Ch 10 Notes - TeacherWeb
advertisement

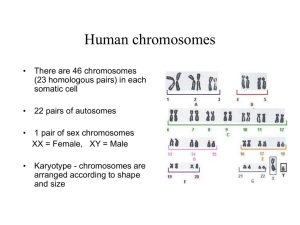
Chapter 10- Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Section 1- Meiosis Human body contains _______ chromosomes o Each parent contributes _________chromosomes o _____________________ chromosomes- a pair, one from each parent carry genes that control the same inherited trait Male sperm and female egg are called gametes o contain 23 chromosomes o haploid (one set of chromosomes from a single parent)- designated as n chromosomes (1 set) Once male sperm and female egg fuse they form a diploid cell- 2 sets of chromosomes (2n), one from each parent o All cells in the human body are diploid EXCEPT the gametes- sperm and egg Meiosis produces gametes o Meiosis is for sexual reproduction (offspring production) o Mitosis is for cellular reproduction (growth and repairing old tissues) Stages of Meiosis o diploid cell with a homologous set of chromosomes go through 2 consecutive cell divisions called meiosis I and meiosis II to become haploid gametes o Meiosis I Interphase I Prophase I- ______________________ produces exchange of genetic information Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I – at this point the cells are still diploid o Meiosis II Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II Cytokinesis- 4 haploid cells form The Importance of Meiosis results in genetic ________________ depending on how the chromosomes line up, four gametes with four different combinations of chromosomes can result (We will see the possible combinations when we do punnet square crosses later) _____________________________- results in genetic variation because segments of the chromosomes may be switched between 2 homologous chromosomes. Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction o o Asexual Reproduction- new individual is genetically _____________________ to its parent Sexual Reproduction- genes from both parents, therefore beneficial genes multiply ____________ over time, survival of the fittest. Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis: In Mitosis: the parent cell (diploid- 2n) forms 2 daughter cells (each diploid- 2n) In Meiosis: the parent cell (diploid-2n) forms four daughter cells (each haploid-1n) Mendelian Genetics ____________________________________________-during Meiosis, the gametes have multiple chromosomal possibilities depending on how they line up. There is a random distribution of alleles during meiosis. ______________- an alternative form of a gene passed on from parent to offspring (you get one allele for each gene from each parent, so a single gene is represented by a pair of alleles) o Ex: B=allele for brown hair b= allele for blonde hair o Capital letters mean the allele is __________________, lower case letters mean the allele is ___________________. o ______________________- both alleles are the same (BB)= B from dad and B from mom o _______________________- both alleles are different (Bb)= B from dad and b from mom