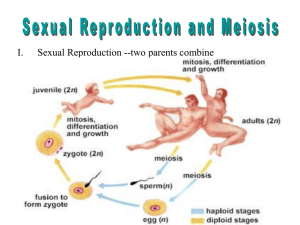
Big Idea 3B Basic Review Which disease is the result of
advertisement

Big Idea 3B Basic Review 1. Which disease is the result of uncontrolled cell division? a. Sickle-cell anemia b. Alzheimer’s c. Chicken Pox d. Cancer 2. Cancer cells do not exhibit , which can lead to the formation of . a. Growth factors, blood clots b. Contact inhibition, tumors c. Metastasis, cellular plaques d. Response to cell cycle control, contact inhibition 3. A malignant tumor differs from a benign tumor in that it? a. Does not harm surrounding tissue b. Does harm other tissues and can spread throughout the body c. Is a result of uncontrolled cell division d. Both b and c 4. Which of the following methods of cancer treatment targets specific areas and destroys DNA a. Radiation b. Bone marrow transplant c. Chemotherapy d. Stem cell transplant 5. Why does chemotherapy often result in hair loss a. It targets formation of mitotic spindles in all rapidly dividing cells, not just cancer cells b. It kills cancer cells in contact with cells that cause hair growth. c. It randomly kills all different types of cells it comes into contact with. d. None of the above 6. What are homologous chromosomes? a. Another term for sister chromatids b. A pair of chromosomes that carry genes for the same traits in the same locations of the chromosome c. A set of identical chromosomes d. All of the above 7. A pair of homologous chromosomes consists of a. One chromosome inherited from the father and one inherited from the mother that each carry genes for the same trait b. Two chromosomes from either the father or the mother www.njctl.org AP Biology Big Idea 3 c. A pair of identical chromosomes with identical genes for the same trait inherited from either parent d. Both b and c 8. A female human somatic (body) cell contains how many chromosomes? a. 22 b. 23 c. 46 d. 92 9. A female human somatic (body) cell contains how many sets of homologous chromosomes? a. 22 b. 23 c. 46 d. 92 10. If an organism’s diploid number of chromosomes is 12, its haploid number of chromosomes is a. 6 b. 12 c. 24 d. 48 11. The process of meiosis results in the formation of? a. Body cells b. Somatic cells c. Sex cells with a haploid number of chromosomes d. Sex cells with homologous chromosomes 12. What are gametes? a. Sex cells b. Sperm or egg cells in humans c. Cells with a haploid number of chromosomes d. All of the above 13. A human gamete contains how many chromosomes? a. 22 b. 23 c. 46 d. 92 14. The process of meiosis is referred to as reduction division because? a. The number of chromosomes is doubled b. It is cell division that results in the formation of new cells with a reduced number of chromosomes www.njctl.org AP Biology Big Idea 3 c. The number of cells is reduced with each division d. Meiosis is not referred to as reduction division 15. The process of meiosis has how many divisions and produces how many cells? a. 2,4 b. 1,2 c. 2,2 d. 1,4 16. The figure to the right depicts a. Mitosis b. Meiosis I c. Meiosis II d. Exocytosis 17. Homologous chromosomes form tetrads and exchange portions of their genes during a. Prophase of Mitosis b. Prophase I of Meiosis I c. Prophase II of Meiosis II d. All of the above 18. During metaphase I the way homologous chromosomes line up in the middle can vary. Therefore, during anaphase I, maternally and paternally inherited genes on the homologues move to one pole or the other, independent of the other genes. This process is referred to as a. Crossing-over b. Independent Assortment c. Lateral gene transfer d. Chromosome reduction 19. Which of the following assort independently? a. Genes on the same chromosome b. Sister chromatids c. Chromosomes d. Alleles 20. Independent assortment of chromosomes results in a. Cells with unique combinations of genes b. Cells with identical arrangements of genes c. Cells with different numbers of chromosomes d. Cells with a haploid number chromosomes www.njctl.org AP Biology Big Idea 3 21. In anaphase I of meiosis I? a. Homologous chromosomes separate b. Sister chromatids separate c. Haploid chromosomes separate d. Portions of chromosomes cross over 22. Which of the following best explains why the number of chromosomes is reduced between meiosis I and meiosis II? a. Metaphase occurs b. DNA replication occurs and the number of chromosomes is doubled c. DNA replication does not occur d. None of the above 23. What is the end product of Mitosis? a. 2 genetically different diploid daughter cells b. 2 genetically identical diploid daughter cells c. 4 genetically different haploid cells d. 4 genetically identical haploid cells 24. What is the end product of Meiosis I? a. 2 genetically different haploid daughter cells b. 2 genetically identical haploid daughter cells c. 4 genetically different haploid cells d. 4 genetically identical haploid cells 25. What is the end product of Meiosis II? a. 2 genetically different diploid daughter cells b. 2 genetically identical haploid daughter cells c. 4 genetically different haploid cells d. 4 genetically identical haploid cells 26. Which of the following is an example of nondisjunction? a. Trisomy b. Substitution c. Insertion d. Deletion 27. Polyploidy is a condition in which a cell has a. A full extra set of chromosomes b. An extra sex chromosome c. A missing sex chromosome d. An extra autosome 28. Which of the following does not involve preparation of a karyotype? a. Genetic testing of parents b. Fetoscopy www.njctl.org AP Biology Big Idea 3 c. Chronic villus sampling d. Amniocentesis 29. A karyotype