Unit 6
End of the Year
Final Review
Unit 6
Name____________________
Date ________________ Per.____
1) Write the equations for the following processes:
Photosynthesis= 6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
Respiration= C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6 O
2
→
CO
2
+ 6 H
2
O + chemical energy
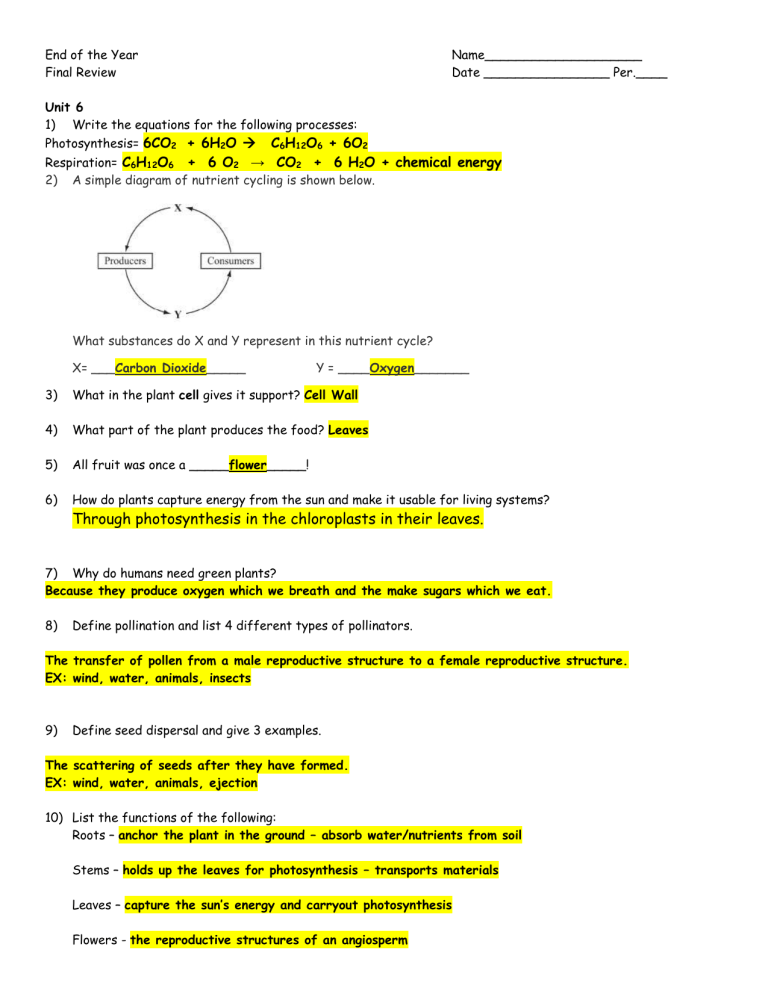
2) A simple diagram of nutrient cycling is shown below.
What substances do X and Y represent in this nutrient cycle?
X= ___Carbon Dioxide_____ Y = ____Oxygen_______
3) What in the plant cell gives it support? Cell Wall
4) What part of the plant produces the food? Leaves
5) All fruit was once a _____flower_____!
6) How do plants capture energy from the sun and make it usable for living systems?
Through photosynthesis in the chloroplasts in their leaves.
7) Why do humans need green plants?
Because they produce oxygen which we breath and the make sugars which we eat.
8) Define pollination and list 4 different types of pollinators.
The transfer of pollen from a male reproductive structure to a female reproductive structure.
EX: wind, water, animals, insects
9) Define seed dispersal and give 3 examples.
The scattering of seeds after they have formed.
EX: wind, water, animals, ejection
10) List the functions of the following:
Roots – anchor the plant in the ground – absorb water/nutrients from soil
Stems – holds up the leaves for photosynthesis – transports materials
Leaves – capture the sun’s energy and carryout photosynthesis
Flowers - the reproductive structures of an angiosperm
11) Label the parts on this flower and state their functions. petals – colorful to attract pollinators
Stamen - where pollen is produced
(male)
(female)
Pistol – contain the ovary where seeds are produced sepal - encloses a flower bud
12) What gases are exchanged in a leaf? Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
13) What are some ways that plants have adapted to survive in a variety of environments?
