- apcseet2013
advertisement

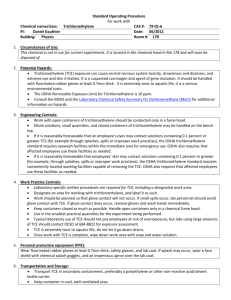
Please sent your abstract(s) in MS Word as an attached file together with e-mail text to apcseet2013@gmail.com by March 15, 2013, if any room in the session) ********************************************************************** Example of the ordinary paper only for regular participants/regular students ********************************************************************** Name of presenter with title (or Mr. or Ms.): Prof. Toshinori KOJIMA: Dept. Materials and Life Science, Seikei Univ., Japan; kojima@st.seikei.ac.jp, kojimaseikei@gmail.com; +81-422-37-3871 (fax) Prior paper: oral; Journal of Chemical Engineering Japan Influence of pH and Dissolved Fe Ion Concentration on Decomposition of Trichloroethylene with Fenton’s Reaction Using Iron Powder Yasuhiko TAKUMA(1), Toshinori KOJIMA(2*), Shigeru KATO(2), Shigeo SATOKAWA(2), Akihiro YAMASAKI(2) (1) Development Div., Tokyo Metropolitan Ind. Technol. Res. Inst,, Japan, takuma.yasuhiko@iri-tokyo.jp (2*) Dept. Materials and Life Sci., Seikei Univ., Japan, kojima@st.seikei.ac.jp Abstract: The decomposition rate of trichloroethylene (TCE) by Fenton’s reaction using iron powder was investigated especially on the influence of pH and dissolved Fe ion concentration in the presence and absence of buffer solution to maintain pH value. The decomposition rate depended on hydrogen peroxide concentration, and the maximum rate was observed. This finding was explained by the consumption of hydroxyl radicals by a competing reaction with hydrogen peroxide against TCE decomposition by the hydroxyl radicals produced from hydrogen peroxide. The most rapid dissolution rate of iron, i.e., the maximum increasing rate of Fe ion concentration, ----max 150 words Keywords: Polluted soil; Trichloroethylene; Fenton’s reaction; Reaction kinetics