reveals _____________________. a. Polygenic traits b. Multiple alleles for a trait c. An abnormal number of chromosomes d. An abnormal number of genes 30. The complete set of genetic material in an organism is called its a. Genome b. Chromosome c. Karyotype d. RNA 31. Different forms of genes are called a. Recessive factors b. Dominant factors c. Chromosomes d. Alleles 32. Organisms that have two identical alleles for a trait are a. Heterozygous b. Homozygous c. Hybrid d. Recessive 33. Which scientist(s) is/are best known as the “Father of Genetics”? a. Stanley Miller b. Frederick Griffith c. Francis Crick & James Watson d. Gregor Mendel 34. The Law of Segregation states that a. Allele pairs separate during meiosis b. Alleles are dominant or recessive c. Alleles come in pairs d. An individual can be homozygous or heterozygous 35. If a plant with white flowers is allowed to self-pollinate and generation after generation it produces plants with white flowers, this is an example of a. Incomplete dominance b. The Law of Segregation c. True breeding d. Hybridization www.njctl.org AP Biology Big Idea 3 36. Recessive traits appear only when an organism is _______________________. a. Fully grown b. Different from its parents c. Heterozygous d. Homozygous 37. What color pod would the F1 plants be if a yellow pod pea plant (Yy) was crossed with a green pod pea plant (yy)? a. All Green b. All Yellow c. Half Green, half yellow d. ¾ green, ¼ yellow 38. What are the chances that a red (Rr) flowering plant and a red (Rr) flowering plant will produce red offspring? a. 0% b. 25% c. 75% d. 100% 39. The Law of Independent Assortment states that a. Alleles separate independently of one another during gamete formation. b. Chromosomes separate independently of one another during gamete formation. c. All traits are inherited independently from one another. d. Dominant and recessive alleles are inherited independently from one another. 40. If a pea plant with white flowers and yellow pods (WwYY) is crossed with a pea plant with white flowers and green pods (WWyy), what is the probability the offspring will have white flowers and yellow pods? a. 1/16 b. 1/4 c. 1/2 d. 1 41. In tomatoes, red fruit (R) is dominant to yellow fruit (r), and tallness (T) is dominant over shortness (t). Which of these properly describes a cross between an individual who is homozygous dominant for color but heterozygous for height and an individual that is recessive for both. a. RRtt X RRTT b. rrtt X RRTt c. RrTT X rrTt d. RrTT X RRTT www.njctl.org AP Biology Big Idea 3 42. If a couple’s first child is a boy, what are the chances that their second child will be a boy? a. 100% b. 75% c. 50% d. 25% 43. In humans a widow’s peak is dominant over a straight hairline. Lucy’s mother has a widow’s peak, but she and her father have a straight hairline. What is the genotype of Lucy’s mother? a. WW b. Ww c. ww d. Not enough information 44. Snap dragons can be red (RR), pink (Rr), or white (rr), this is an example of a. Incomplete dominance b. Codominance c. Polygenic dominance d. Multiple alleles 45. When a gene has more than two alleles this is known as a. Codominance b. Polygenic dominance c. Complete dominance d. Multiple alleles 46. Traits that are formed by the interaction of many genes are a. Dominant b. Linked c. Polyploid d. Polygenic 47. If a man with Type A blood marries a woman with Type B blood, which of the following is not a possible genotype for their offspring? a. AO b. AA c. BO d. OO 48. ABO blood groups are an example of a. Incomplete dominance b. Codominance c. Polygenic Inheritance d. Pleiotropy www.njctl.org AP Biology Big Idea 3 49. Which parental pair would always produce colorblind female offspring? a. Homozygous normal-vision mother and a colorblind father b. Heterozygous normal-vision and normal-vision father c. Heterozygous normal-vision mother and colorblind father d. Colorblind mother and a colorblind father 50. Assuming black fur in cats is caused by a dominant allele and a white coat is caused by the recessive allele. Two black cats produce a kitten with a white coat. What is the probability of their second kitten having a white coat? a. 0 b. ¼ c. ½ d. ¾ 51. What are the chances that two carriers of sickle-cell disease will produce an affected offspring? a. 0% b. 25% c. 75% d. 100% 52. If two sisters and one of two brothers are colorblind, which are most likely the phenotypes of the parents? a. Both colorblind b. Both not colorblind c. Colorblind Mom, normal-vision Dad d. Colorblind Dad, normal-vision Mom 53. In order for a male to exhibit male patterned baldness, which of the following must be true? a. Mother does not possess the allele b. Father must possess one allele c. Father must possess two alleles d. Mother must possess at least one allele 54. If a trait is X-linked, males pass the X-linked allele to __________________ of their daughters. a. None b. ¼ c. ½ d. All 55. A mother and a father are at the opposite extremes for a polygenic trait. Their children will a. Look like one parent or the other b. Have the middle phenotype between their two parents www.njctl.org AP Biology Big Idea 3 c. Be a phenotype typical of a 9:3:3:1 ratio d. Be bell shaped Answers 1. d 2. b 3. b 4. a 5. a 6. b 7. a 8. c 9. b 10. a 11. c 12. d 13. c 14. b 15. a 16. c 17. b 18. b 19. c 20. a 21. a 22. c 23. b 24. a 25. c 26. a 27. a 28. b www.njctl.org 29. c 30. a 31. d 32. b 33. d 34. a 35. c 36. d 37. c 38. c 39. a 40. d 41. b 42. c 43. b 44. a 45. d 46. d 47. b 48. a 49. d 50. b 51. b 52. d 53. d 54. d 55. b AP Biology Big Idea 3