Neurons
advertisement
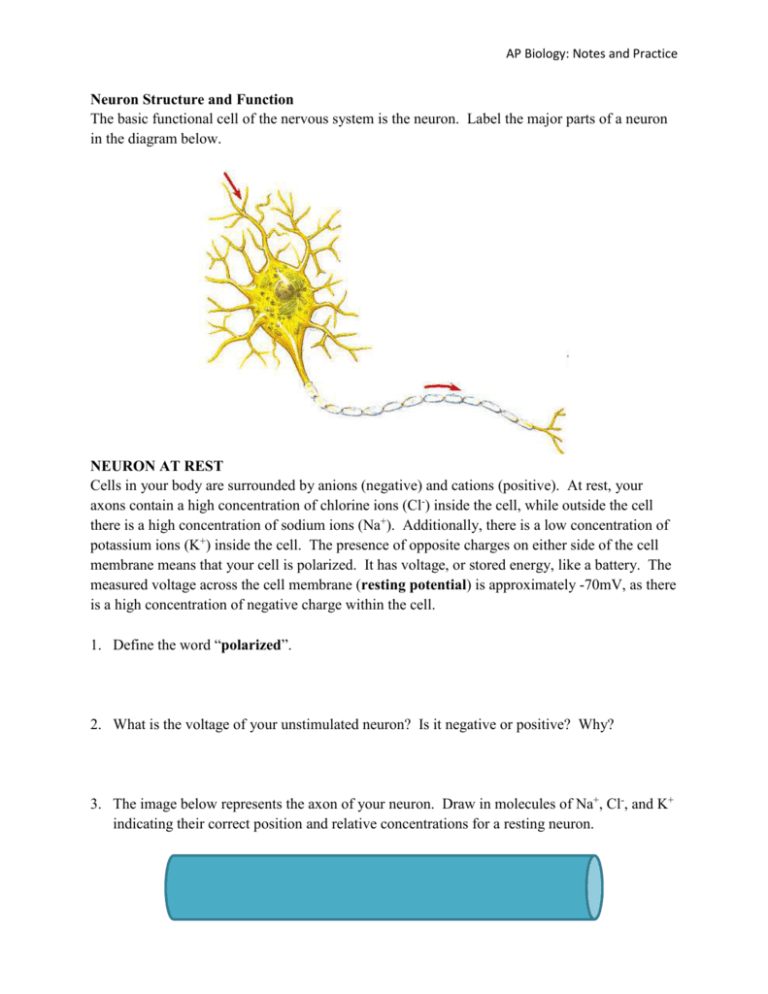
AP Biology: Notes and Practice Neuron Structure and Function The basic functional cell of the nervous system is the neuron. Label the major parts of a neuron in the diagram below. NEURON AT REST Cells in your body are surrounded by anions (negative) and cations (positive). At rest, your axons contain a high concentration of chlorine ions (Cl-) inside the cell, while outside the cell there is a high concentration of sodium ions (Na+). Additionally, there is a low concentration of potassium ions (K+) inside the cell. The presence of opposite charges on either side of the cell membrane means that your cell is polarized. It has voltage, or stored energy, like a battery. The measured voltage across the cell membrane (resting potential) is approximately -70mV, as there is a high concentration of negative charge within the cell. 1. Define the word “polarized”. 2. What is the voltage of your unstimulated neuron? Is it negative or positive? Why? 3. The image below represents the axon of your neuron. Draw in molecules of Na+, Cl-, and K+ indicating their correct position and relative concentrations for a resting neuron. AP Biology: Notes and Practice NEURON STIMULUS Hopefully your neuron has enjoyed its nap…it can quickly jump to action when it receives a stimulus, like seeing a baseball projecting towards your head at a rapid speed. This will cause your neuron to open the sodium channels in the cell membrane, allowing Na+ to diffuse into the axon. If the nerve membrane reaches a minimum threshold potential of approximately -55 mV, the signal will be allowed to proceed… 4. Upon receiving a stimulus, what occurs across the cell membrane of a neuron? Draw a diagram of this below, including Na+, Cl-, and K+. 5. Does the movement of Na+ across the cell membrane require energy? Why or why not? 6. Based on your answer to question 4, what will happen to the charge inside the axon when a neuron is stimulated? What will happen to the charge outside the axon? 7. Compare the values of a resting potential and a threshold potential. Which is more negative? Why? 8. A stimulus causes a neuron cell membrane to become depolarized. Predict the definition for “depolarized” based on the information provided. 9. It is common for a neuron to receive a stimulus that only allows the neuron to reach a membrane potential of -60mV. Based on the information in the passage, what is likely to happen in a neuron reaching this membrane potential? AP Biology: Notes and Practice NEURON SIGNAL PROPAGATION Congrats! Your neuron has received a strong enough stimulus to allow the impulse to continue its journey through your neuron. As sodium ions begin to move into the axon, they activate the opening of sodium channels in the cell membrane along the length of the axon, so sodium will continue to diffuse into the cell. Your cell membrane will eventually reach an action potential around +40mV when the impulse has traveled all the way through the axon. Good thing for you, because your muscle cells will receive the stimulus to duck away from that high-speed baseball! 10. Why does sodium continue to move into the axon of a neuron even after the initial stimulus? 11. What will happen to the charge inside an axon as Na+ continues to diffuse into the neuron? What will happen to the charge outside an axon? 12. Compare the voltage values of a threshold potential and an action potential. Which is more negative? Why? NEURON RESET Once the impulse has been transmitted through your neuron, your neuron needs to get itself back into fighting shape in case any other baseballs come whirling by your head. In order to stop the movement of sodium ions into your neuron, the cell membrane will now open its potassium channels. The diffusion of potassium stops the diffusion of sodium into the cell. 13. Which direction (into or out of the neuron) will potassium diffuse? Explain your answer. 14. After an impulse is carried through a neuron, which ions move across the cell membrane? Draw a diagram of this below, including Na+, Cl-, and K+, indicating which ions move. 15. The diffusion of potassium across the membrane of a neuron is called repolarization. Predict the definition of “repolarization” based on the information provided. AP Biology: Notes and Practice Polarized Depolarized Repolarized Polarized Action Potential