Support - stems - strong cell walls and vascular tissue
Obtaining water – roots absorb from soil
Retain water - cuticle
Reproduction - without water
Transport Materials - vascular tissue
14) What sources of energy can replace traditional sources? Solar, wind, water
15) Define and give examples of the following: a. Limiting factor - environmental factors that cause a population to decrease.
1. Food 2. Water 3. Space 4. Weather Conditions b. Herbivore - consumers who eat only plants – deer, caterpillars c .Carnivore - consumers that only eat animals – lions/spiders d. Omnivore - consumers that eat both plants and animals – people, bears e. Decomposer - organisms that breakdown wastes and dead organisms and return the raw materials to the ground – bacteria/fungi f. Consumer/heterotroph - organisms that obtain energy by feeding on other organisms – people g. Producer/autotroph - organisms that can make their own food – source of all food in an ecosystem – plants
16) Explain carrying capacity.
The largest population that an area can support.
17) How does energy and matter flow and cycle between plants and animals?
Sun --> Producers --> 1 st Level Consumers --> 2 nd Level Consumers --> 3 rd Level Consumers
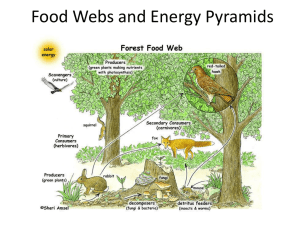
18) Why do we organize living things using food webs and energy pyramids?
It’s the order in which the energy flows through the food chain. It shows how much energy is available at each level.
19) A prairie ecosystem includes many different organisms, such as grasses, coyotes, trees, mushrooms, snakes, and mice, as shown in the picture below. The energy needed by all the organisms in the ecosystem comes from one primary source.
a) Identify the primary source of energy in the prairie ecosystem. ______Sun__________ b) Identify one of each of the following: producer: ____grass/tree_____ consumer: _____snake/coyote/mouse/____ decomposer: _____mushroom____ c) Explain how the energy from the primary source you identified in previously moves through the prairie ecosystem. Be sure to include producers, consumers, and decomposers in your answer.
The producers get their energy from the sun and convert it into glucose. The consumers eat the producers and/or other consumers to get their energy. The decomposer breakdown all leftover biotic materials and return the nutrients to the soil for the producers to use.
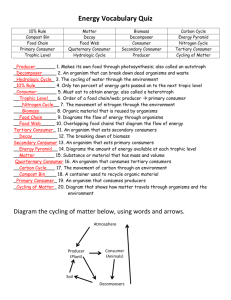
20) Label the Energy Pyramid.
Trophic level 4– carnivores/scavengers tertiary/3 rd level consumers (10kcal)
Trophic level 3 – carnivores/omnivores
Secondary/2 nd level consumers (100kcal)
Trophic level 2 – herbivores/omnivores
How much chemical energy would be available at the 3 this pyramid starts with 10,000kcal?
_________
rd
100kcal
trophic level if
________
Primary/1 st level consumers (1,000kcal)
Trophic level 1 – Producers (10,000kcal)
21) Which level has the most energy? _trophic level 1/producers__ The least? tropic level 4/tertiary consumers
22) Complete the food web with the following organisms:
Fungi Ground Squirrel
Grass
Trees
Coyote
Rabbit
Wolf
Snake
Mouse
Wolf
Coyote
Rabbit
Grass
Ground
Squirrel
Nuts
Mouse
Snake
Grasshopper
Berries
Trees
Grasshopper
Berries
Nuts
Decomposer
23) Why do we say plants and animals are interdependent?
Plants use the suns energy to provide energy to the rest of the ecosystem, plants also take in CO
2
and let out
O
2
. They also provide habitat for other organisms. Animals release CO
2
and take in the O
2
. Animals also pollinate
Flowers and disperse seeds.
24) What is biomass?
Combined mass of all the living and recently living organisms in an area.
25) Why is there more biomass in some parts of Idaho or the United States then others?
(Ex: Why some areas are heavily forested and others have no trees at all?)
Areas with plenty of moisture, temperate climates, and rich soil can support more biomass than areas with extremes (deserts, artic, etc.).
26) What factors limit the amount of biomass?
Biomass is limited by rainfall, temperatures, soil bacteria, etc.
27) If we all started life as a single microscopic cell and we are all now very much bigger, where did all the “stuff” that we now consist of come from? (How do we get the energy and matter we need to grow bigger? What does the saying “You are what you eat” mean?)
Cells make more cells and use the energy and matter that comes from food to do this.