charge (ii) F2 and Cl2 Cl>F because more electrons and greater intermolecular van der waal’s forces 2. (a) State and explain the term electronegativity. The ability of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons. (b). state and explain the trend in electronegativity across period 3 from Na to Cl. Electronegativity increases from Na to Cl because the number of protons increases so nuclear charge increases so that the electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus and size of atoms decrease (c ) explain why Cl2 rather than Br2 would react more vigorously with the solution of I- Cl2 is a stronger oxidizing agent because it is on a lower energy level so that its valence electrons are closer to the nucleus so that is an increase in nuclear charge. It has a greater attraction for electrons so has a higher electron affinity. 3. Define the following terms (i) Atomic number: number of protons in the nucleus (ii) Mass number: number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus 4. Explain the following statements. The first ionization energy of sodium is (i) Less than that of magnesium. (ii) Greater than that of potassium b. The electronegativity of chlorine is higher than that of sulfur. 5. (a) nitrogen is found in period 2 and group 5 of the periodic table. (i) distinguish between the terms period and group : period is a horizontal row and all elements on this horizontal row have the same number of energy levels, where group is the vertical column and all these elements have the same number of valence electrons. (ii) state the electron arrangement of nitrogen and explain why it is found in period 2 and group 5 of the periodic table 2,5 electrons are found in 2 energy levels which is meaning fro period two and have 5 valence electrons which is why in group 5 (b) Table 8 of the data booklet gives the atomic and ionic radii of elements. State and explain the difference between (i) the atomic radius of nitrogen and oxygen atomic radius of nitrogen > oxygen because oxygen has a greater nuclear charge so has greater attraction for the outer electrons (ii) tha atomic radius of nitrogen and phosphorus: atomic radius of P> N because P has outer electrrons in an energy level further from the nucleus so more nuclear shielding (iii) The atomic and ionic radius of nitrogen 6. Explain the following statements: A. The first ionization energy of sodium is (I) Less that magnesium: Na has lower nuclear charge because of the number of protons so will have a larger atomic radius because electrons are further from nucleus (II) Greater than potassium: Na is on a fewer energy levels and so electrons are closer to the nucleus on a lower energy level than K which has a greater shielding effect because on higher energy level and more electrons. B. the electronegativity of chlorine is higher than that of sulfur. Chlorine is more electronegative than sulfur because it has a higher nuclear charge, it attracts the electron pair. 7. Table 6 of the Data booklet lists melting points of the elements. Explain the trend in the melting points of the alkali metals, halogens and period 3 elements. Alkali metals: metallic bonding is a bed of cations in a sea of electrons and as radius increases down the group , valence electrons are further away from nucleus due to nuclear shielding so strength of metallic bonding decreases Halogens: non-polar so held together by van der waal’s forces between molecules as size increases van der waals forces increases and so will melting point. Period 3 elements: increase in melting points of na , Mg and Al due to increase in number of valence electrons and a decrease in size due to nuclear charge Silicon: network covalent solid with very high melting point Phosphorus to Argon simple molecular substances with weak van der waal’s forces and lower melting points because of decreasing mass or size (b) (i) explain how the first ionization energy of k compares with that of Na and Ar. K is less than Na because electron removed from K is from higher energy level so further from nucleus so will have less nuclear charge and greater nuclear shielding . K is less than Ar because is from higher energy level the electrons are further from the nucleus so greater shielding effect and smaller nuclear charge (iii) explain the difference between the first ionization energies of Na and Mg. Mg has greater nuclear charge because has one more proton on same energy level so greater pull and smaller atomic radius so more strongly attract to nucleus (iv) Suggest why more energy is needed to remove an electron from Na+ than from Mg+. Na +1 is more stable because outer energy level is full so much pull from lower energy level, n=2 whereas taking one electron from Mg leaves behind one more electron in n=3. 8. Explain why (i) The first ionization energy of magnesium is lower than that of fluorine? Electron removed from higher energy level so valence electrons are further from the nucleus which means a greater atomic radius so there is an increase shielding effect (ii) Magnesium has a higher melting point than sodium? Mg has twice as many delocalized electrons in outer energy level (2 not 1) so the ionic charge is twice as big Mg2+ to Na+ so electrostatic attraction between ions and electrons is greater. 9. Which is related to the number of electrons in the outer main level of the elements form the alkali metals to the halogens? I. 10. a. b. c. d. 11. I. a. b. c. d. GROUP NUMBER II. PERIOD NUMBER A. I only B. II only C. Both I and II D. Neither I nor II. Which pair of elements reacts more readily? Li + Br2 Li + Cl2 K + Br2 K +Cl2 Which of the following properties of the halogens increase from F to I? ATOMIC RADUIS II. MELTING POINT III. ELECTRONEGATIVITY A. I ONLY B. I AND II ONLY C. I AND III ONLY D. I, II AND III 12. Element X is in group 2 and element Y is in group 7, of the periodic table. Which ions will be present in the compound formed when X and Y react together? a. X+ and Yb. X2+ and Y – c. X + and Y 2d. X2- and Y + 13. For which element are the group number and the period number the same? a. Li b. Be c. B d. Mg 14. Which of the physical properties below decrease with increasing atomic number for both the alkali metals and the halogens? I. ATOMIC RADIUS II. IONIZATION ENERGY II. MELTING POINT I only II only III only I and III only 15. Rubidium is an element in the same group of the periodic table as lithium and sodium. It is likely to be a metal which has a a. High melting point and reacts slowly with water. b. High melting point and reacts vigorously with water. c. Low melting point and reacts vigorously with water. d. Low melting point and reacts slowly with water. 