AP Biology Name CH 10: Photosynthesis ANSWER ON A

AP Biology
CH 10: Photosynthesis
Name ____________________________
ANSWER ON A SEPARATE SHEET
1. Draw a diagram to summarize the activities of photosynthesis. . Include labels for all parts and molecules involved.
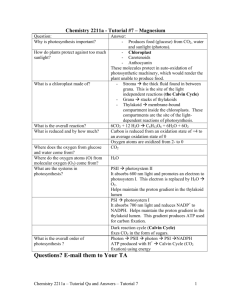
2. CO 2 and H 2 O are the reactants of photosynthesis. Where do the atoms of each compound end up?
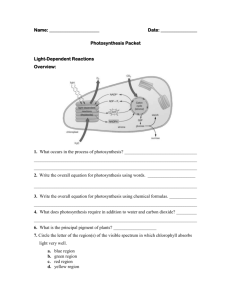
3. Describe the organization of a photosystem. How is photosystem I different from photosystem II ?
4. How does photosynthesis convert light energy into chemical energy? Explain what happens during cyclic and noncyclic electron flow; indicate the paths of electrons and any products that are made.
5. Compare and contrast chemiosmosis in mitochondria and chloroplasts.
6. Summarize what goes into the Calvin cycle and what comes out. Start with an input of 3 molecules of
CO 2 . How are the chemical products of the light-trapping reactions coupled to the synthesis of carbohydrates?
7. What is photorespiration?
8. Describe two (2) photosynthetic adaptations that have evolved in response to hot or dry adverse conditions. Indicate how they separate carbon fixation from the Calvin cycle.
AP Biology
CH 10: Photosynthesis
Name ____________________________
ANSWER ON A SEPARATE SHEET
1. Draw a diagram to summarize the activities of photosynthesis. . Include labels for all parts and molecules involved.
2. CO 2 and H 2 O are the reactants of photosynthesis. Where do the atoms of each compound end up?
3. Describe the organization of a photosystem. How is photosystem I different from photosystem II ?
4. How does photosynthesis convert light energy into chemical energy? Explain what happens during cyclic and noncyclic electron flow; indicate the paths of electrons and any products that are made.
5. Compare and contrast chemiosmosis in mitochondria and chloroplasts.
6. Summarize what goes into the Calvin cycle and what comes out. Start with an input of 3 molecules of
CO 2 . How are the chemical products of the light-trapping reactions coupled to the synthesis of carbohydrates?
7. What is photorespiration?
8. Describe two (2) photosynthetic adaptations that have evolved in response to hot or dry adverse conditions. Indicate how they separate carbon fixation from the Calvin cycle.
AP Biology
CH 10: Photosynthesis
Name ____________________________
ANSWER ON A SEPARATE SHEET
1. Draw a diagram to summarize the activities of photosynthesis. . Include labels for all parts and molecules involved.
2. CO 2 and H 2 O are the reactants of photosynthesis. Where do the atoms of each compound end up?
3. Describe the organization of a photosystem. How is photosystem I different from photosystem II ?
4. How does photosynthesis convert light energy into chemical energy? Explain what happens during cyclic and noncyclic electron flow; indicate the paths of electrons and any products that are made.
5. Compare and contrast chemiosmosis in mitochondria and chloroplasts.
6. Summarize what goes into the Calvin cycle and what comes out. Start with an input of 3 molecules of
CO 2 . How are the chemical products of the light-trapping reactions coupled to the synthesis of carbohydrates?
7. What is photorespiration?
8. Describe two (2) photosynthetic adaptations that have evolved in response to hot or dry adverse conditions. Indicate how they separate carbon fixation from the Calvin cycle.