16. When the following species are arranged in order of increasing radius, what is the correct order? a. Cl-, Ar, K+ b. K+, Ar, Clc. Cl-, K+, Ar d. Ar, Cl- K+ 17. a. b. c. d. 18. a. b. c. d. 19. I. II. a. b. c. d. a. b. c. d. What increases in equal steps of one from left to right in the periodic table for the elements lithium to neon? The number of occupied electron energy levels The number of neutrons in the most common isotope The number of electrons in the atom The atomic mass Which two elements react most vigorously with each other Chlorine and lithium Chlorine and potassium Iodine and lithium Iodine and potassium Which factors lead to an element having a low value of first ionization energy? Large atomic radius III high nuclear charge High number of occupied energy levels a. I and II only b. I and III only c. II and III only d. I , II and III 20. Which statement about electronegativity is correct? a. Electronegativity decreases across the period b. Electronegativity increases down the group c. Metals generally have lower electronegativity values than nonmetals. d. Noble gases have the highest electronegativity values. 21. Which statement is correct for a periodic table? a. Ionization energy increases from Li to Cs. b. Melting point increases from Li to Cs. c. Ionization energy increases from F to I d. Melting point increases from F to I. 22. Which of the following statements are correct? I. The melting points decrease from LiCs for the alkali metals II. The melting points increase from FI for the halogens III. The melting points decrease from NaAr for the period 3 elements I and II only I and III only II and III only I, II and III 23. Which properties decrease in value when descending group I? I. Atomic radius II. Ionization energy III. Electronegativity I and II only I and III only II and III only I, II and III 24. The ionization energies of three consecutive elements in the periodic table are 1680, 2080 and 494 k? mol-1 respectively. Which of the following shows the elements with these values? a. O F Ne b. F Ne Na c. Ne Na Mg d. Na Mg Al 25. Analytical chemists can detect amounts of amino acids as small as 2.0 x 10 -21 mol of a substance. How many molecules does this represent? a. 2.0 x 10 -21 b. 1.2 x 103 c. 6.0 x 1023 d. 3.0 x 10 44 26. In what order are the elements listed in the periodic table? a. In order of relative atomic mass b. In order of reactivity c. In order of nuclear charge d. In order of electronegativity The graph shows the trend in a physical property down group 7 in the periodic table F 27. a. b. c. d. 28. a. b. c. d. 29. a. b. c. d. 30. a. b. c. d. 31. a. b. c. d. 32. Cl Br I What is the physical property? Atomic radius Electronegativity Density Melting point Which is the best definition of electronegativity? Electronegativity is the energy required for a gaseous atom to gain an electron. Electronegativity is the attraction of an atom for a bonding pair of electrons. Electronegativity is the attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons of an atom. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons from another atom. Which sample has the greatest mass? 6.0 x 1025 molecules of hydrogen 5.0 mol of neon atoms 1.2 x 1024 atoms of silver 1.7 x 102 grams of iron Which is the correct definition of the mass number of an atom? The total mass of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of the atom The total mass of neutrons, protons, and electrons in the atom The number of protons in the nucleus of the atom The total number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of the atom. Which statement describes the trends of electronegativity values in the periodic table? Values increase from left to right across a period and increase down a group. Values increase from left to right across a period and decrease down a group. Values decrease from left to right across a period and increase down a group. Values decrease from left to right across a period and decrease down a group. Which statement is correct for all elements in the same period? a. b. c. d. 33. (I) (II) (III) (IV) (V) They have the same number of electrons in the highest occupied energy level. They have the same chemical reactivity. They have the same number of occupied energy levels. They have the same number of neutrons. The graph o f the first ionization energy plotted against atomic number for the first twenty elements show periodicity Define the term first ionization energy and state what is meant by the term periodicity? The minimum energy to remove one electron from a gaseous atom. Or the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms and periodicity is the repeating pattern of physical and chemical properties State the electron arrangement of argon and explain why the noble gases, helium, neon and argon show the highest first ionization energies for their respective periods. 2,8,8 and the outer energy level is full and the increased nuclear charge so has greatest attraction for electrons. A graph of atomic radius plotted against atomic number shows that the atomic radius decreases across the period. Explain why chlorine has a smaller atomic radius than sodium. 17 protons in chlorine is greater than 11 protons in Na so Cl has a greater nuclear charge which will attract more outer electrons. Explain why a sulfide ion, S2- is larger than a chloride ion, Cl-.S2- has 16 protons and 18 electrons where Cl- has 17 protons and 18 electrons so S will be larger cause has 1 less proton and will have less nuclear charge than Cl so outer level electrons not held as strongly as Cl Explain why the melting point of the Group 1 metals(LiCs) decrease down a group whereas the melting points of the group 7 elements(fI) increase down the group. The radii of the metal atoms increase from Li to Cs so the forces of attraction are less between them. The forces of attraction between halogen molecules are van der waals forces increase with increasing mass and number of electrons.